Abstract
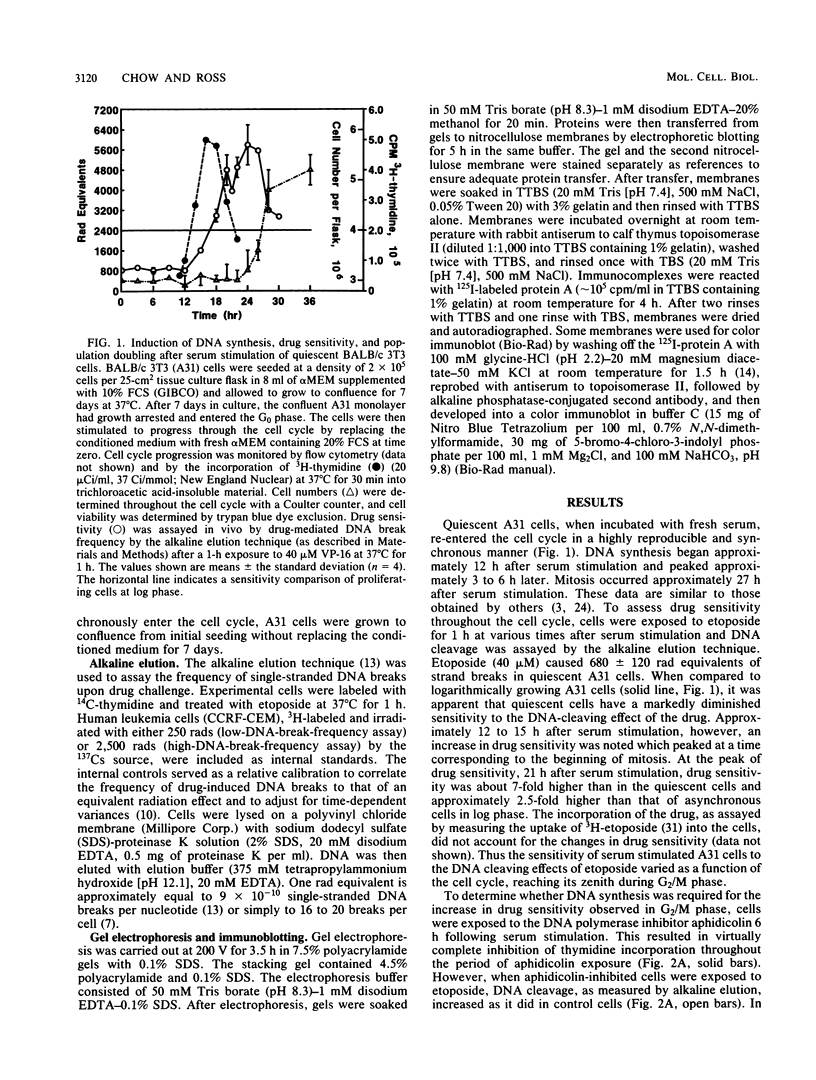
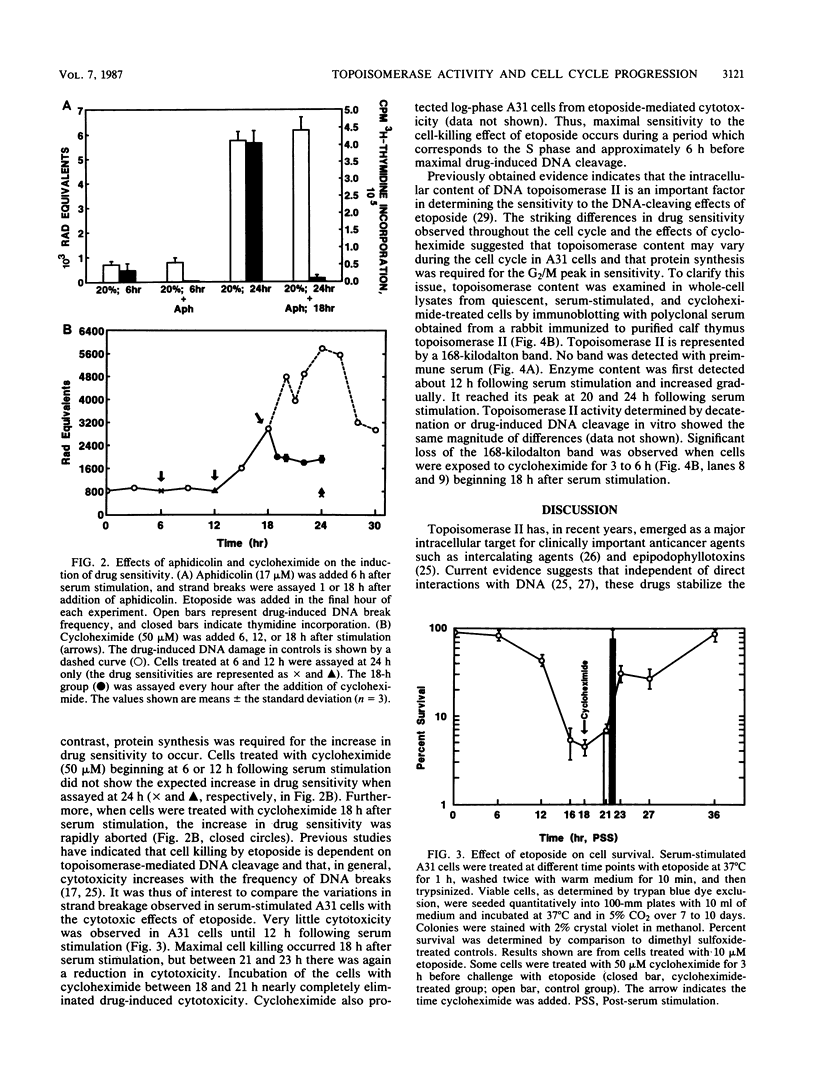
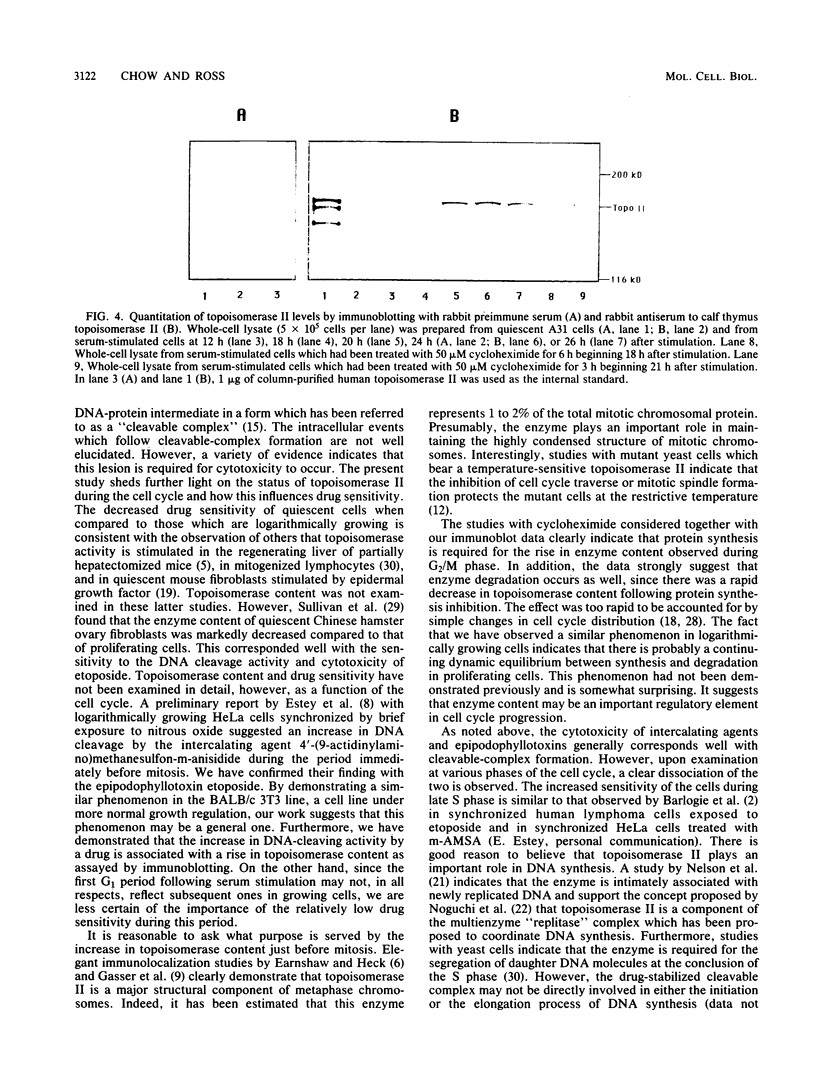
The nuclear enzyme DNA topoisomerase II catalyzes the breakage and resealing of duplex DNA and plays an important role in several genetic processes. It also mediates the DNA cleavage activity and cytotoxicity of clinically important anticancer agents such as etoposide. We have examined the activity of topoisomerase II during the first cell cycle of quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells following serum stimulation. Etoposide-mediated DNA break frequency in vivo was used as a parameter of topoisomerase II activity, and enzyme content was assayed by immunoblotting. Density-arrested A31 cells exhibited a much lower sensitivity to the effects of etoposide than did actively proliferating cells. Upon serum stimulation of the quiescent cells, however, there was a marked increase in drug sensitivity which began during S phase and reached its peak just before mitosis. Maximal drug sensitivity during this period was 2.5 times greater than that of log-phase cells. This increase in drug sensitivity was associated with an increase in intracellular topoisomerase II content as determined by immunoblotting. The induction of topoisomerase II-mediated drug sensitivity was aborted within 1 h of exposure of cells to the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide, but the DNA synthesis inhibitor aphidicolin had no effect. In contrast to the sensitivity of cells to drug-induced DNA cleavage, maximal cytotoxicity occurred during S phase. A 3-h exposure to cycloheximide before etoposide treatment resulted in nearly complete loss of cytotoxicity. Our findings indicate that topoisomerase II activity fluctuates with cell cycle progression, with peak activity occurring during the G2 phase. This increase in topoisomerase II is protein synthesis dependent and may reflect a high rate of enzyme turnover. The dissociation between maximal drug-induced DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity indicates that the topoisomerase-mediated DNA breaks may be necessary but are not sufficient for cytotoxicity and that the other factors which are particularly expressed during S phase may be important as well.