Abstract
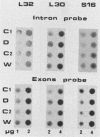
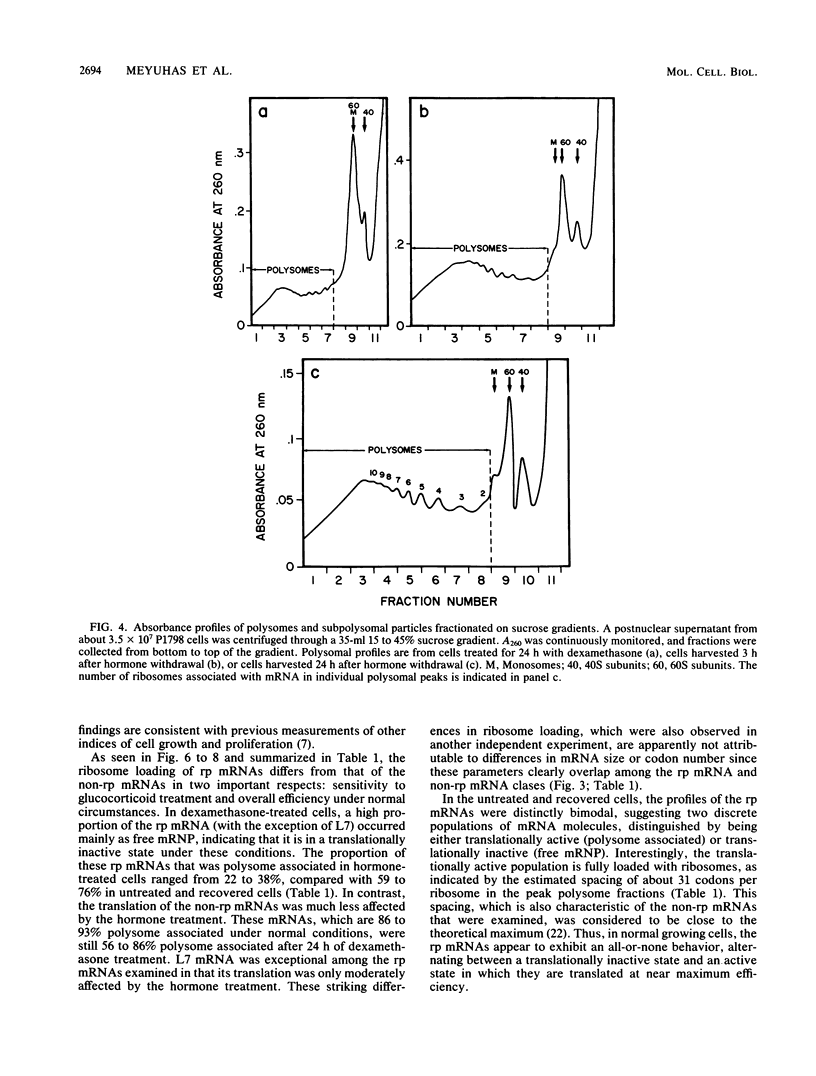
When P1798 murine lymphosarcoma cells are exposed to 10(-7) M dexamethasone, there is a dramatic inhibition of rRNA synthesis, which is completely reversible when the hormone is withdrawn. In the present experiments we examined whether dexamethasone treatment causes any alteration in the accumulation or utilization of mRNAs that encode ribosomal proteins (rp mRNAs). No effect on the accumulation of six different rp mRNAs was detected. However, the translation of five of six rp mRNAs was selectively inhibited in the presence of the hormone, as judged by a substantial decrease in ribosomal loading. Normal translation of rp mRNA was resumed within a few hours after hormone withdrawal. In untreated or fully recovered cells, the distribution of rp mRNAs between polyribosomes and free ribonucleoprotein is distinctly bimodal, suggesting that rp mRNAs are subject to a particular form of translational control in which they are either translationally inactive or fully loaded with ribosomes. A possible relationship between this mode of translational control and the selective suppression of rp mRNA translation by glucocorticoids is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Gritz L., Tung L., Rosbash M. Effect of RP51 gene dosage alterations on ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3429–3435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal M. G., Bowman L. H. Transcriptional and translational regulation of ribosomal protein formation during mouse myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4868–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Atia G. R., Fruscoloni P., Jacobs-Lorena M. Translational regulation of mRNAs for ribosomal proteins during early Drosophila development. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5798–5803. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum E. Z., Wormington W. M. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Gokal P. K., Lawther R. P., Thompson E. A., Jr Glucocorticoid inhibition of initiation of transcription of the DNA encoding rRNA (rDNA) in lymphosarcoma P1798 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):718–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA: glucocorticoid effects upon initiation and elongation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3357–3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavannaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Inhibition of transcription during glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of proliferation of lymphosarcoma P1798 cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9768–9773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Lin A., McNally J., Peleg D., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L19. A determination from the sequence of nucleotides in a cDNA and from the sequence of amino acids in the protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1111–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N., Perry R. P. Persistent cytoplasmic synthesis of ribosomal proteins during the selective inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 20;229(3):75–80. doi: 10.1038/newbio229075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Warner J. R. Autogenous regulation of splicing of the transcript of a yeast ribosomal protein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5854–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePhilip R. M., Rudert W. A., Lieberman I. Preferential stimulation of ribosomal protein synthesis by insulin and in the absence of ribosomal and messenger ribonucleic acid formation. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1662–1669. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. M., Jr, Barker K. L. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Translational regulation of synthesis and regulation of processing of the enzyme in the uterus by estradiol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 10;739(2):148–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Transcriptional regulation of ribosomal proteins during a nutritional upshift in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2429–2435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faliks D., Meyuhas O. Coordinate regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA level in regenerating rat liver. Study with the corresponding mouse cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):789–801. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P., Johnson L. F. Regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA content and translation in growth-stimulated mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):685–693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., Folk W. R. Structure and organization of a mammalian 5 S gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11706–11711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Vassarotti A., Friesen J. D. Molecular cloning and biosynthetic regulation of cry1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):500–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00341453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz G. G., Hokari S., DePhilip R. M., Tsukada K., Lieberman I. Lodish model and regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis by insulin-deficient chick embryo fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2550–2558. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs F. A., Bird R. C., Sells B. H. Differentiation of rat myoblasts. Regulation of turnover of ribosomal proteins and their mRNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 15;150(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C. The cocoonase zymogen cells of silk moths: a model of terminal cell differentiation for specific protein synthesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1972;7:125–191. