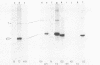
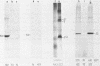
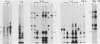Abstract
Immune complex kinase assays in the simian virus 40 system were performed by incubation of immunoprecipitates containing tumor antigens with [gamma-32P]ATP, followed by analysis of any phosphoacceptor proteins. These assays yielded mainly the viral large T-antigen and, in particular, the associated cellular p53 as endogenous substrates. The nature of these substrates was confirmed by proteolysis techniques. Under specific conditions, casein could be used as an exogenous substrate as well. The kinase reactions showed preference for ATP and MgCl2 instead of GTP or MnCl2. Both phosphoserine and phosphothreonine, but in no case phosphotyrosine, were detected after an immune complex kinase reaction. Apparently, several in vivo phosphorylation sites were recognized in vitro in both large T-antigen and p53, but the presence of some artifactual sites could not be completely excluded. Although contaminating kinases were detectable in the immune complexes, at least the p53 molecules were phosphorylated in vitro in a more specific way. This followed from several characteristics of the immune complex kinase reactions and especially from the strong inhibition of p53 phosphorylation by two anti-large-T monoclonal antibodies. It was shown that large T-antigen showed associated kinase activity, although none of our results could unambiguously demonstrate an intrinsic kinase activity of this protein. Finally, anti-p53 monoclonal antibodies only slightly affected in vitro phosphorylation reactions, whereas a p53 molecule from a simian virus 40-free, chemically transformed human cell line was not phosphorylated in vitro under any condition tested. Thus, it is highly unlikely that the p53 molecule per se carries intrinsic or even associated kinase activities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benchimol S., Pim D., Crawford L. Radioimmunoassay of the cellular protein p53 in mouse and human cell lines. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Gurney E. G., Goodfellow P., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of a common feature in several human tumor cell lines--a 53,000-dalton protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 tumor antigens: analysis of antigenic binding sites, using adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):478–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.478-482.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W., Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T. An activity phosphorylating tyrosine in polyoma T antigen immunoprecipitates. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Changes in gene expression and protein phosphorylation in murine cells, transformed or abortively infected with wild type and mutant simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5276–5290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Spangler G., Livingston D. M. Protein kinase activity associated with simian virus 40 T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2610–2614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Functions of T antigens of SV40 and polyomavirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 31;651(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(81)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Pim D. C., Crawford L. V. Complex of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and host 53,000-molecular-weight protein in monkey cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):564–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.564-573.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., DeLeo A. B., Dippold W. G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection of an associated phosphotransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Resche-Rigon M., Feunteun J. Phosphorylation pattern of large T antigens in mouse cells infected by simian virus 40 wild type or deletion mutants. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):761–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.761-771.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G. The transformation of cell growth and transmogrification of DNA synthesis by simian virus 40. Adv Cancer Res. 1981;34:1–68. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S., Park D. K., Arnstein P., Huebner R. J., Weisburger E. K., Nelson-Rees W. A. Transformation of human cells in culture by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):751–753. doi: 10.1038/256751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Witte O. N., Coffman R., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced tumors elicit antibodies against a host cell protein, P50. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.547-555.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V. p53, a transformation-related cellular-encoded protein, can be used as a biochemical marker for the detection of primary mouse tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2613–2617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K. Temperature-sensitive transformation by Rous sarcoma virus and temperature-sensitive protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):220–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.220-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Ito Y. Differential subcellular localization of in vivo-phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated middle-sized tumor antigen of polyoma virus and its relationship to middle-sized tumor antigen phosphorylating activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6812–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A., Clark R. Catalytic properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):103–111. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A. Enzymatic activities associated with a purified simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Metabolic turnover of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):442–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.442-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Phosphorylation patterns of tumour antigens in cells lytically infected or transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):28–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.28-44.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Improved localization of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):315–331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.315-331.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]