Abstract
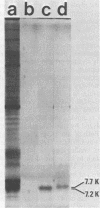
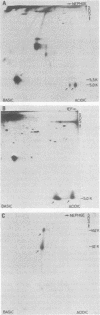
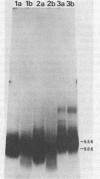
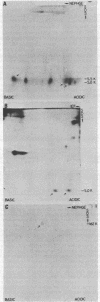
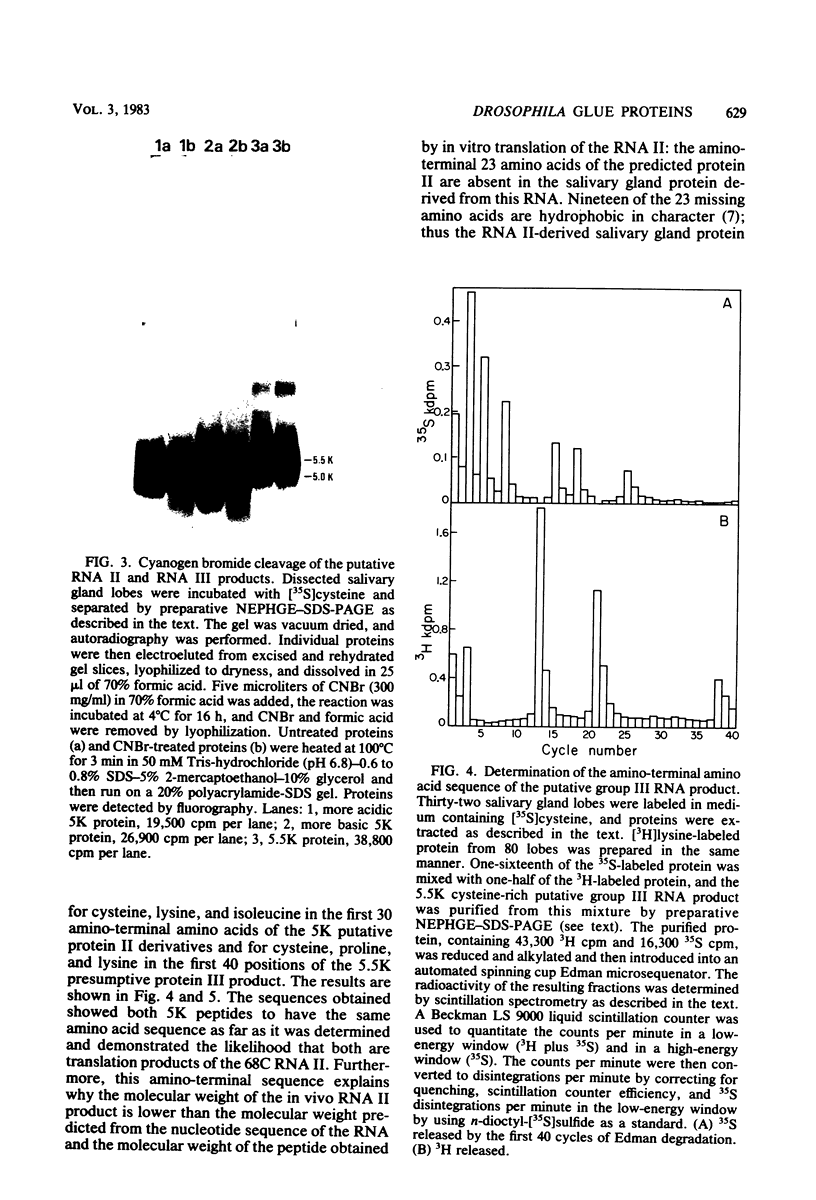
The polytene chromosome puff at 68C on the Drosophila melanogaster third chromosome is thought from genetic experiments to contain the structural gene for one of the secreted salivary gland glue polypeptides, sgs-3. Previous work has demonstrated that the DNA included in this puff contains sequences that are transcribed to give three different polyadenylated RNAs that are abundant in third-larval-instar salivary glands. These have been called the group II, group III, and group IV RNAs. In the experiments reported here, we used the nucleotide sequence of the DNA coding for these RNAs to predict some of the physical and chemical properties expected of their protein products, including molecular weight, amino acid composition, and amino acid sequence. Salivary gland polypeptides with molecular weights similar to those expected for the 68C RNA translation products, and with the expected degree of incorporation of different radioactive amino acids, were purified. These proteins were shown by amino acid sequencing to correspond to the protein products of the 68C RNAs. It was further shown that each of these proteins is a part of the secreted salivary gland glue: the group IV RNA codes for the previously described sgs-3, whereas the group II and III RNAs code for the newly identified glue polypeptides sgs-8 and sgs-7.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. E., Roberts D. B., Richards G. P., Ashburner M. Drosophila: the genetics of two major larval proteins. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21(4):398–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00336950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Richards G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. III. Consequences of ecdysone withdrawal. Dev Biol. 1976 Dec;54(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman J. N., Todd C. W., Shively J. E. Chemical deglycosylation of carcinoembryonic antigen for amino acid sequence studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Pongs O. Localization of ecdysterone on polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbach U. Chromosomen-Aktivitat und biochemische Zelldifferenzierung in den Speicheldrüsen von Camptochironomus. Chromosoma. 1969;28(2):136–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00331528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. New protein sequenator with increased sensitivity. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):523–525. doi: 10.1126/science.7352258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodani M. The Protein of the Salivary Gland Secretion in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1948 Apr;34(4):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.34.4.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Larval saliva in Drosophila melanogaster: production, composition, and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Guild G. M., Prestidge L. S., Hogness D. S. A new high-capacity cosmid vector and its use. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Hogness D. S. Molecular organization of a Drosophila puff site that responds to ecdysone. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Diazotizable arylamine cellulose papers for the coupling and hybridization of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velissariou V., Ashburner M. Cytogenetic and genetic mapping of a salivary gland secretion protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):173–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00399129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velissariou V., Ashburner M. The secretory proteins of the larval salivary gland of Drosophila melanogaster: Cytogenetic correlation of a protein and a puff. Chromosoma. 1980;77(1):13–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00292038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]