Abstract
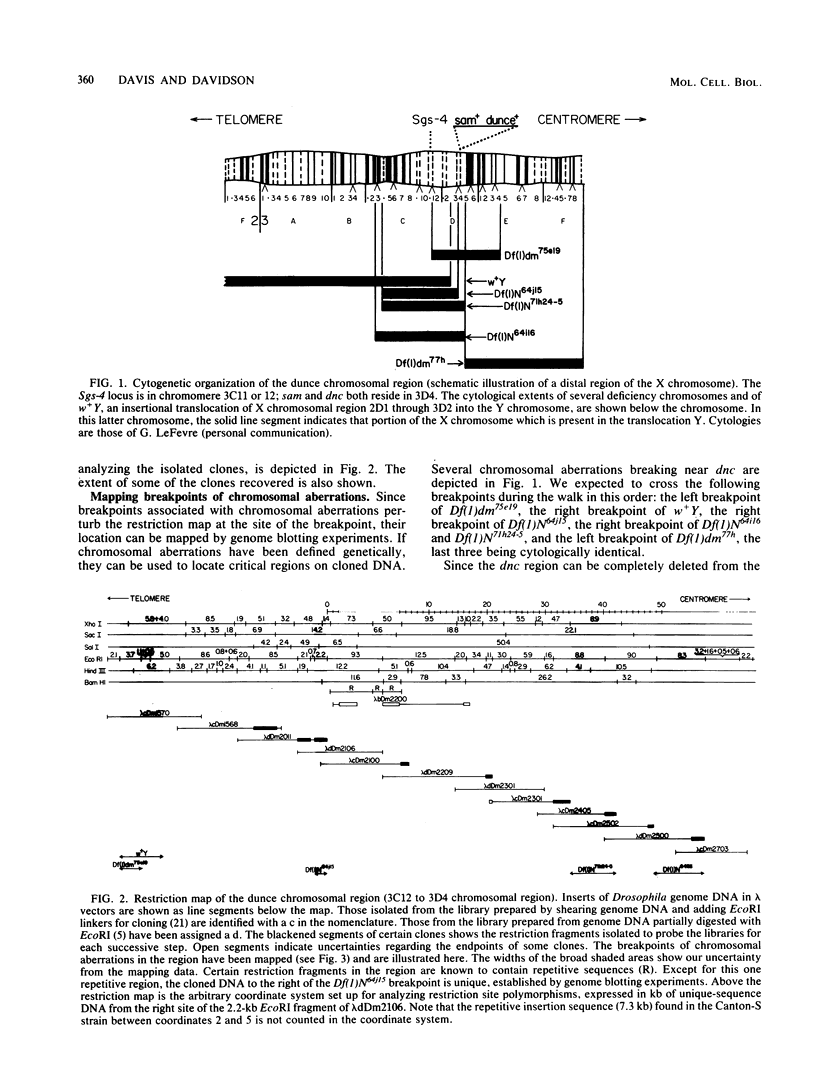
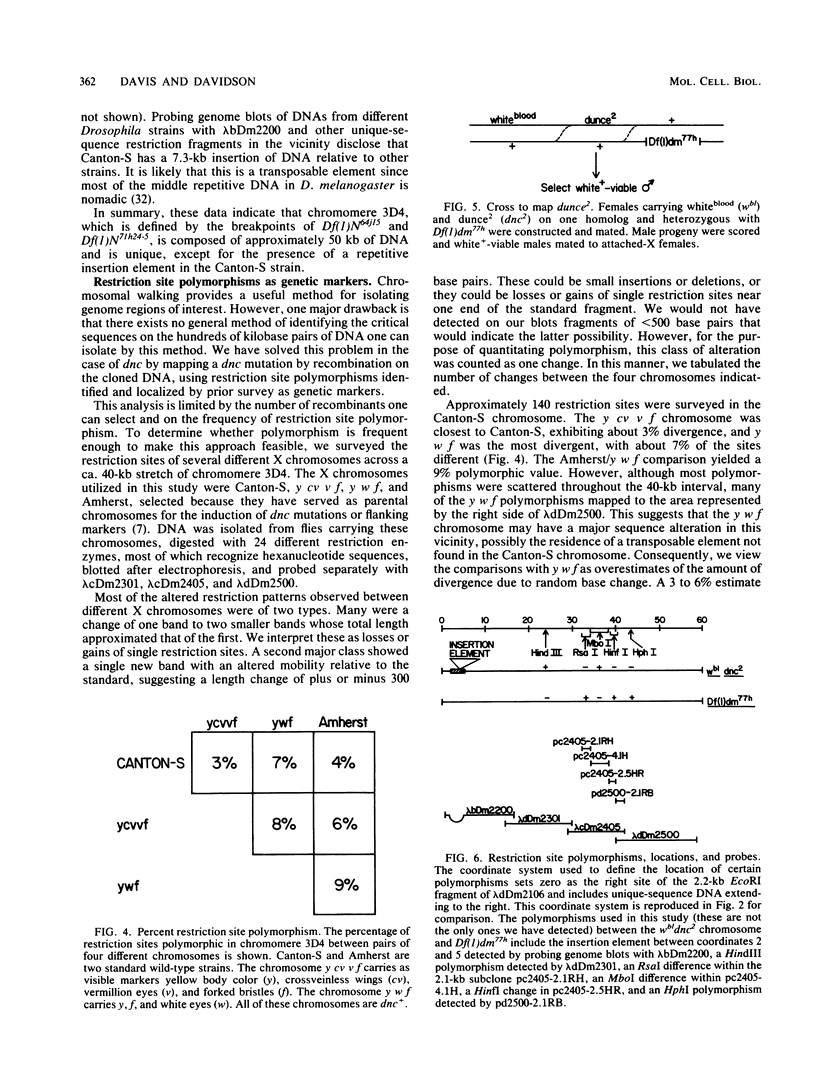
Using the method of chromosomal walking, we have isolated a contiguous region of the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome which corresponds to salivary gland chromosome bands 3C12 to 3D4. This five-band region contains approximately 100 kilobases of DNA, including those sequences comprising dunce, a gene which functions in memory and cyclic nucleotide metabolism. Genome blots of DNA from flies carrying several different chromosomal aberrations with breakpoints in the region have been probed with the isolated clones to map the breakpoints on the cloned DNA and to delimit dunce sequences. This has localized dunce to a 50-kilobase region. In addition, we have searched this 50-kilobase region for restriction site polymorphisms between X chromosomes from different Drosophila strains by genome blotting experiments, and we have followed the segregation of detected polymorphisms and dunce alleles after meiotic recombination. The data map one dunce mutation between two polymorphisms located 10 to 12 kilobases apart.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves-Piña E. O., Quinn W. G. Learning in normal and mutant Drosophila larvae. Science. 1979 Oct 5;206(4414):93–96. doi: 10.1126/science.206.4414.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Muskavitch M. A., Yedvobnick B. Molecular cloning of Notch, a locus affecting neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker R., Quinn W. G. Conditioning of leg position in normal and mutant Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3940–3944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers D., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Defect in cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase due to the dunce mutation of learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):79–81. doi: 10.1038/289079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr A partial characterization of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases of Drosophila melanogaster. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Aug;203(1):412–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Dunce mutants of Drosophila melanogaster: mutants defective in the cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase enzyme system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):101–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y., Jan Y. N., Byers D., Quinn W. G., Benzer S. dunce, a mutant of Drosophila deficient in learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailey D. A., Jackson F. R., Siegel R. W. Male courtship in Drosophila: the conditioned response to immature males and its genetic control. Genetics. 