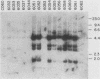
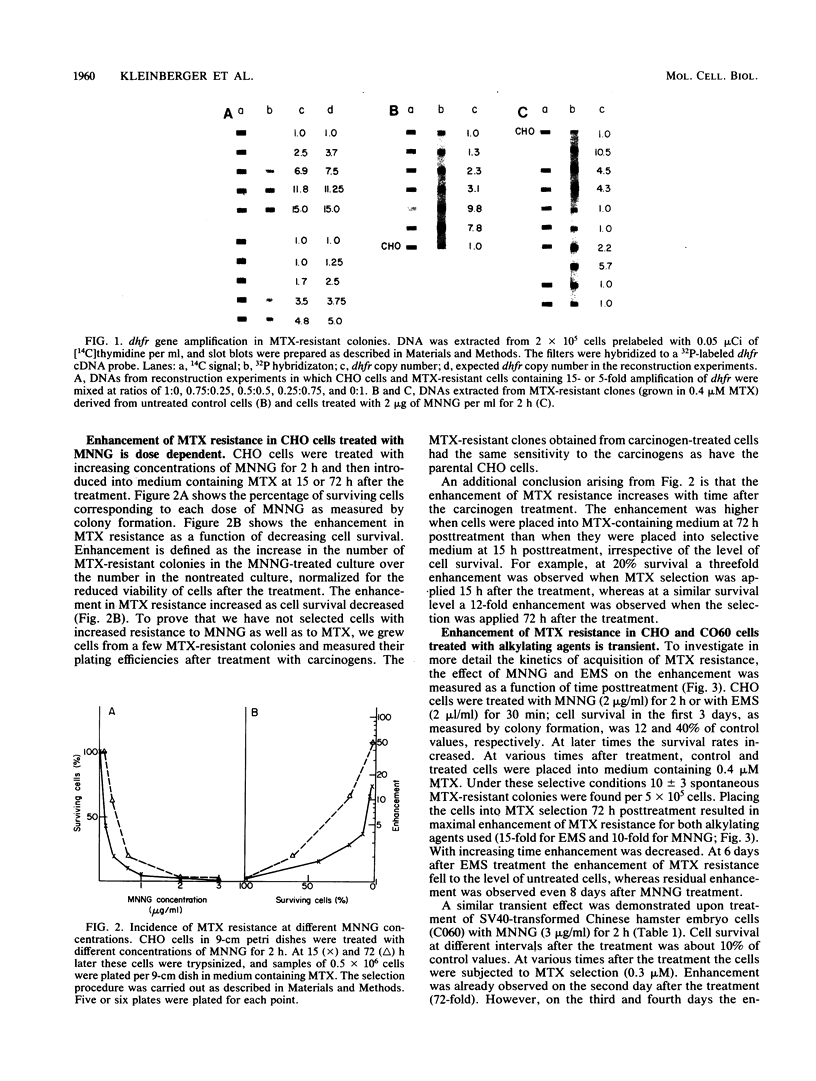
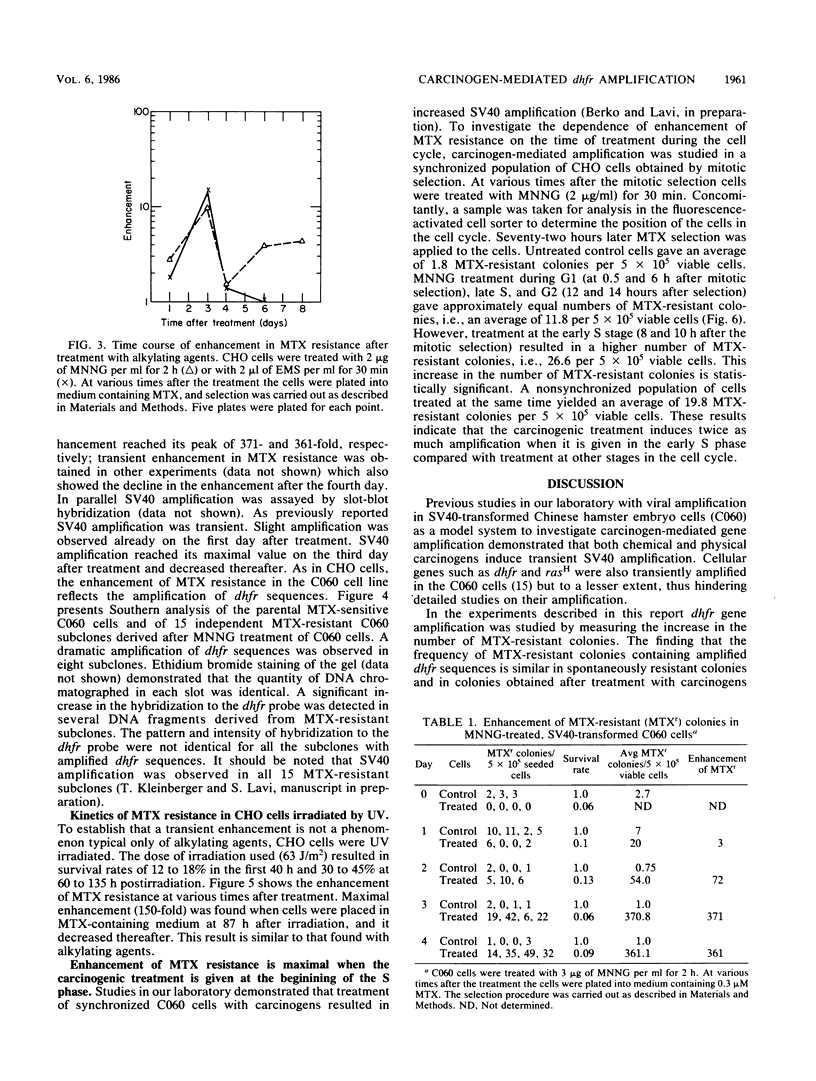
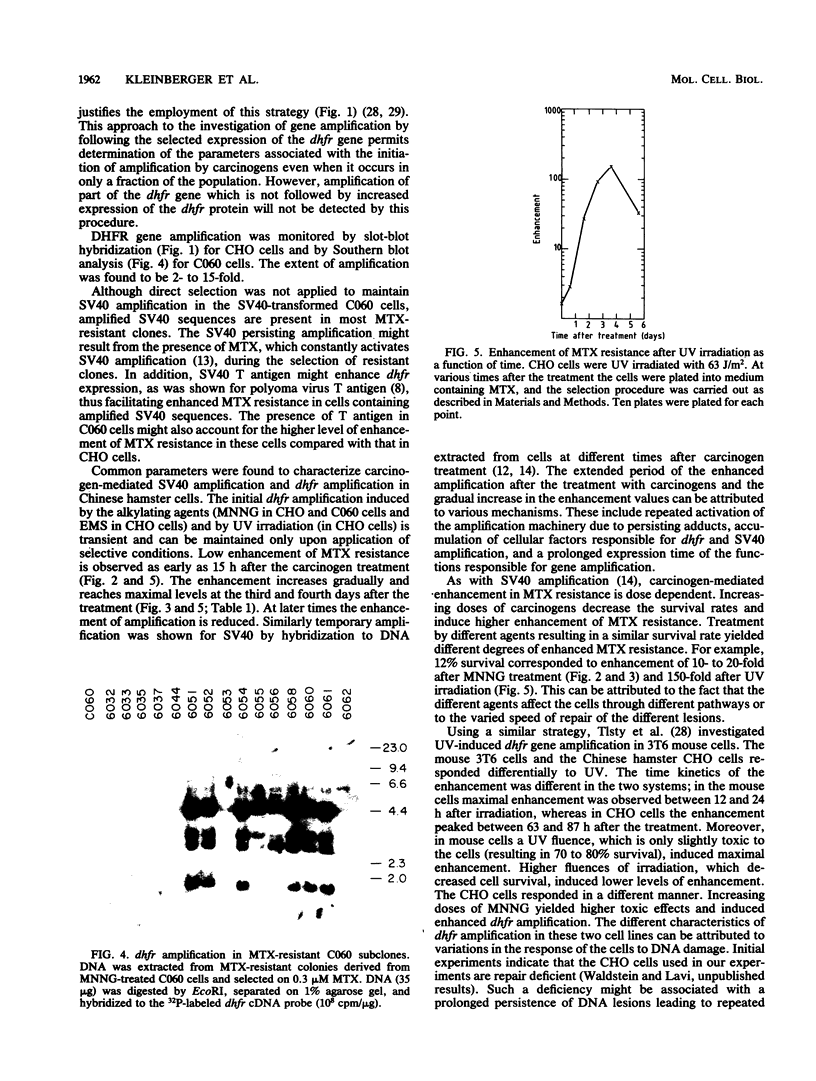
Abstract
We have investigated different parameters characterizing carcinogen-mediated enhancement of methotrexate resistance in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo (C060) cells. We show that this enhancement reflects dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) gene amplification. The carcinogens used in this work are alkylating agents and UV irradiation. Both types of carcinogens induce a transient enhancement of methotrexate resistance which increases gradually from the time of treatment to 72 to 96 h later and decreases thereafter. Increasing doses of carcinogens decrease cell survival and increase the enhancement of methotrexate resistance. Enhancement was observed when cells were treated at different stages in the cell cycle, and it was maximal when cells were treated during the early S phase. These studies of carcinogen-mediated dhfr gene amplification coupled with our earlier studies on viral DNA amplification in simian virus 40-transformed cells demonstrate that the same parameters characterize the amplification of both genes. Possible cellular mechanisms responsible for the carcinogen-mediated gene amplification phenomenon are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baran N., Neer A., Manor H. "Onion skin" replication of integrated polyoma virus DNA and flanking sequences in polyoma-transformed rat cells: termination within a specific cellular DNA segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cancer genes come of age. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1018–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresser J., Doering J., Gillespie D. Quick-blot: selective mRNA or DNA immobilization from whole cells. DNA. 1983;2(3):243–254. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Tlsty T. D., Schimke R. T. Enhancement of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by treatment of mouse 3T6 cells with hydroxyurea. