Abstract
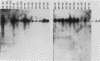
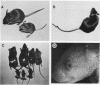
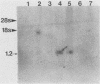
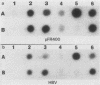
We have produced 17 lines of transgenic mice by microinjecting a full-length cDNA clone of an altered dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) gene. The protein specified by this gene carries a point mutation which triples its Km for dihydrofolate and reduces substrate turnover 20-fold relative to the wild-type enzyme. Transgenic mice from different pedigrees, several of which carry a single copy of this gene in different integration sites, manifest an array of similar developmental abnormalities including growth stunting, reduced fertility, pigmentation changes, and skeletal defects. These defects appear in animals heterozygous for the foreign gene. RNA analyses demonstrate significant expression of the cDNA in newborn mice and adult tissues. These findings show that the additional dhfr gene exerts its mutational effects in a dominant fashion, and therefore the data indicate that transgenic mice can serve as models for elucidating mechanisms of dominant mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M., Senear A. W., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. Somatic expression of herpes thymidine kinase in mice following injection of a fusion gene into eggs. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90376-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Ritchie K. A., Hammer R. E., O'Brien R. L., Arp B., Storb U. Expression of a microinjected immunoglobulin gene in the spleen of transgenic mice. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):332–336. doi: 10.1038/306332a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Raphael K., Radice G., Lacy E., Costantini F. Specific expression of a foreign beta-globin gene in erythroid cells of transgenic mice. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):377–380. doi: 10.1038/314377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Lee B. K. Association of the lethal yellow (Ay) coat color mutation with an ecotropic murine leukemia virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):247–249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F., Lacy E. Introduction of a rabbit beta-globin gene into the mouse germ line. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):92–94. doi: 10.1038/294092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk D. R. Genetic mosaics of the rudimentary locus of Drosophila melanogaster: a genetical investigation into the physiology of pyrimidine synthesis. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):134–147. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Ruddle F. H. DNA-mediated genetic transformation of mouse embryos and bone marrow--a review. Gene. 1985;33(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Ruddle F. H. Gene transfer into mouse embryos: production of transgenic mice by pronuclear injection. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:411–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Ruddle F. H. Integration and stable germ line transmission of genes injected into mouse pronuclei. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1244–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.6272397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Scangos G. A., Plotkin D. J., Barbosa J. A., Ruddle F. H. Genetic transformation of mouse embryos by microinjection of purified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7380–7384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Beverley S. M., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Properties of an altered dihydrofolate reductase encoded by amplified genes in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9501–9510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Kuehn M., Delius H., Jaenisch R. Insertion of retrovirus into the first intron of alpha 1(I) collagen gene to embryonic lethal mutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Germ line integration and Mendelian transmission of the exogenous Moloney leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1260–1264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Harbers K., Schnieke A., Löhler J., Chumakov I., Jähner D., Grotkopp D., Hoffmann E. Germline integration of moloney murine leukemia virus at the Mov13 locus leads to recessive lethal mutation and early embryonic death. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOFSKY D. A., MURPHY M. L. Effect of azaserine and other growth-inhibiting agents on fetal development of the rat. Cancer. 1956 Sep-Oct;9(5):955–962. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195609/10)9:5<955::aid-cncr2820090515>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Roberts S., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Costantini F. D. A foreign beta-globin gene in transgenic mice: integration at abnormal chromosomal positions and expression in inappropriate tissues. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Correcting an immune-response deficiency by creating E alpha gene transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):38–42. doi: 10.1038/316038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Hammer R. E., Kuenzel E. A., Brinster R. L. Expression of the chicken transferrin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing A., Chen H. Y., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Peripheral neuropathies, hepatocellular carcinomas and islet cell adenomas in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):461–463. doi: 10.1038/316461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Messing A., Brinster R. L. SV40 enhancer and large-T antigen are instrumental in development of choroid plexus tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):457–460. doi: 10.1038/316457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Wilkie T. M., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Transmission distortion and mosaicism in an unusual transgenic mouse pedigree. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Schachter B. S., Herman A. B., Durgerian S., Krieger D. T. Characterization and localization of proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA in the adult rat testis. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):632–634. doi: 10.1126/science.6740329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie K. A., Brinster R. L., Storb U. Allelic exclusion and control of endogenous immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in kappa transgenic mice. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):517–520. doi: 10.1038/312517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Louis C., Tsubota S., Schedl P., Rawls J. M., Jarry B. P. The rudimentary locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 5;175(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Blair D. G., Showalter S. D., Scangos G. A. Analysis of a transgenic mouse containing simian virus 40 and v-myc sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):642–648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward T. A., Wagner E. F., Mintz B. Human beta-globin gene sequences injected into mouse eggs, retained in adults, and transmitted to progeny. Science. 1982 Sep 10;217(4564):1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.6287575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., O'Brien R. L., McMullen M. D., Gollahon K. A., Brinster R. L. High expression of cloned immunoglobulin kappa gene in transgenic mice is restricted to B lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):238–241. doi: 10.1038/310238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. T., Chen H. Y., Brennand J., Caskey C. T., Brinster R. L. Expression of human HPRT in the central nervous system of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):250–252. doi: 10.1038/317250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Hammer R. E., MacDonald R. J., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of the rat pancreatic elastase I gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIERSCH J. B. Effect of certain 2,4-diaminopyrimidine antagonists of folic acid on pregnancy and rat fetus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Dec;87(3):571–577. doi: 10.3181/00379727-87-21448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Covarrubias L., Stewart T. A., Mintz B. Prenatal lethalities in mice homozygous for human growth hormone gene sequences integrated in the germ line. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Stewart T. A., Davis L. G., D'Eustachio P., Leder P. An inherited limb deformity created by insertional mutagenesis in a transgenic mouse. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):36–40. doi: 10.1038/318036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]