Abstract
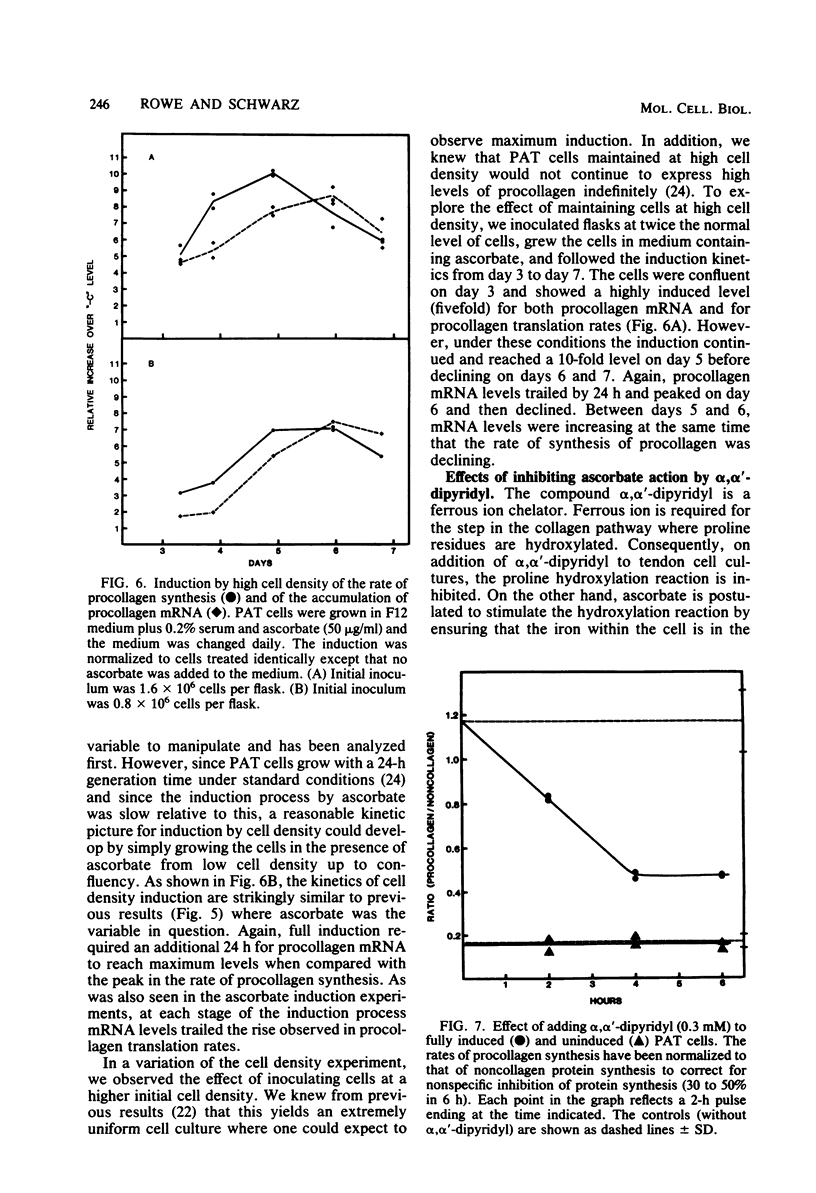
Two factors must be present for primary avian tendon cells to commit 50% of their total protein production to procollagen: ascorbate and high cell density. Scorbutic primary avian tendon cells at high cell density (greater than 4 X 10(4) cells per cm2) responded to the addition of ascorbate by a sixfold increase in the rate of procollagen synthesis. The kinetics were biphasic, showing a slow increase during the first 12 h followed by a more rapid rise to a maximum after 36 to 48 h. In contrast, after ascorbate addition, the level of accumulated cytoplasmic procollagen mRNA (alpha 2) showed a 12-h lag followed by a slow linear increase requiring 60 to 72 h to reach full induction. At all stages of the induction process, the relative increase in the rate of procollagen synthesis over the uninduced state exceeded the relative increase in the accumulation of procollagen mRNA. A similar delay in mRNA induction was observed when the cells were grown in an ascorbate-containing medium but the cell density was allowed to increase. In all cases, the rate of procollagen synthesis peaked approximately 24 h before the maximum accumulation of procollagen mRNA. The kinetics for the increase in procollagen synthesis are not, therefore, in agreement with the simple model that mRNA levels are the rate-limiting factor in the collagen pathway. We propose that the primary control point is at a later step. Further support for this idea comes from inhibitor studies, using alpha, alpha'-dipyridyl to block ascorbate action. In the presence of 0.3 mM alpha, alpha'-dipyridyl there was a specific two- to threefold decrease in procollagen production after 4 h, but this was unaccompanied by a drop in procollagen mRNA levels. Therefore, inhibitor studies give further support to the idea that primary action of ascorbate is to release a post-translational block.
