Abstract
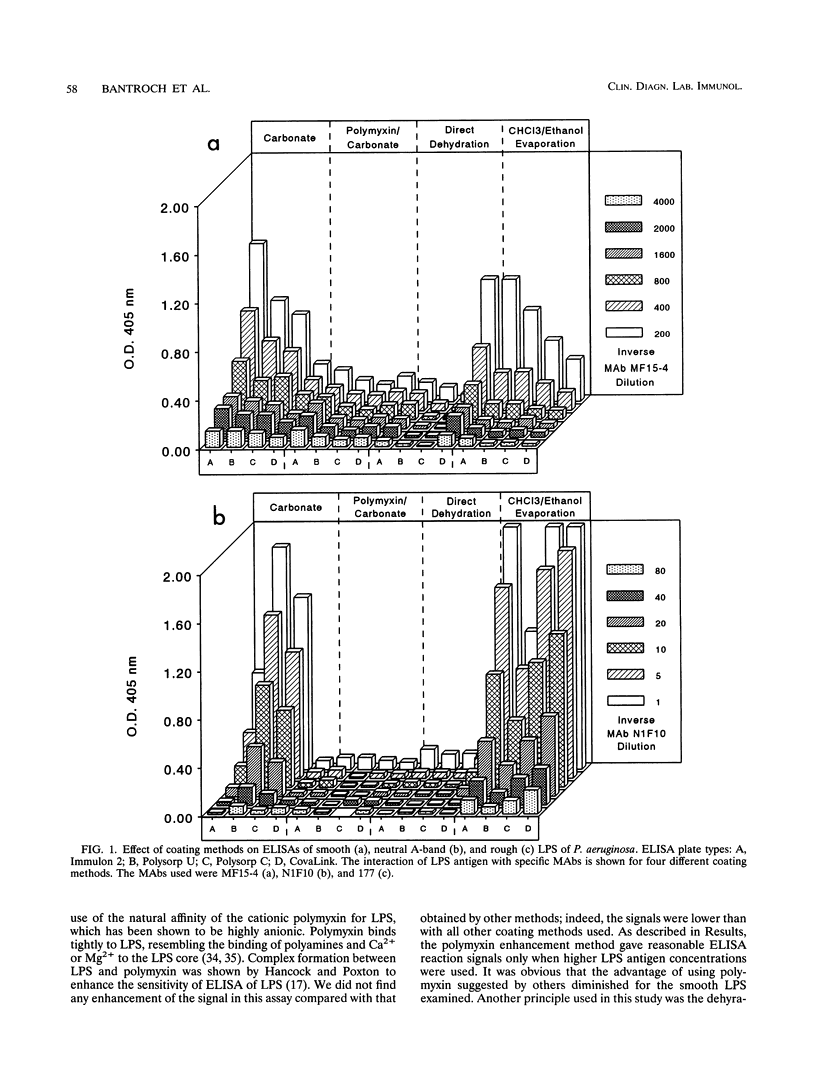
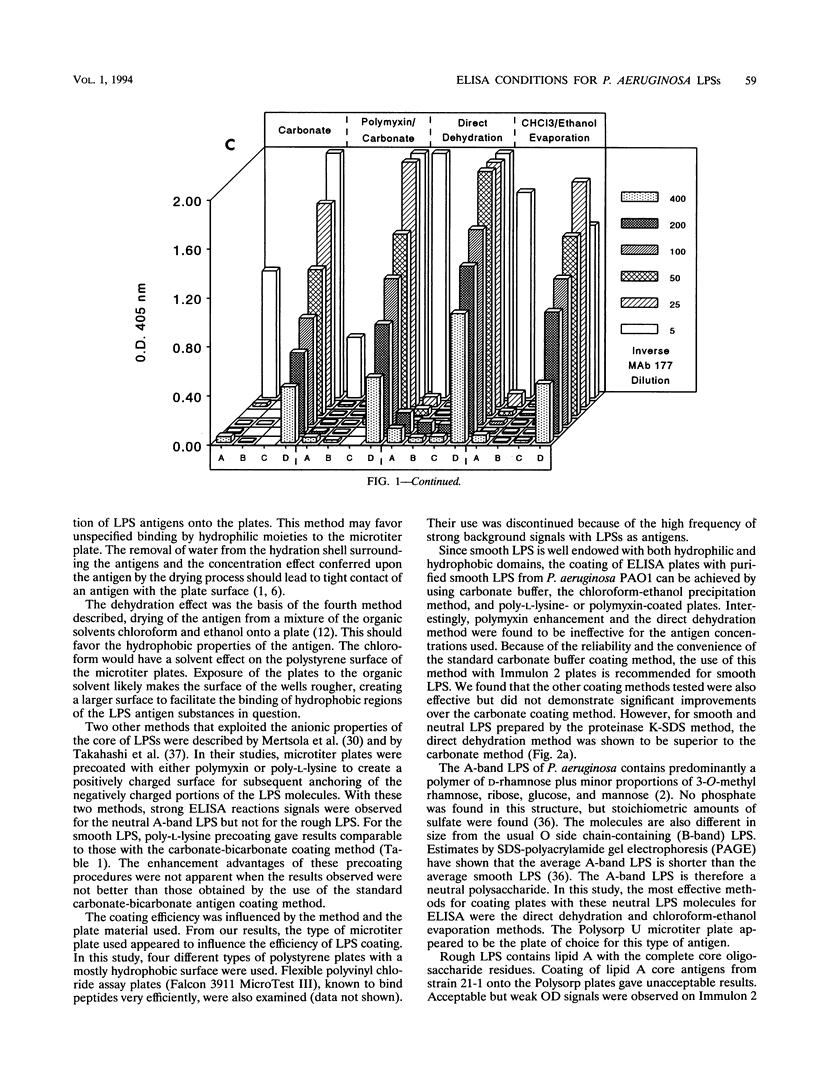
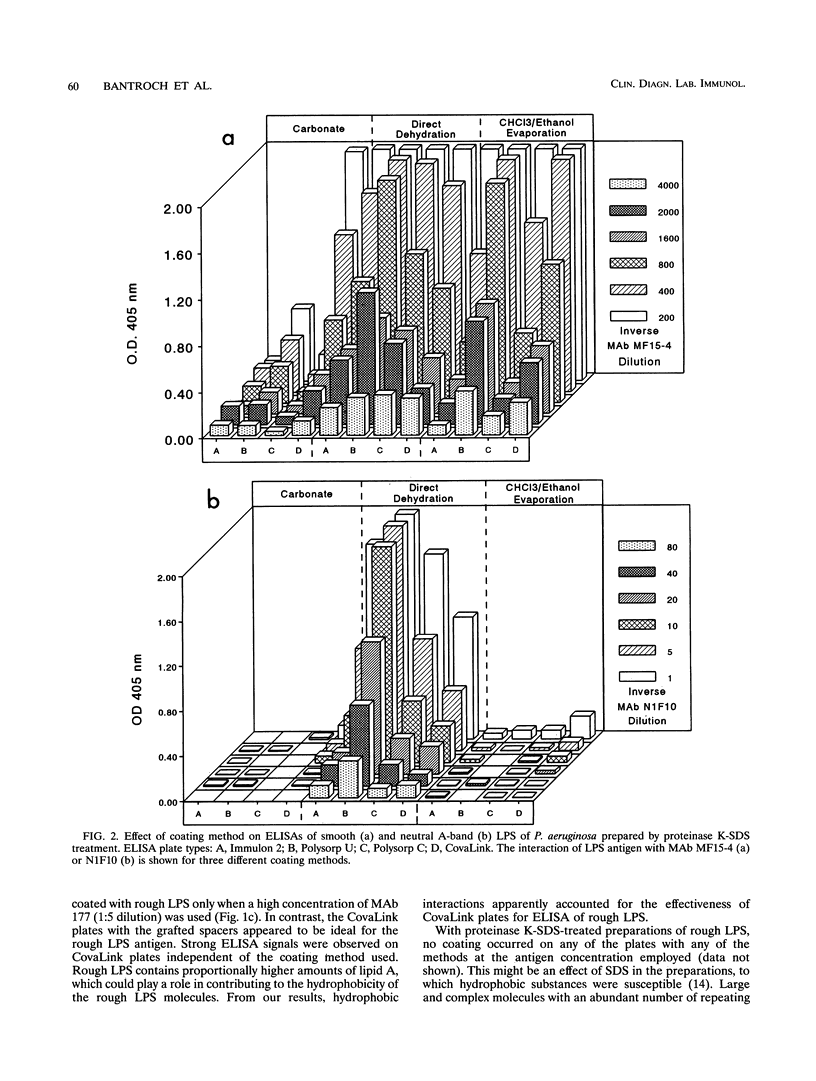
Smooth, rough, and neutral forms of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa were used to assess the appropriate conditions for effective enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of LPS. Each of these forms of well-defined LPS was tested for the efficiency of antigen coating by various methods as well as to identify an appropriate type of microtiter plate to use. For smooth LPS, the standard carbonate-bicarbonate buffer method was as efficient as the other sensitivity-enhancing plate-coating methods compared. The rough LPS, which has an overall hydrophobic characteristic, was shown to adhere effectively, regardless of the coating method used, to only one type of microtiter plate, CovaLink. This type of plate has secondary amine groups attached on its polystyrene surface by carbon chain spacers, which likely favors hydrophobic interactions between the rough LPS and the well surfaces. Dehydration methods were effective for coating microtiter plates with the neutral LPS examined, which is composed predominantly of a D-rhamnan. For the two dehydration procedures, LPS suspended in water or the organic solvent chloroform-ethanol was added directly to the wells, and the solvent was allowed to dehydrate or evaporate overnight. Precoating of plates with either polymyxin or poly-L-lysine did not give any major improvement in coating with the various forms of LPS. The possibility of using proteinase K- and sodium dodecyl sulfate-treated LPS preparations for ELISAs was also investigated. Smooth LPS prepared by this method was as effective in ELISA as LPS prepared by the hot water-phenol method, while the rough and neutral LPSs prepared this way were not satisfactory for ELISA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastin D. A., Stevenson G., Brown P. K., Haase A., Reeves P. R. Repeat unit polysaccharides of bacteria: a model for polymerization resembling that of ribosomes and fatty acid synthetase, with a novel mechanism for determining chain length. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D., Kropinski A. M. Effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations and temperature on plasmid transformation efficiency in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1986 May;32(5):436–438. doi: 10.1139/m86-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantarero L. A., Butler J. E., Osborne J. W. The adsorptive characteristics of proteins for polystyrene and their significance in solid-phase imunoassays. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90473-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Chaby R., Karibian D., Perry J., Deprun C., Szabó L. Variations in the carbohydrate regions of Bordetella pertussis lipopolysaccharides: electrophoretic, serological, and structural features. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1121–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1121-1128.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M. Heterogeneity of the lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):273–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Fomsgaard A., Mitov I., Galanos C. ELISA for antibodies to lipid A, lipopolysaccharides and other hydrophobic antigens. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):322–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01650719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardas A., Lewartowska A. Coating of proteins to polystyrene ELISA plates in the presence of detergents. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Webb J. W., Yamasaki R., Fisher S. J., Burlingame A. L., Mandrell R. E., Schneider H., Griffiss J. M. Structure and heterogeneity of the oligosaccharides from the lipopolysaccharides of a pyocin-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):17–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., O'Brien J. P., Yamasaki R., Williams G. D., Rice P. A., Schneider H. Physical heterogeneity of neisserial lipooligosaccharides reflects oligosaccharides that differ in apparent molecular weight, chemical composition, and antigenic expression. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1792–1800. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1792-1800.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Leive L., Mäkelä P. H., Rietschel E. T., Strittmatter W., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide nomenclature--past, present, and future. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.699-705.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knirel Y. A. Polysaccharide antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):273–304. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L. C., Milazzo F. H. The extraction and analysis of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO, and three rough mutants. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):390–398. doi: 10.1139/m79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Kuzio J., Angus B. L., Hancock R. E. Chemical and chromatographic analysis of lipopolysaccharide from an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):310–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Handelsman M. Y., Chivers T. R., MacDonald L. A. Monoclonal antibodies as probes to examine serotype-specific and cross-reactive epitopes of lipopolysaccharides from serotypes O2, O5, and O16 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2178–2184. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2178-2184.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., MacDonald L. A., Lam M. Y., Duchesne L. G., Southam G. G. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against serotype strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1051–1057. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1051-1057.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam M. Y., McGroarty E. J., Kropinski A. M., MacDonald L. A., Pedersen S. S., Høiby N., Lam J. S. Occurrence of a common lipopolysaccharide antigen in standard and clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):962–967. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.962-967.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H. U., Stammler P., Fischer E. A. Covalent binding of detergent-solubilized membrane glycoproteins to 'Chemobond' plates for ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 25;129(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90441-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertsola J., Ramilo O., Sáez-Llorens X., Hanson M. S., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Specific detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide by a polymyxin B monoclonal antibody assay. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Sep 1;122(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E. Surface localization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane porin protein F by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz C., Nieto A., Gayá A., Martínez J., Vives J. New experimental criteria for optimization of solid-phase antigen concentration and stability in ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 20;94(1-2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Bryan L. E., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: analysis of lipopolysaccharide chain length. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.512-521.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Fukada M., Kawai M., Yokochi T. Detection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and identification of its serotype by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using poly-L-lysine. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Aug 30;153(1-2):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90306-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