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Wierzbicki A., Frommer B., Hoess R. H. Bacteriophage P1 Cre-loxP site-specific recombination. Site-specific DNA topoisomerase activity of the Cre recombination protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlogie B., Drewinko B., Johnston D. A., Freireich E. J. The effect of adriamycin on the cell cycle traverse of a human lymphoid cell line. Cancer Res. 1976 Jun;36(6):1975–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Lavenot C., Harper F., Mirambeau G., De Recondo A. M. DNA topoisomerases from rat liver: physiological variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1059–1075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkind M. M. DNA damage and cell killing. Cause and effect? Cancer. 1985 Nov 15;56(10):2351–2363. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19851115)56:10<2351::aid-cncr2820561002>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisson B. S., Smallwood S. E., Ross W. E. Characterization of VP-16-induced DNA damage in isolated nuclei from L1210 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 5;783(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Erickson L. C., Ewig R. A., Friedman C. A. Fractionation of DNA from mammalian cells by alkaline elution. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4629–4637. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Multiple immunoreplica Technique: screening for specific proteins with a series of different antibodies using one polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90577-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long B. H., Musial S. T., Brattain M. G. Comparison of cytotoxicity and DNA breakage activity of congeners of podophyllotoxin including VP16-213 and VM26: a quantitative structure-activity relationship. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1183–1188. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medrano E. E., Pardee A. B. Prevalent deficiency in tumor cells of cycloheximide-induced cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4123–4126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins R., Miskimins W. K., Bernstein H., Shimizu N. Epidermal growth factor-induced topoisomerase(s). Intracellular translocation and relation to DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jun;146(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra N. C., Roberts D. W. Inhibition by 4'-demethyl-epipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-2-thenylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside) of human lymphoblast cultures in G2 phase of the cell cycle. