Abstract
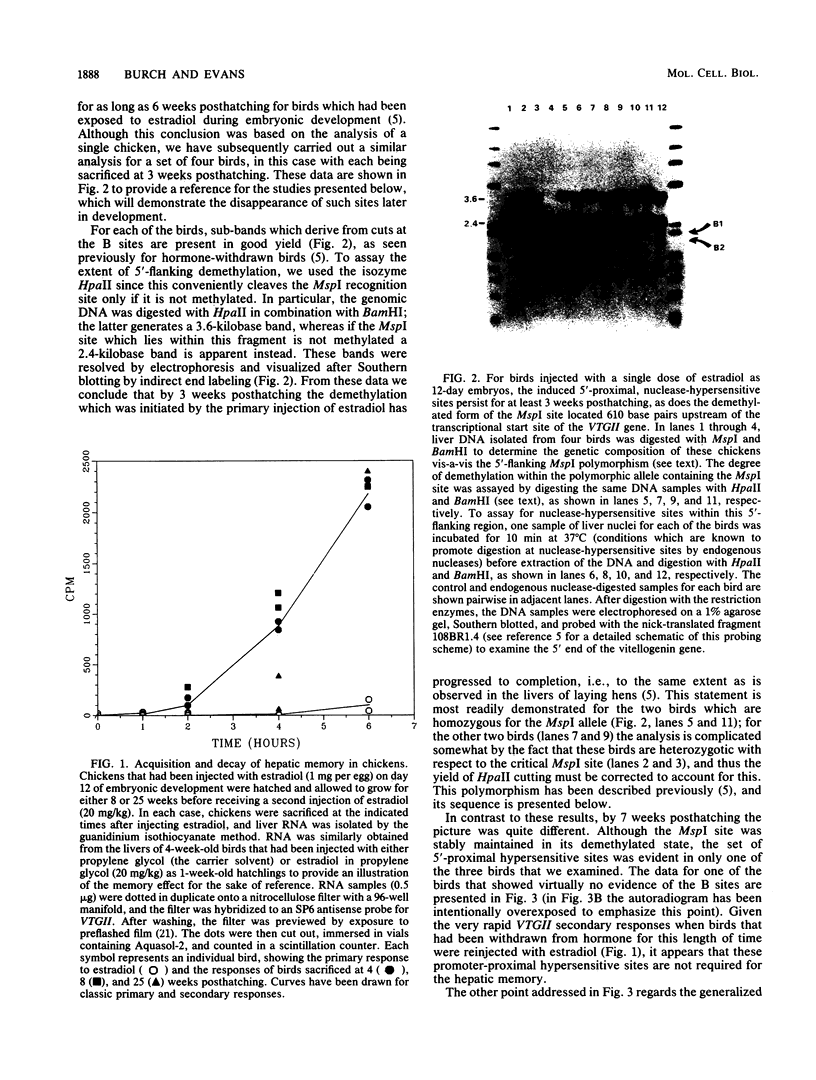
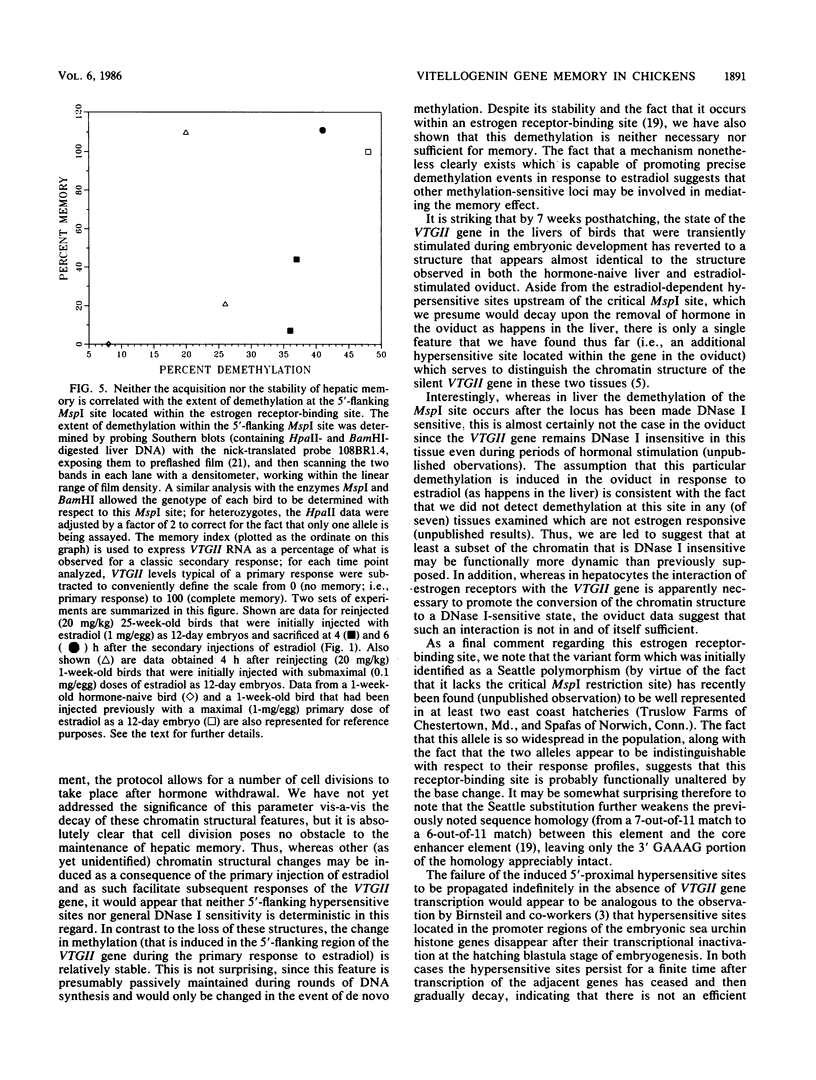
We have previously shown that the steroid hormone-mediated transcriptional activation of the chicken vitellogenin II gene (VTGII) in the liver is accompanied by a series of chromatin structural changes, including the formation of two sets of 5'-proximal nuclease-hypersensitive sites and the demethylation of a single 5'-flanking MspI site which lies within a region of DNA that recently has been shown by Jost and co-workers to specifically bind the estrogen receptor complex in vitro. To assay the stability and possible functional significance of these induced structural changes, we transiently activated the VTGII gene during embryonic development and then allowed the chickens to hatch and grow for various periods of time before analyzing their livers. By 7 weeks posthatching all of the induced 5'-flanking hypersensitive sites had decayed. Moreover, the loss of these sites occurred without consequence to the "memory effect," that is, these structural features did not need to be present in hormone withdrawn birds to allow this gene to be activated more rapidly in response to a secondary presentation of estradiol. Although the demethylation was more stable, it also appeared not to be the basis of the memory phenomenon. The birds that still exhibited memory after 25 weeks of hormone withdrawal were not more extensively demethylated within the receptor-binding site than were the birds which failed to show memory at this age. A similar uncoupling of these two parameters was also observed when embryos were first injected with submaximal doses of estradiol and then assayed 1 week after hatching; the chickens which acquired memory were not demethylated to any greater extent than those which did not acquire memory. Other parameters that may be relevant to memory are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker H. J., Shapiro D. J. Kinetics of estrogen induction of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA as measured by hybridization to complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8428–8434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergink E. W., Kloosterboer H. J., Gruber M., Ab G. Estrogen-induced phosphoprotein synthesis in roosters. Kinetics of induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan P. N., Olah J., Birnstiel M. L. Major changes in the 5' and 3' chromatin structure of sea urchin histone genes accompany their activation and inactivation in development. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' end of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1117–1135. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina-Salada J., Moore J. P., Chan L. Kinetics of primary and secondary stimulation of the mRNA for APOVLDL-II, a major yolk protein, in the cockerel liver by estrogen. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):1158–1160. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Udell D. S., Burns A. T., Gordon J. I., Goldberger R. F. Kinetics of avian vitellogenin messenger RNA induction. Comparison between primary and secondary response to estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7913–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis G. J., Tata J. R. Differential sensitization to deoxyribonuclease I of Xenopus vitellogenin and albumin genes during primary and secondary induction of vitellogenesis by oestradiol. