Abstract
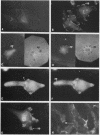
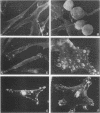
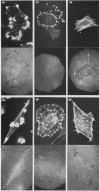
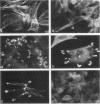
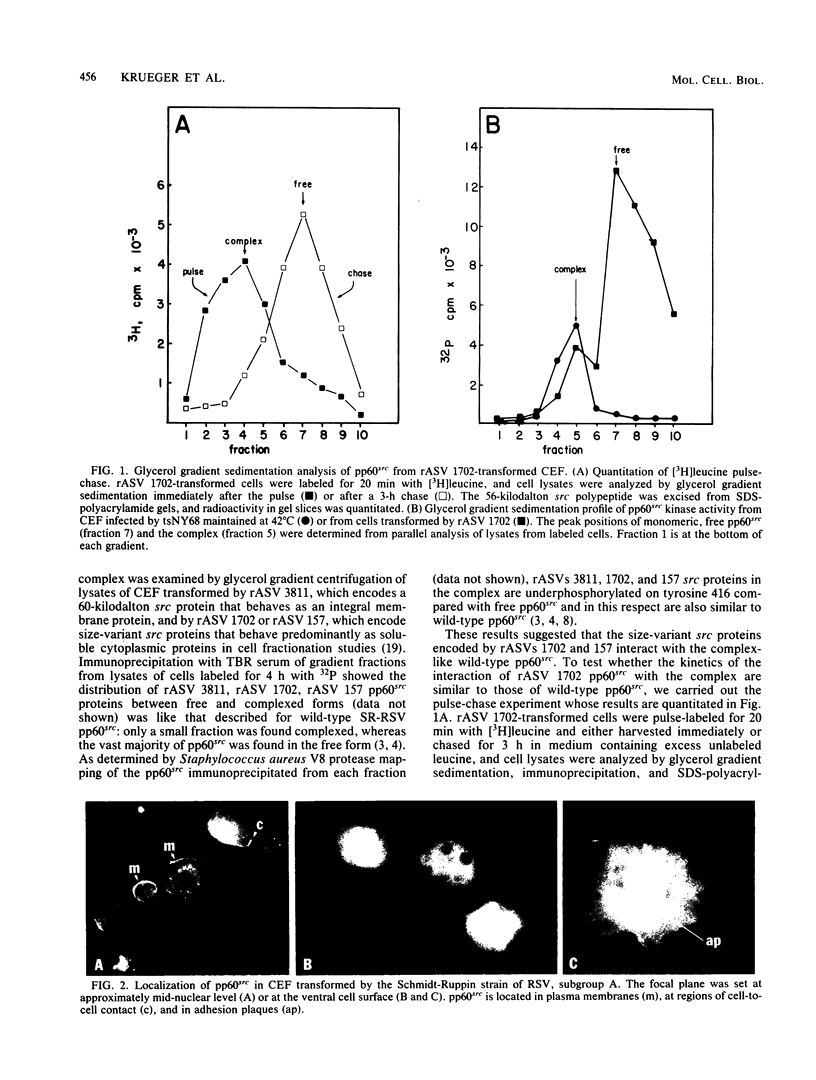
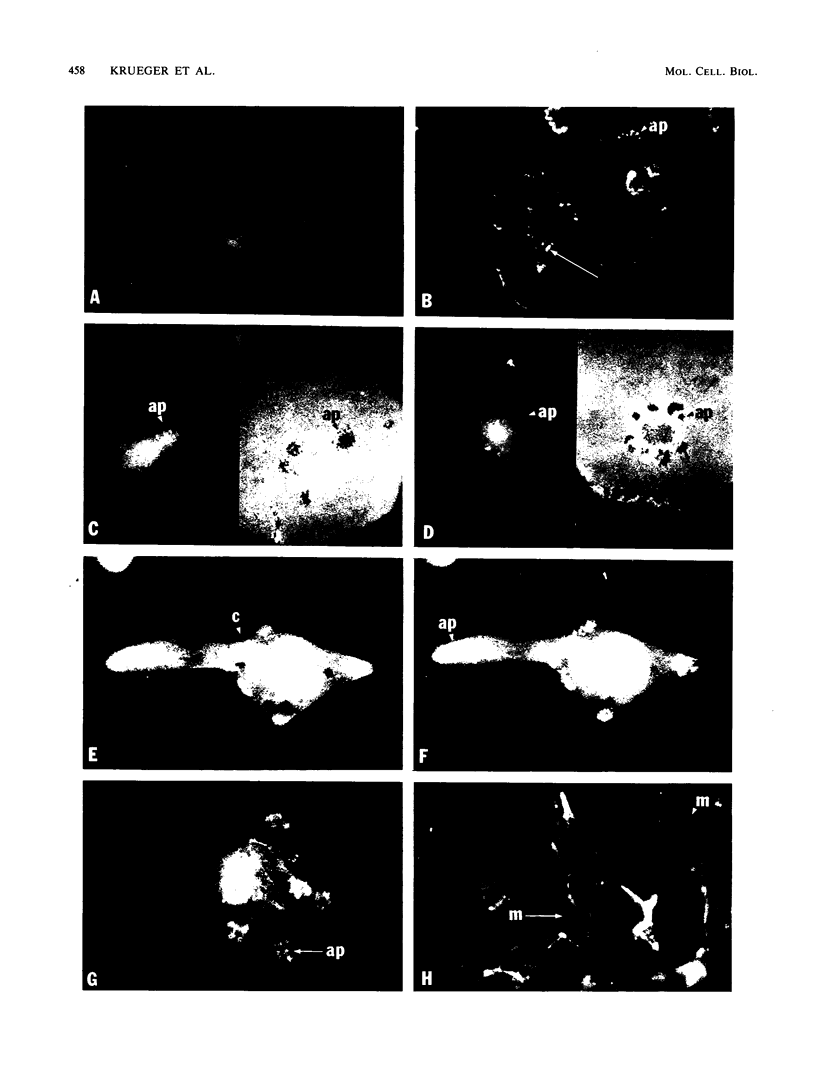
