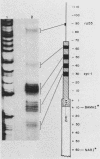
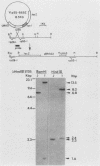
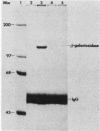
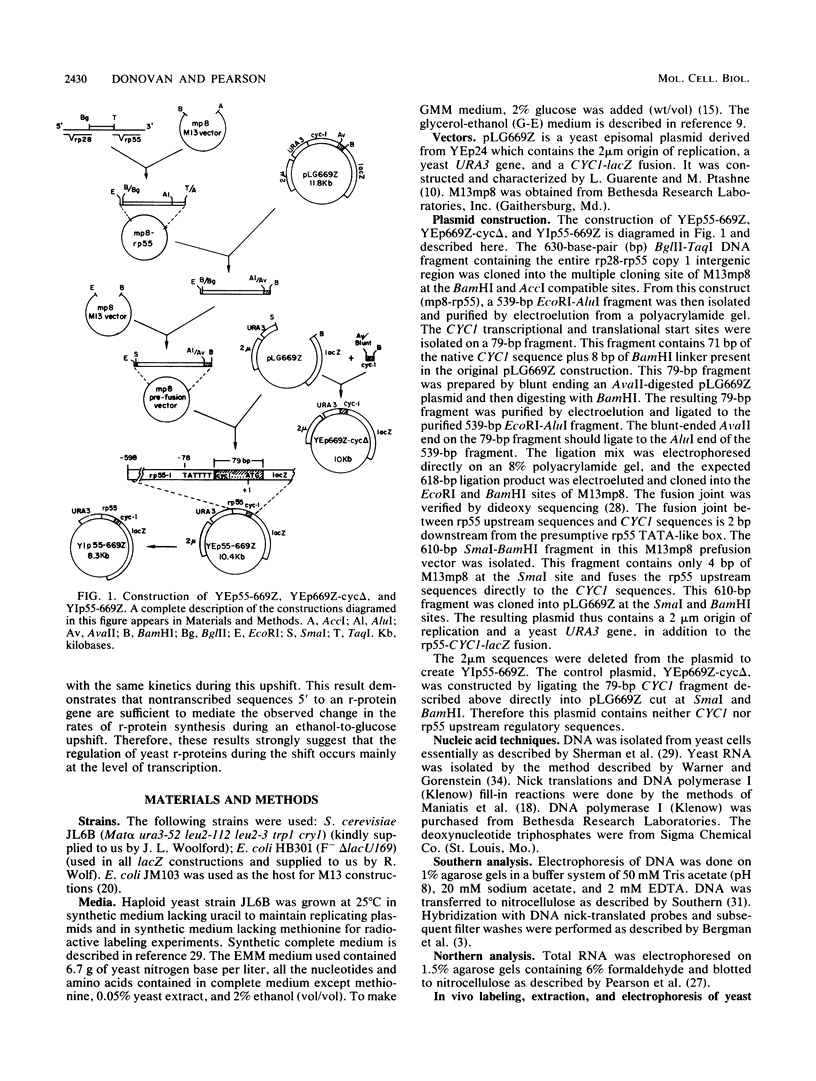
Abstract
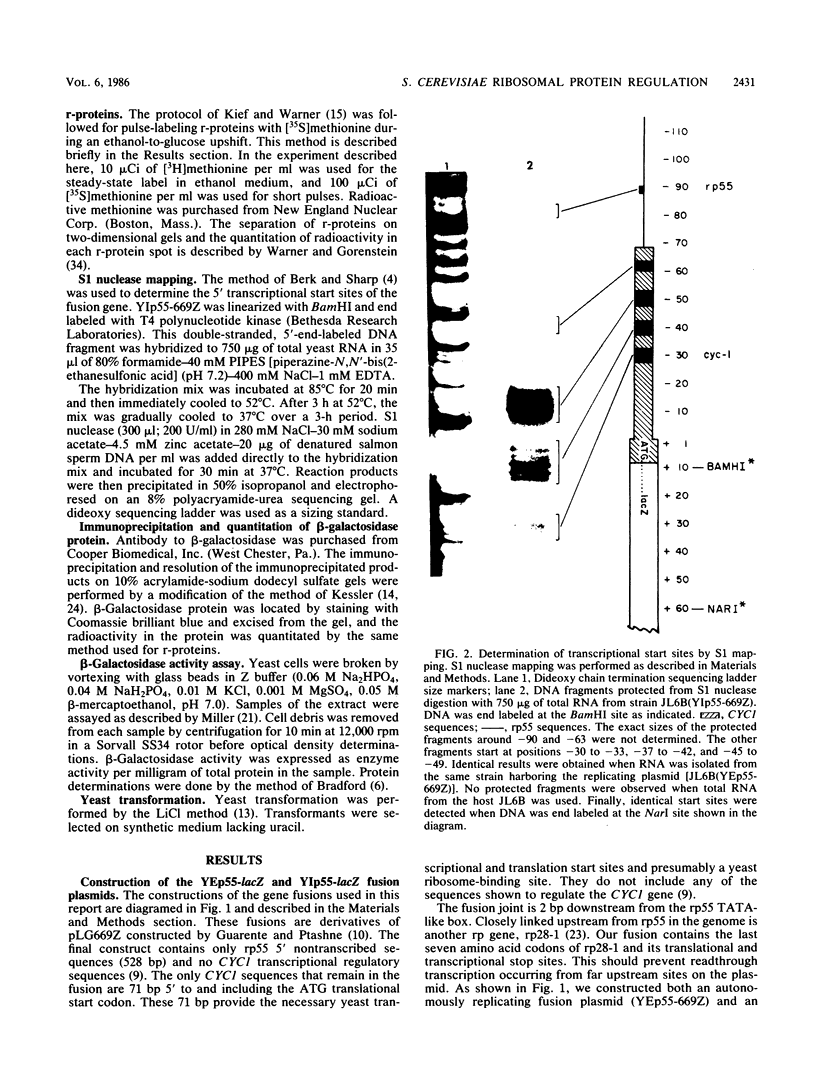
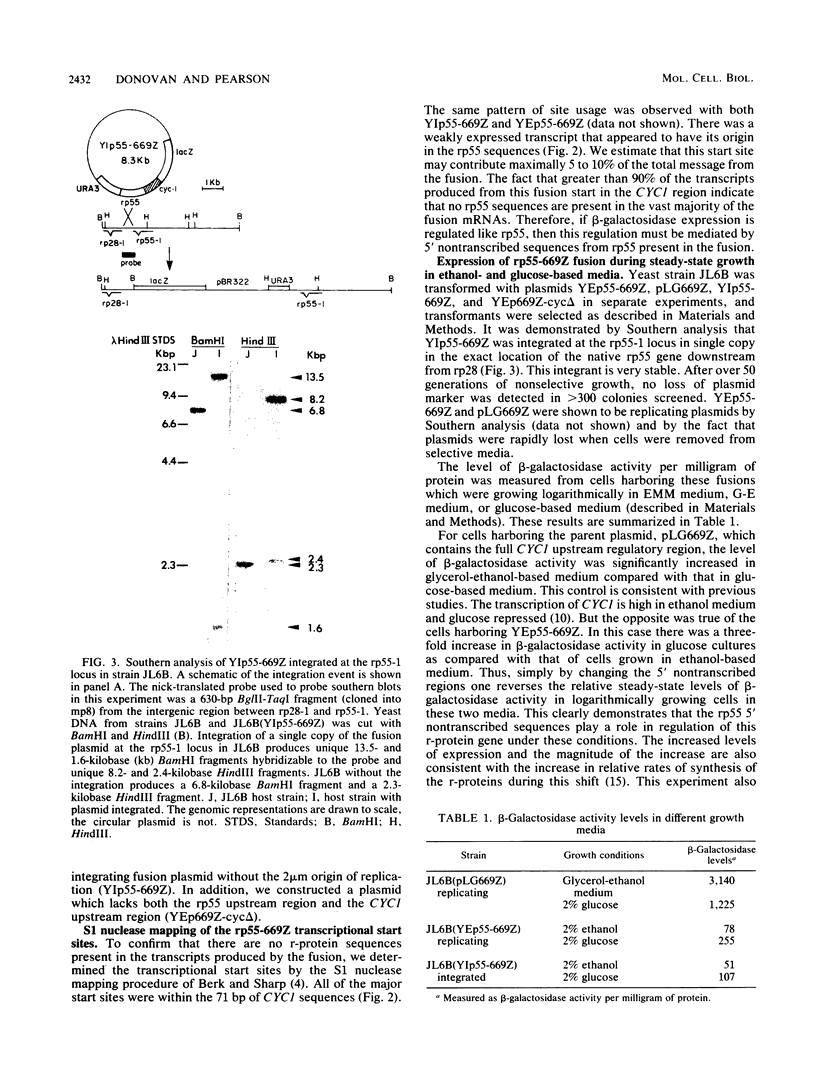
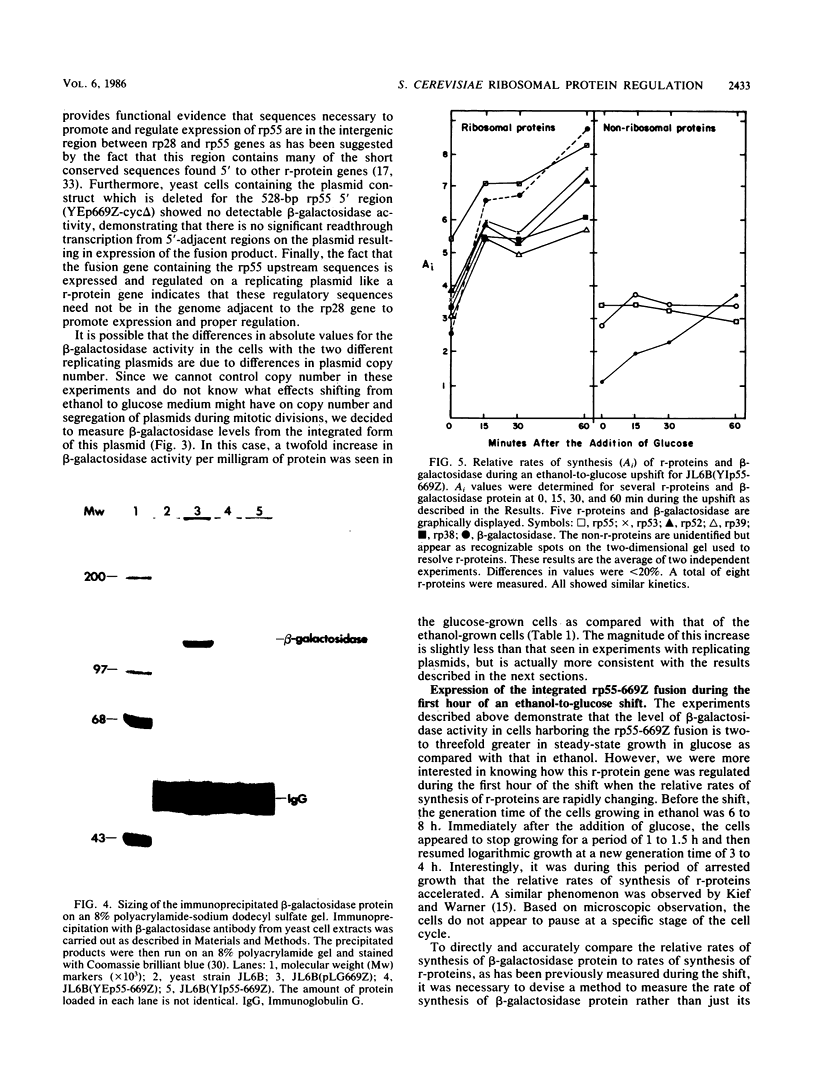
The relative rates of synthesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal proteins increase coordinately during a nutritional upshift. We constructed a gene fusion which contained 528 base pairs of sequence upstream from and including the TATA box of ribosomal protein gene rp55-1 (S16A-1) fused to a CYC1-lacZ fusion. This fusion was integrated in single copy at the rp55-1 locus in the yeast genome. During a nutritional upshift, in which glucose was added to cells growing in an ethanol-based medium, we found that the increase in the relative rate of synthesis of the beta-galactosidase protein product followed the same kinetics as the change in relative rates of synthesis of several ribosomal proteins measured in the same experiment. This demonstrates that the nontranscribed sequences upstream from the rp55-1 gene, which are present in the fusion, are sufficient to mediate the change in rates of synthesis characteristic of ribosomal proteins under these conditions. The results also suggest that a change in transcription rates is mainly responsible for the increase in relative rates of synthesis of ribosomal proteins during a nutritional upshift in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Atia G. R., Fruscoloni P., Jacobs-Lorena M. Translational regulation of mRNAs for ribosomal proteins during early Drosophila development. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5798–5803. