Abstract
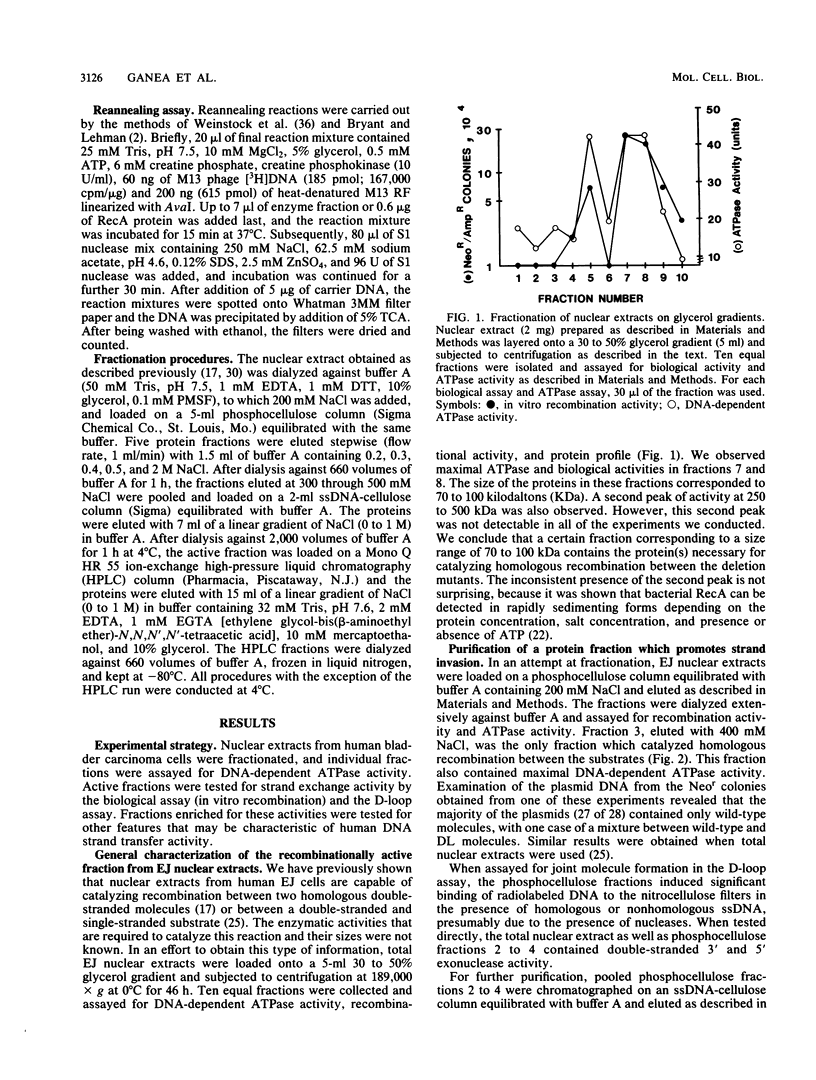
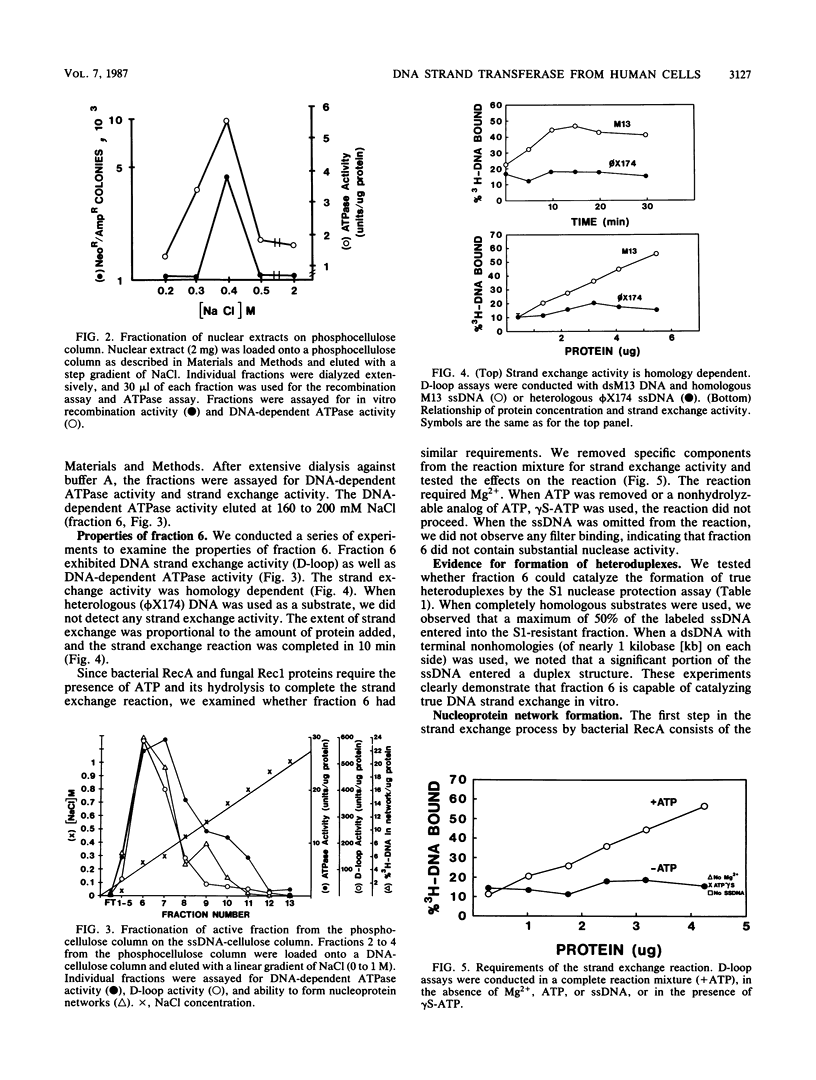
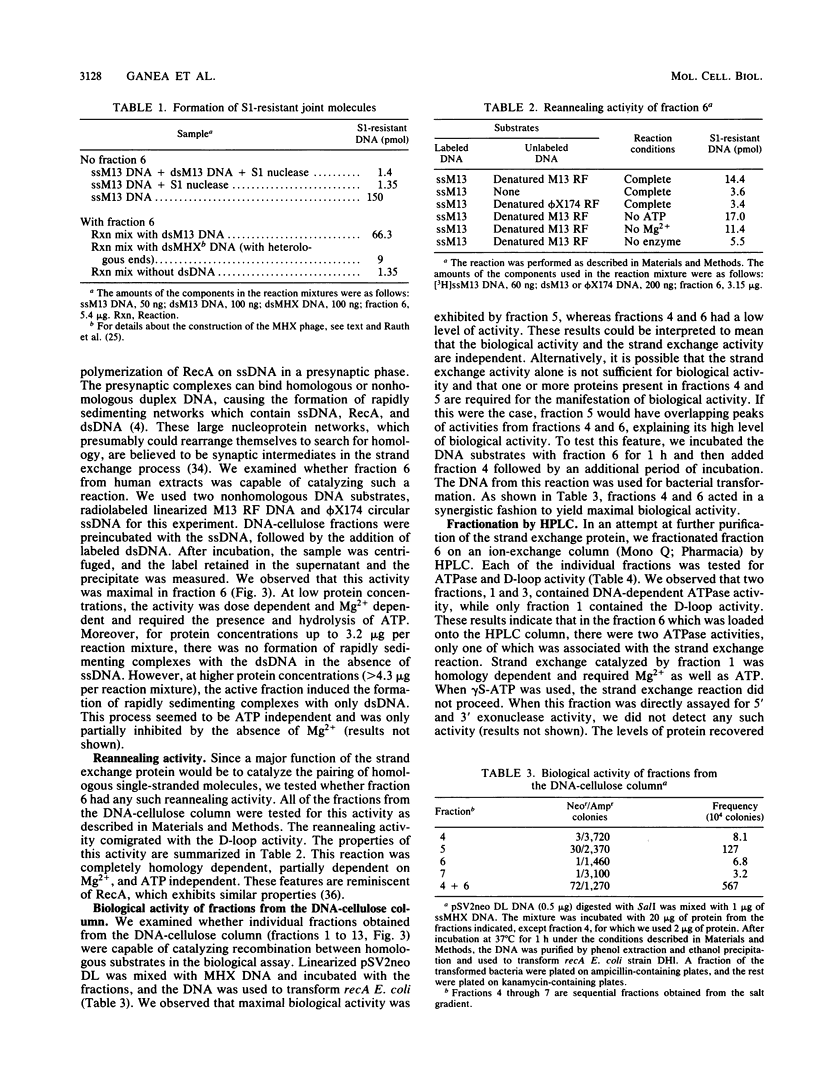
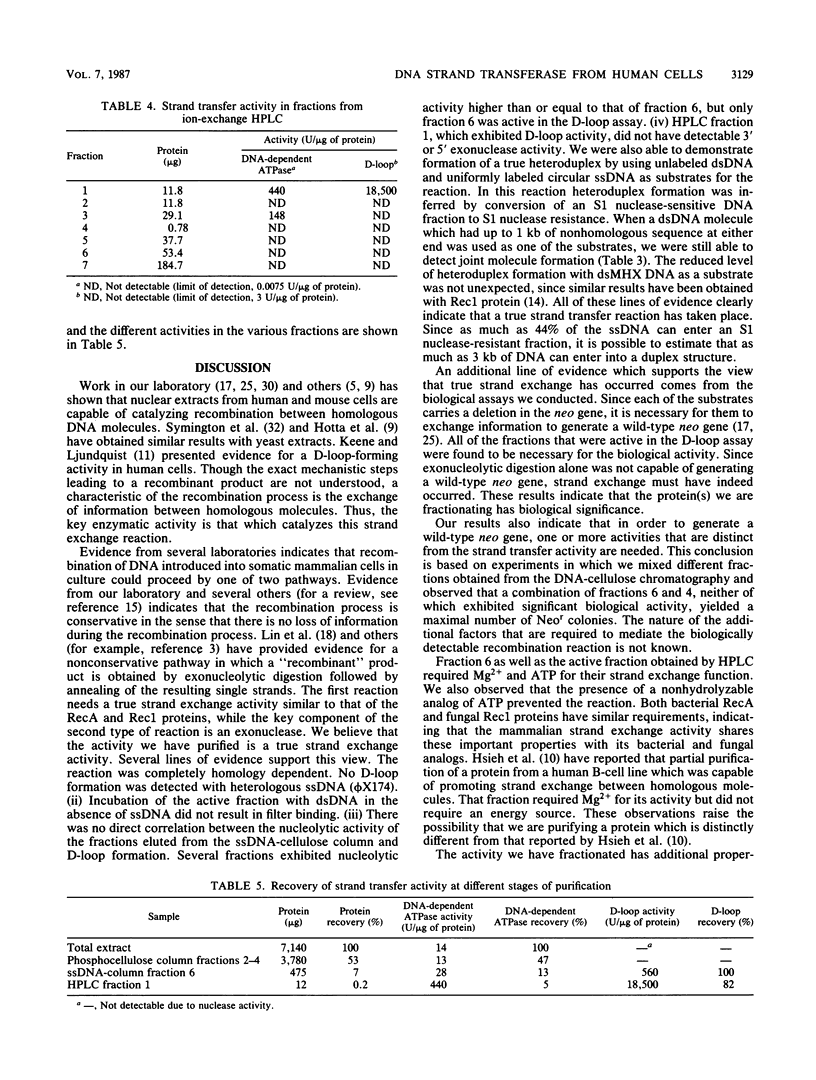
We have characterized an enzymatic activity from human cell nuclei which is capable of catalyzing strand exchange between homologous DNA sequences. The strand exchange activity was Mg2+ dependent and required ATP hydrolysis. In addition, it was capable of promoting reannealing of homologous DNA sequences and could form nucleoprotein networks in a fashion reminiscent of purified bacterial RecA protein. Using an in vitro recombination assay, we also showed that the strand exchange activity was biologically important. The factor(s) responsible for the activity has been partially purified.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie K. L., Wiegand R. C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. II. Characterization of the reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):783–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Lehman I. R. On the mechanism of renaturation of complementary DNA strands by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Seidman M. M. Intramolecular recombination between transfected repeated sequences in mammalian cells is nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2520–2526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Radding C. M. Ionic inhibition of formation of RecA nucleoprotein networks blocks homologous pairing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5646–5650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby V., Blattner F. Homologous recombination catalyzed by mammalian cell extracts in vitro. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1213–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.6334360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta C., Wu A. M., Kahn R., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Concerted strand exchange and formation of Holliday structures by E. coli RecA protein. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tabata S., Bouchard R. A., Piñon R., Stern H. General recombination mechanisms in extracts of meiotic cells. Chromosoma. 1985;93(2):140–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00293161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Meyn M. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Partial purification and characterization of a recombinase from human cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne K., Ljungquist S. A DNA-recombinogenic activity in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3057–3068. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Heteroduplex formation and polarity during strand transfer promoted by Ustilago rec 1 protein. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):857–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Synapsis promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules promoted by a protein from Ustilago. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R. S., Eves E. M., Song K. Y., Morse B. S., Smithies O. Homologous recombination between plasmids in mammalian cells can be enhanced by treatment of input DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3153–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R. S., Spencer J., Moore P. D. Homologous recombination catalyzed by human cell extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):714–720. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA T., HOMMA J., SONOHARA H. Improved method for obtaining thymineless mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:602–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.602-603.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Wabiko H., Tsurimoto T., Horii T., Masukata H., Ogawa H. Characteristics of purified recA protein and the regulation of its synthesis in vivo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):909–915. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth S., Song K. Y., Ayares D., Wallace L., Moore P. D., Kucherlapati R. Transfection and homologous recombination involving single-stranded DNA substrates in mammalian cells and nuclear extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L., Phizicky E. M. Activity of the Escherichia coli recA-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):917–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J., Scangos G. Recombination during gene transfer into mouse cells can restore the function of deleted genes. Science. 1983 Jan 14;219(4581):174–176. doi: 10.1126/science.6294829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K. Y., Chekuri L., Rauth S., Ehrlich S., Kucherlapati R. Effect of double-strand breaks on homologous recombination in mammalian cells and extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Fogarty L. M., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of homologous plasmids catalyzed by cell-free extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Muniyappa K., Azhderian E., Gonda D. K., Radding C. M., Flory J., Chase J. W. Intermediates in homologous pairing promoted by recA protein. Isolation and characterization of active presynaptic complexes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90405-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):126–130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Characterization of ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8829–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Wahl G. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells mediates formation of a functional gene from two overlapping gene fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