Full text
PDF

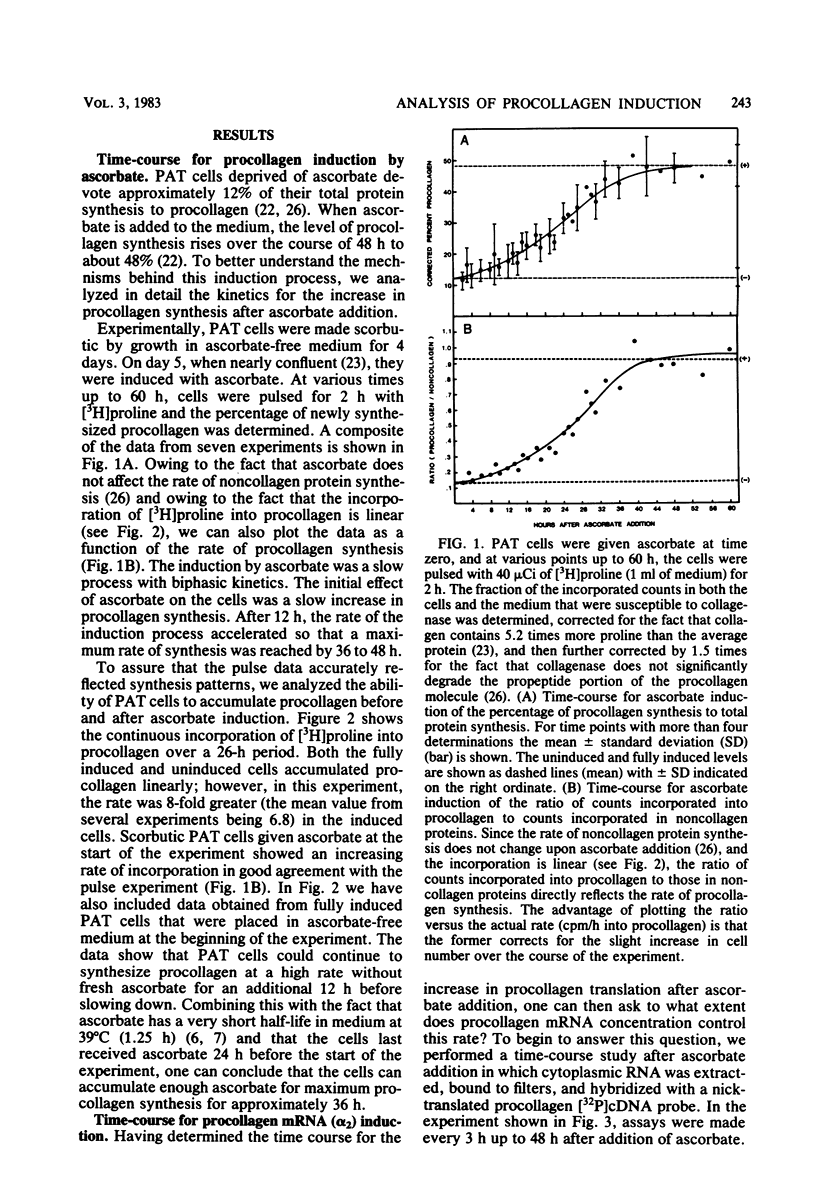
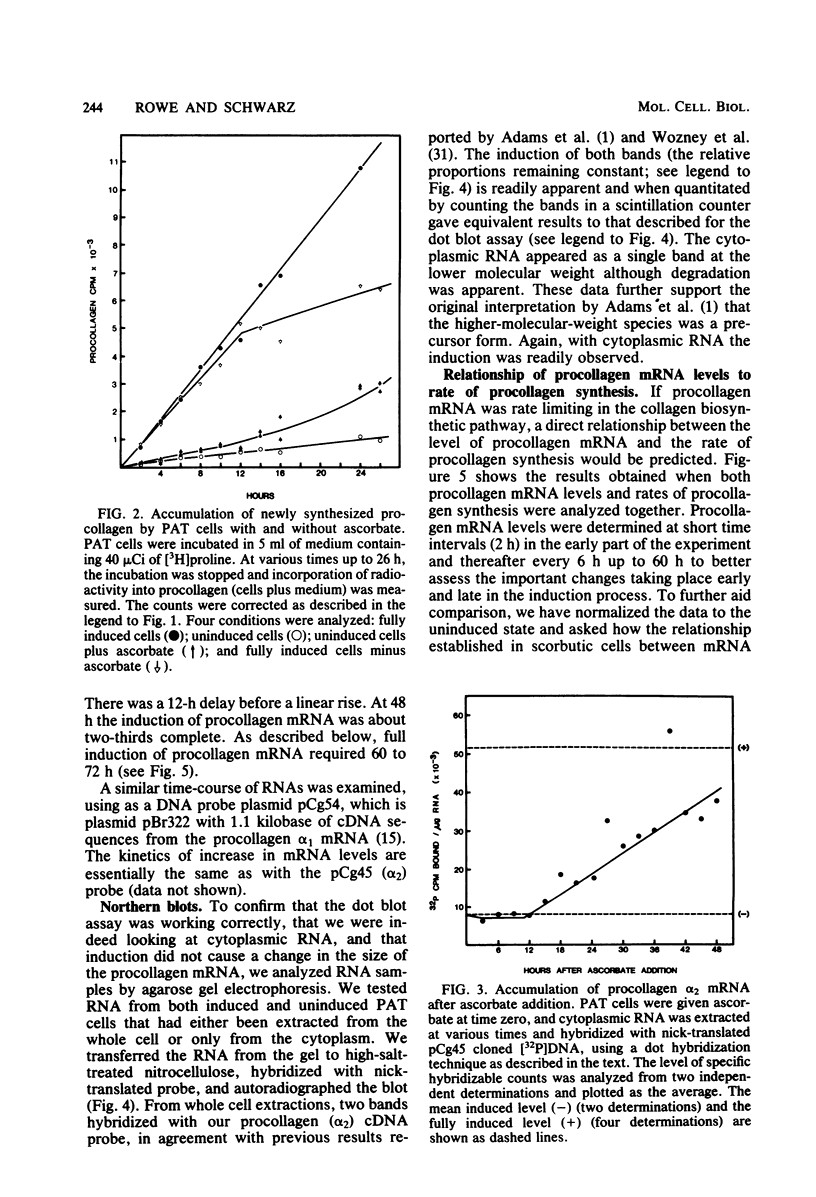
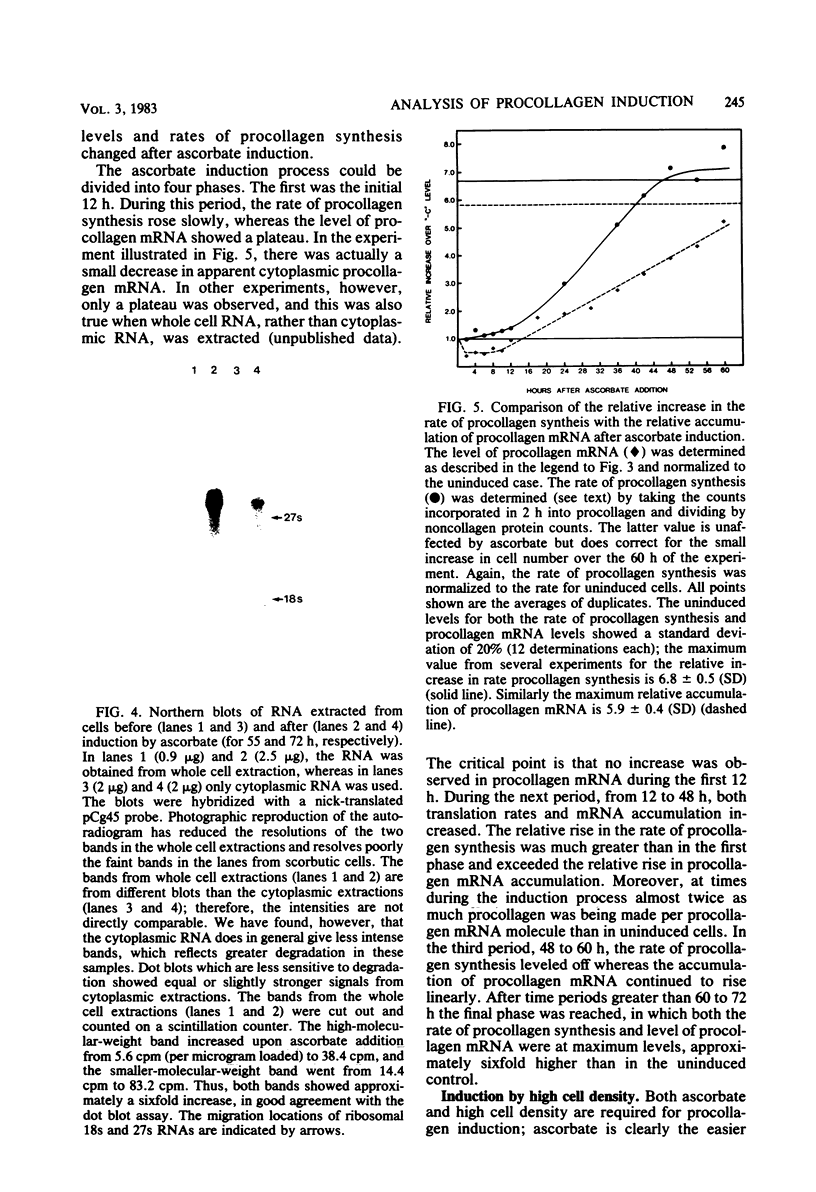



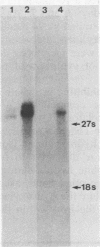
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Alwine J. C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Use of recombinant plasmids to characterize collagen RNAs in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4935–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes M. J. Function of ascorbic acid in collagen metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Sep 30;258:264–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Wallace D. M., Siegal G. P., Hitchcock M. J., Birkenmeier C. S., Reber S. B. Preparation of interferon messenger RNAs with the use of ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):59–68. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J., Hatie C., Farson D. A., Schwarz R. I., Soo W. J. Ascorbic acid inhibits replication and infectivity of avian RNA tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2711–2715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J. The differentiated state of normal and malignant cells or how to define a "normal" cell in culture. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;70:27–100. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck T. J., Peterkofsky B. The stimulation of collagen secretion by ascorbate as a result of increased proline hydroxylation in chick embryo fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegelmann R. F., Peterkofsky B. Collagen biosynthesis during connective tissue development in chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1972 Jul;28(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Harsch