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum E. Z., Wormington W. M. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kramer R. A. Modulation of chromatin structure associated with derepression of the acid phosphatase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7223–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P., Johnson L. F. Regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA content and translation in growth-stimulated mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):685–693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Vassarotti A., Friesen J. D. Molecular cloning and biosynthetic regulation of cry1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):500–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00341453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kief D. R., Warner J. R. Coordinate control of syntheses of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal proteins during nutritional shift-up in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Warner J. R. Mild temperature shock alters the transcription of a discrete class of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):457–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Smith M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC1 mRNA 5'-end positioning: analysis by in vitro mutagenesis, using synthetic duplexes with random mismatch base pairs. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3545–3551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura A., Krueger J. H., Itoh S., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Growth-rate-dependent regulation of ribosome synthesis in E. coli: expression of the lacZ and galK genes fused to ribosomal promoters. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Woudt L. P., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Structure and organization of two linked ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7345–7358. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Nam H. G., Hereford L. M., Fried H. M. Identification of a nuclear localization signal of a yeast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Higo K., Osawa S. Isolation of seventeen proteins and amino-terminal amino acid sequences of eight proteins from cytoplasmic ribosomes of yeast. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4545–4550. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Yeast use translational control to compensate for extra copies of a ribosomal protein gene. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Miura A., Bedwell D. M., Tam M., Nomura M. Increased expression of ribosomal genes during inhibition of ribosome assembly in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The synthesis of eucaryotic ribosomal proteins in vitro. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Mitra G., Schwindinger W. F., Studeny M., Fried H. M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae coordinates accumulation of yeast ribosomal proteins by modulating mRNA splicing, translational initiation, and protein turnover. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1512–1521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Transcriptional control of the S10 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli after a shift to higher temperature. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):140–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.140-147.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]