1982 Dec;102(4):771–782. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Molecular biology of learning: modulation of transmitter release. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):433–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6289442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauvar L. M. Defective cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in the Drosophila memory mutant dunce. J Neurosci. 1982 Oct;2(10):1347–1358. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-10-01347.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiger J. A., Jr, Golanty E. A cytogenetic analysis of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities in Drosophila. Genetics. 1977 Apr;85(4):609–622. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiger J. A., Jr The consequences of nullosomy for a chromosomal region affecting cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase activity in Drosophila. Genetics. 1977 Apr;85(4):623–628. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.4.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Direct correlation between a chromosome puff and the synthesis of a larval saliva protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1977 Jul 5;62(2):155–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00292637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Farrell J., Jr, Beckendorf S. K. Molecular limits on the size of a genetic locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7367–7371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Casey J. W., Nicolson M. O., Burck K. B., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement and biological activity of cloned feline leukemia virus proviruses from a virus-productive human cell line. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):688–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.688-703.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A. Genetic Analysis of Chromomere 3d4 in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: The DUNCE and SPERM-AMOTILE Genes. Genetics. 1982 Apr;100(4):587–596. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Stavnezer J., Artzt K., Bennett D. Genetic structure and origin of t haplotypes of mice, analyzed with H-2 cDNA probes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Bonini N., Dawson D. R., Quinn W. G. Reward learning in normal and mutant Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. W. Middle repetitive DNA: a fluid component of the Drosophila genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6274–6278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]