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Liu L. F., Coffey D. S. Newly replicated DNA is associated with DNA topoisomerase II in cultured rat prostatic adenocarcinoma cells. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):187–189. doi: 10.1038/322187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Rapid incorporation of label from ribonucleoside disphosphates into DNA by a cell-free high molecular weight fraction from animal cell nuclei. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N. Eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Characterization of enzyme turnover. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9944–9950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Gray H. E., Godeau F. Growth-dependent synthesis of c-myc-encoded proteins: early stimulation by serum factors in synchronized mouse 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2903–2912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E., Bradley M. O. DNA double-stranded breaks in mammalian cells after exposure to intercalating agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 26;654(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E., Zwelling L. A., Kohn K. W. Relationship between cytotoxicity and DNA strand breakage produced by adriamycin and other intercalating agents. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979 Aug;5(8):1221–1224. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90642-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Rowe T., Glisson B., Yalowich J., Liu L. Role of topoisomerase II in mediating epipodophyllotoxin-induced DNA cleavage. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5857–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossow P. W., Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Synthesis of labile, serum-dependent protein in early G1 controls animal cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. M., Glisson B. S., Hodges P. K., Smallwood-Kentro S., Ross W. E. Proliferation dependence of topoisomerase II mediated drug action. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2248–2256. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taudou G., Mirambeau G., Lavenot C., der Garabedian A., Vermeersch J., Duguet M. DNA topoisomerase activities in concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalowich J. C., Ross W. E. Verapamil-induced augmentation of etoposide accumulation in L1210 cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1651–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



