Abstract
Within the past decade, certain strains of Bacteroides fragilis have been associated with diarrhea in humans and cytotoxic activity on certain colon carcinoma cell lines. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detecting the enterotoxin of B. fragilis in cultures and stools was developed by using high-titer monospecific goat and rabbit antitoxins in an indirect format. The lower limit of detection for purified toxin was approximately 0.05 micrograms/ml; the linear range was from 0.05 to 10 microgram/ml. Using the ELISA to screen cultures of toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of B. fragilis, we observed 100% correlation with 16 known toxigenic strains which had various cytotoxic activities on HT-29 cells. In addition, we found 6 of 62 previously untested strains also to be positive in both assays. Stability studies revealed that although the cytotoxic activities of crude and purified toxin preparations incubated at elevated temperatures were rapidly lost, the ELISA responses were not significantly reduced. Sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and SDS-capillary electrophoresis showed that the purified toxin autodigested to several stable peptides. Studies on partially purified membranes from the toxigenic strains revealed the presence of several membrane-associated components which were noncytotoxic but strongly immunoreactive in the ELISA. Preliminary studies with spiked feces indicated that the ELISA may be useful for screening not only cultures for the enterotoxigenic B. fragilis but also stool specimens. Ongoing studies are focusing on determining the nature of the toxin's apparent proteolytic capabilities and investigating the feasibility of using the ELISA on stool specimens from healthy and diarrheic humans.
Full text
PDF

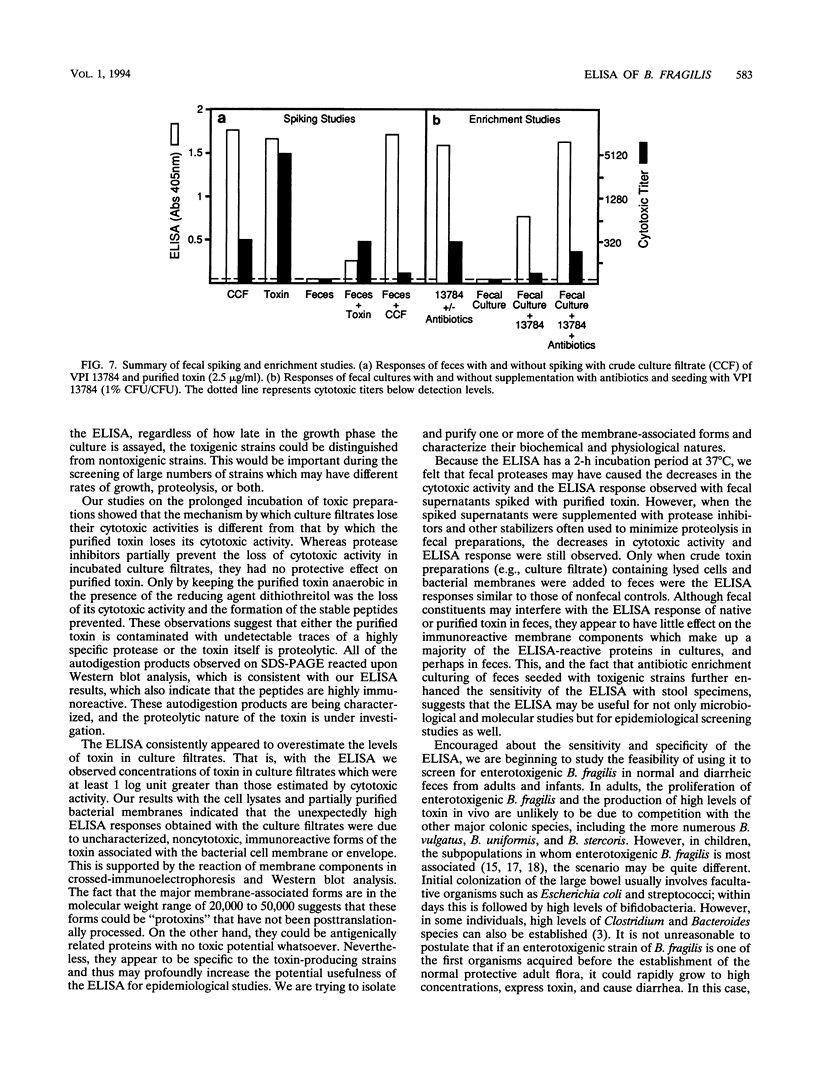

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Border M., Firehammer B. D., Shoop D. S., Myers L. L. Isolation of Bacteroides fragilis from the feces of diarrheic calves and lambs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):472–473. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.472-473.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I. Effect of encapsulated Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides fragilis on the growth of aerobic and facultative bacteria in mixed infections. J Surg Res. 1989 Jul;47(1):92–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(89)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duimstra J. R., Myers L. L., Collins J. E., Benfield D. A., Shoop D. S., Bradbury W. C. Enterovirulence of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in gnotobiotic pigs. Vet Pathol. 1991 Nov;28(6):514–518. doi: 10.1177/030098589102800608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Sullivan N. M., Wilkins T. D. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.72-78.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Some current concepts in intestinal bacteriology. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Oct;31(10 Suppl):S33–S42. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.10.S33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P. Polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis of soluble proteins for studies of bacterial floras. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):900–907. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.900-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Firehammer B. D., Shoop D. S., Border M. M. Bacteroides fragilis: a possible cause of acute diarrheal disease in newborn lambs. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):241–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.241-244.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S. Association of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis with diarrheal disease in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):774–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Byars T. D. Diarrhea associated with enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Nov;48(11):1565–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Collins J. E., Bradbury W. C. Diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in infant rabbits. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2025–2030. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2025-2030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Collins J. E. Rabbit model to evaluate enterovirulence of Bacteroides fragilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1658–1660. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1658-1660.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Firehammer B. D., Border M. M. Association of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis with diarrheal disease in calves. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1344–1347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Shoop D. S., Stackhouse L. L., Newman F. S., Flaherty R. J., Letson G. W., Sack R. B. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis from humans with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2330–2333. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2330-2333.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L., Cisneros R. L., Bartlett J. G. The capsular polysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis as a virulence factor: comparison of the pathogenic potential of encapsulated and unencapsulated strains. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):82–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Albert M. J., Alam K., Neogi P. K., Akbar M. S. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis from Bangladeshi children with diarrhea: a controlled study. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Apr;32(4):960–963. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.4.960-963.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Myers L. L., Almeido-Hill J., Shoop D. S., Bradbury W. C., Reid R., Santosham M. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: epidemiologic studies of its role as a human diarrhoeal pathogen. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1992 Mar;10(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G. L., Gorbach S. L. Intestinal flora in health and disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):174–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tassel R. L., Lyerly D. M., Wilkins T. D. Production of antisera against the enterotoxin of Bacteroides fragilis and their use in a cytotoxicity neutralization assay of HT-29 cells. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1994 Jul;1(4):473–476. doi: 10.1128/cdli.1.4.473-476.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tassell R. L., Lyerly D. M., Wilkins T. D. Purification and characterization of an enterotoxin from Bacteroides fragilis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1343-1350.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikel C. S., Grieco F. D., Reuben J., Myers L. L., Sack R. B. Human colonic epithelial cells, HT29/C1, treated with crude Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin dramatically alter their morphology. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):321–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.321-327.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M. The chlorine controversy. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):15–16. doi: 10.1126/science.8211120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]