M., Murphy L., Rosenbloom J. Effects of temperature on conformation, hydroxylation, and secretion of chick tendon procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S., Harsch M., Rosenbloom J. Hydroxyproline stabilizes the triple helix of chick tendon collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):106–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90960-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao W. W., Prockop D. J., Berg R. A. Kinetics for the secretion of nonhelical procollagen by freshly isolated tendon cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2234–2243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Boedtker H. Construction and characterization of pro alpha 1 collagen complementary deoxyribonucleic acid clones. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3146–3152. doi: 10.2196/47873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I., Tuderman L., Guzman N. A. The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):13–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S., Gallis B., Bornstein P. Coordinate transcriptional regulation of type I procollagen genes by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5022–5028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. I., Bissell M. J. Dependence of the differentiated state on the cellular environment: modulation of collagen synthesis in tendon cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4453–4457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. I., Farson D. A., Bissell M. J. Requirements for maintaining the embryonic state of avian tendon cells in culture. In Vitro. 1979 Dec;15(12):941–948. doi: 10.1007/BF02619153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. I., Farson D. A., Soo W. J., Bissell M. J. Primary avian tendon cells in culture. An improved system for understanding malignant transformation. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):672–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. I., Mandell R. B., Bissell M. J. Ascorbate induction of collagen synthesis as a means for elucidating a mechanism of quantitative control of tissue-specific function. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):843–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R., Colarusso L., Doty P. Maintenance of differentiation in primary cultures of avian tendon cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel M. R., Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Regulation or procollagen messenger ribonucleic acid levels in Rous sarcoma virus transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2678–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Berg R. A., Rennard S. I., Bradley K. H., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen production and procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity in human lung fibroblasts during periods of rapid and stationary growth. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3135–3140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Haber R., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity and collagen synthesis during the fetal development of sheep lung, tendon, and skin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9672–9679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannoni V., Lynch M., Goldstein S., Sato P. A rapid micromethod for the determination of ascorbic acid in plasma and tissues. Biochem Med. 1974 Sep;11(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]