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. A., Jacobs-Lorena M. Selective translational regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3583–3592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kief D. R., Warner J. R. Coordinate control of syntheses of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal proteins during nutritional shift-up in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Warner J. R. Mild temperature shock alters the transcription of a discrete class of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):457–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K. S., Soeiro R., Nadal-Ginard B. Unco-ordinate regulation of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal protein synthesis during L6E9 myoblast differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 15;142(2):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarca M. J., Wassarman P. M. Relationship between rates of synthesis and intracellular distribution of ribosomal proteins during oogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Aft R., Ross J., Mueller G. C. Control of globin gene expression by steroid hormones in differentiating Friend leukemia cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Model for the regulation of mRNA translation applied to haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):385–388. doi: 10.1038/251385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Ruberti I., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Nucleotide sequence of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis: remarkable sequence homology among introns. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Construction and identification of cDNA clones for mouse ribosomal proteins: application for the study of r-protein gene expression. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Characterization of productive and sterile transcripts from the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: processing of micron and muS mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1317–1332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panabières F., Piechaczyk M., Rainer B., Dani C., Fort P., Riaad S., Marty L., Imbach J. L., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the messenger RNA coding for chicken muscle glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91461-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou J., Stewart J. A., Rabek J. P., McClintock P. R., Wong E. Y. Glucocorticoids inhibit the coordinated translation of alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):542–551. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90483-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Yeast use translational control to compensate for extra copies of a ribosomal protein gene. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennequin P., Robins D. M., Schimke R. T. Regulation of translation of ovalbumin messenger RNA by estrogens and progesterone in oviduct of withdrawn chicks. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Immunoglobulin messenger RNAs in murine cell lines that have characteristics of immature B lymphocytes. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1333–1339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Ribosomal protein production in normal and anucleolate Xenopus embryos: regulation at the posttranscriptional and translational levels. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):317–323. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H. P., Akhayat O., Martins De Sa C., Puvion F., Koehler K., Scherrer K. The prosome: an ubiquitous morphologically distinct RNP particle associated with repressed mRNPs and containing specific ScRNA and a characteristic set of proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T., Chen P. S., Pellegrini M. The induction of ribosome biosynthesis in a nonmitotic secretory tissue. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7645–7650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. The second Sir Hans Krebs Lecture. Informosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Aug;10(1):20–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Jr Properties of a cell-culture line derived from lymphosarcoma P1798. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Feb;17(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the multigene family encoding the mouse S16 ribosomal protein: strategy for distinguishing an expressed gene from its processed pseudogene counterparts by an analysis of total genomic DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3560–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. In the absence of ribosomal RNA synthesis, the ribosomal proteins of HeLa cells are synthesized normally and degraded rapidly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Mitra G., Schwindinger W. F., Studeny M., Fried H. M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae coordinates accumulation of yeast ribosomal proteins by modulating mRNA splicing, translational initiation, and protein turnover. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1512–1521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the expressed gene and several processed pseudogenes for the mouse ribosomal protein L30 gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2518–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:719–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yenofsky R., Bergmann I., Brawerman G. Messenger RNA species partially in a repressed state in mouse sarcoma ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5876–5880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- elBaradi T. T., van der Sande C. A., Mager W. H., Raué H. A., Planta R. J. The cellular level of yeast ribosomal protein L25 is controlled principally by rapid degradation of excess protein. Curr Genet. 1986;10(10):733–739. doi: 10.1007/BF00405095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]