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1097–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower R. C., Myers C. E., Chabner B. A. New developments on the mechanisms of action of antineoplastic drugs. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 2;25(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Powers V. E. Amplified DNA sequences in Y1 mouse adrenal tumor cells: association with double minutes and localization to a homogeneously staining chromosomal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1597–1601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellems R. E., Morhenn V. B., Pfendt E. A., Alt F. W., Schimke R. T. Polyoma virus and cyclic AMP-mediated control of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA abundance in methotrexate-resistant mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogoma T., Lark K. G. Characterization of the replication of Escherichia coli DNA in the absence of protein synthesis: stable DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G. Homogeneously staining regions on marker chromosomes in malignancy. Int J Cancer. 1979 Mar 15;23(3):299–301. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Gattoni-Celli S., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B. Benzo[a]pyrene induction of extrachromosomal viral DNA synthesis in rat cells transformed by polyoma virus. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(5):587–593. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S. Carcinogen-mediated amplification of viral DNA sequences in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6144–6148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Etkin S. Carcinogen-mediated induction of SV40 DNA synthesis in SV40 transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(5):417–423. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.5.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levan A., Levan G., Mitelman F. Chromosomes and cancer. Hereditas. 1977;86(1):15–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1977.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitelman F., Levan G. Clustering of aberrations to specific chromosomes in human neoplasms. IV. A survey of 1,871 cases. Hereditas. 1981;95(1):79–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1981.tb01331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Oishi M. UV Irradiation induces an activity which stimulates Simian virus 40 rescue upon cell fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1159–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D., Testa J. R. Chromosome abnormalities in malignant hematologic diseases. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;36:103–148. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden J. R., Emanuel B. S., Wang E., Cannizzaro L., Palumbo A., Erikson J., Nowell P. C., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Amplified C lambda and c-abl genes are on the same marker chromosome in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7289–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi K., Strauss B. S. Accumulation of DNA growing points in caffeine-treated human lymphoblastoid cells. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):435–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tlsty T. D., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. UV radiation facilitates methotrexate resistance and amplification of the dihydrofolate reductase gene in cultured 3T6 mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1050–1056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Do stalled replication forks synthesize a specific alarmone? J Theor Biol. 1983 Dec 21;105(4):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Phorbol ester dramatically increases incidence of methotrexate-resistant mouse cells: possible mechanisms and relevance to tumor promotion. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]