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):491–497. doi: 10.1042/bj2020491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrecht A., Lazier C. B., Protter A. A., Williams D. L. Independent developmental programs for two estrogen-regulated genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):639–641. doi: 10.1126/science.6740331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K., Anderson J. N., Hayward M. A., Shapiro D. J. Nuclease sensitivity and DNA methylation in estrogen regulation of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8908–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber-Huber S., Felber B. K., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Estrogen induces tissue specific changes in the chromatin conformation of the vitellogenin genes in Xenopus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2475–2494. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. D., Tata J. R. Direct induction by estradiol on vitellogenin synthesis in organ cultures of male Xenopus laevis liver. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grippo P., Iaccarino M., Parisi E., Scarano E. Methylation of DNA in developing sea urchin embryos. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):195–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W. Specific binding of estradiol to the liver chromatin of estrogenized roosters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):84–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward M. A., Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Activation of vitellogenin gene transcription is a direct response to estrogen in Xenopus laevis liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8273–8284. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok K., Snippe L., Ab G., Gruber M. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in chromatin of the estrogen-inducible apoVLDL II gene of chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5189–5202. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F. C., Philipsen J. N., Gruber M., Ab G. Methylation of the chicken vitellogenin gene: influence of estradiol administration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1361–1373. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman A. J., Wolffe A. P., Champion J., Tata J. R. Regulation by estrogen receptor of vitellogenin gene transcription in Xenopus hepatocyte cultures. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Dec;38(2-3):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., James T. C., Watson C. S., Williams J. L., Wolffe A. P. Hormonal regulation and expression of vitellogenin multigene family. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;98:96–110. doi: 10.1002/9780470720790.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Knowland J. Estrogen causes a rapid, large and prolonged rise in the level of nuclear estrogen receptor in Xenopus laevis liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91531-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B. The relationship of the estrogen receptor to the induction of vitellogenin in chicken and Xenopus liver. Differentiation. 1979;15(2):67–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Estrogen induces a demethylation at the 5' end region of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4252–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Seldran M., Jost J. P. An estrogen-dependent demethylation at the 5' end of the chicken vitellogenin gene is independent of DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1163–1177. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. L., Tata J. R. Simultaneous analysis of conformation and transcription of A and B groups of vitellogenin genes in male and female Xenopus during primary and secondary activation by estrogen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1151–1166. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip A. D., Meijlink F. C., Strijker R., Gruber M., van Vliet A. J., van de Klundert J. A., Ab G. The nucleotide sequence of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2529–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]