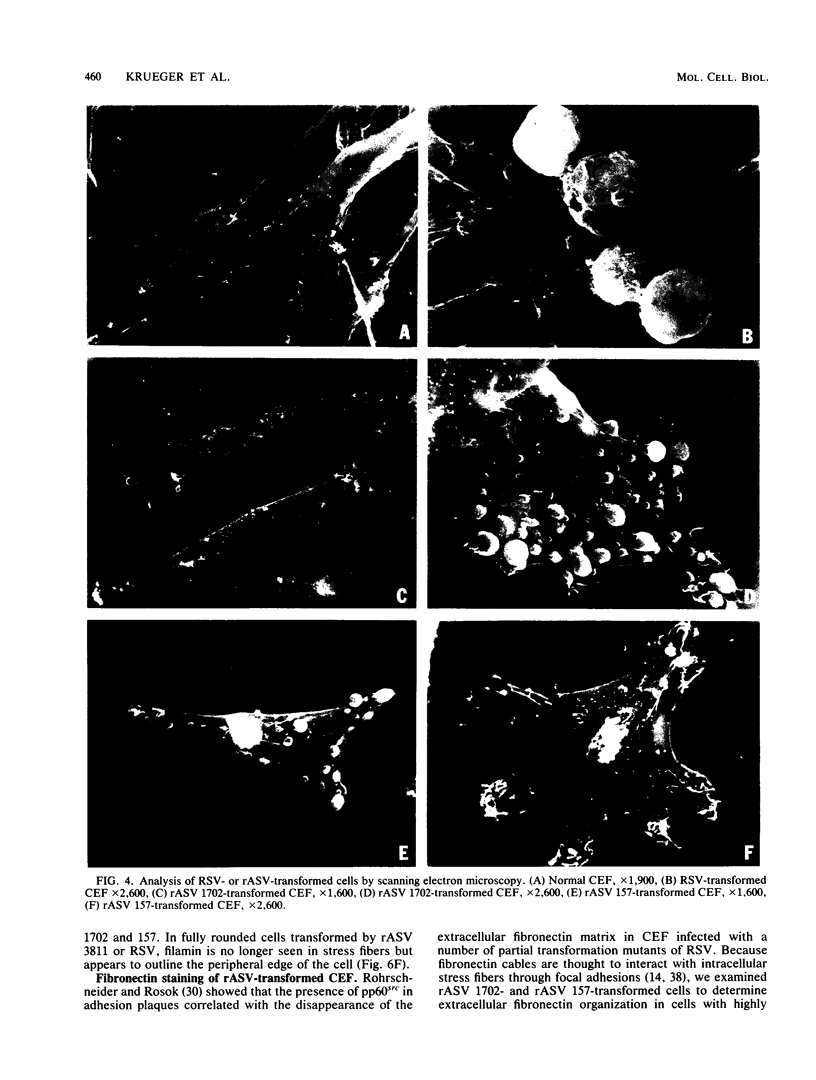
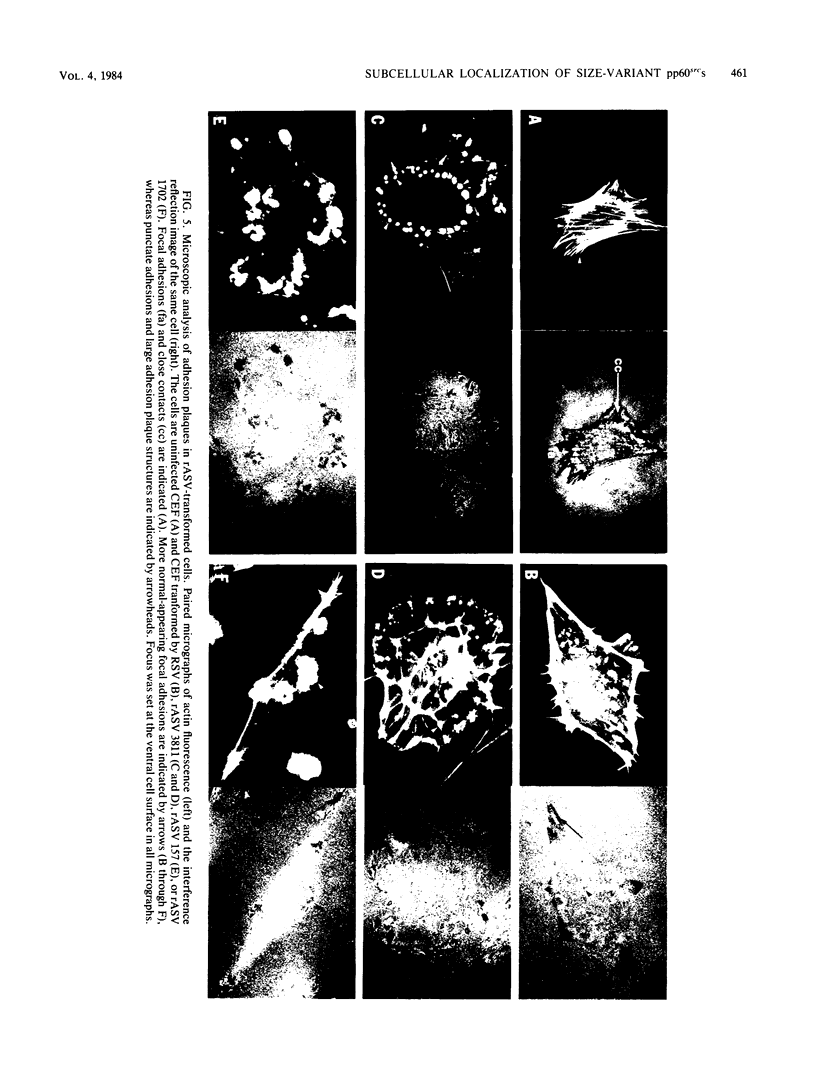
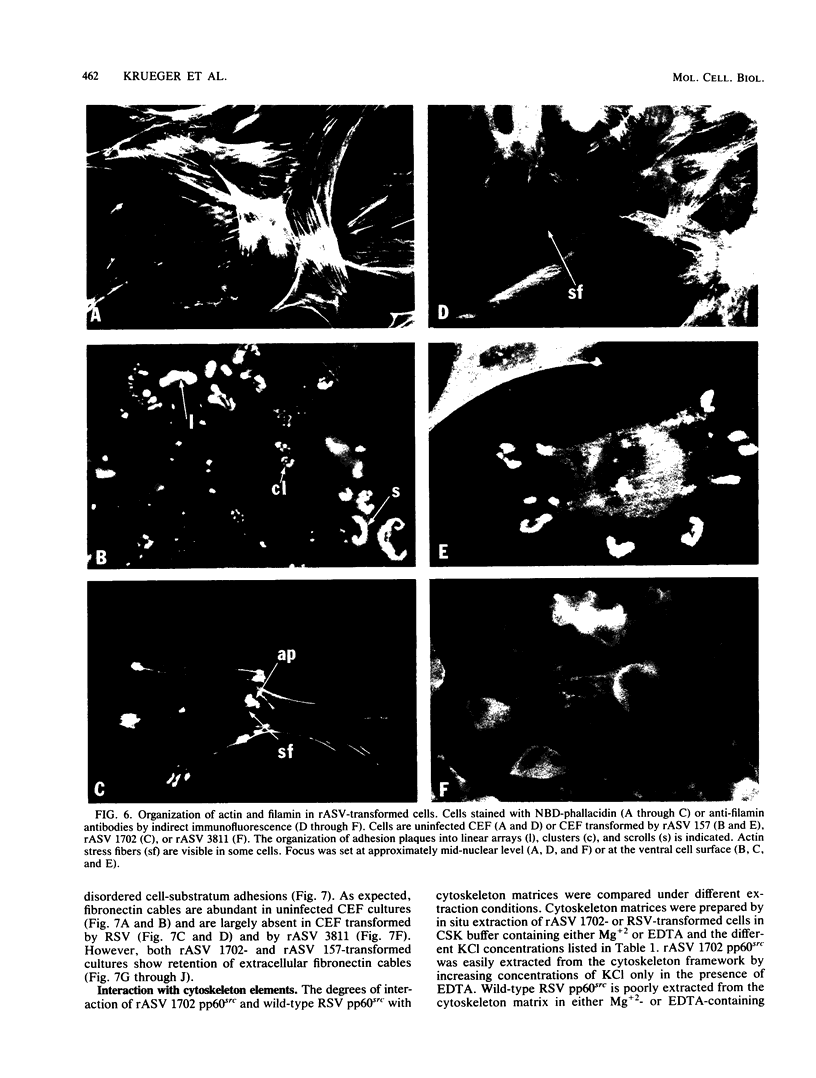
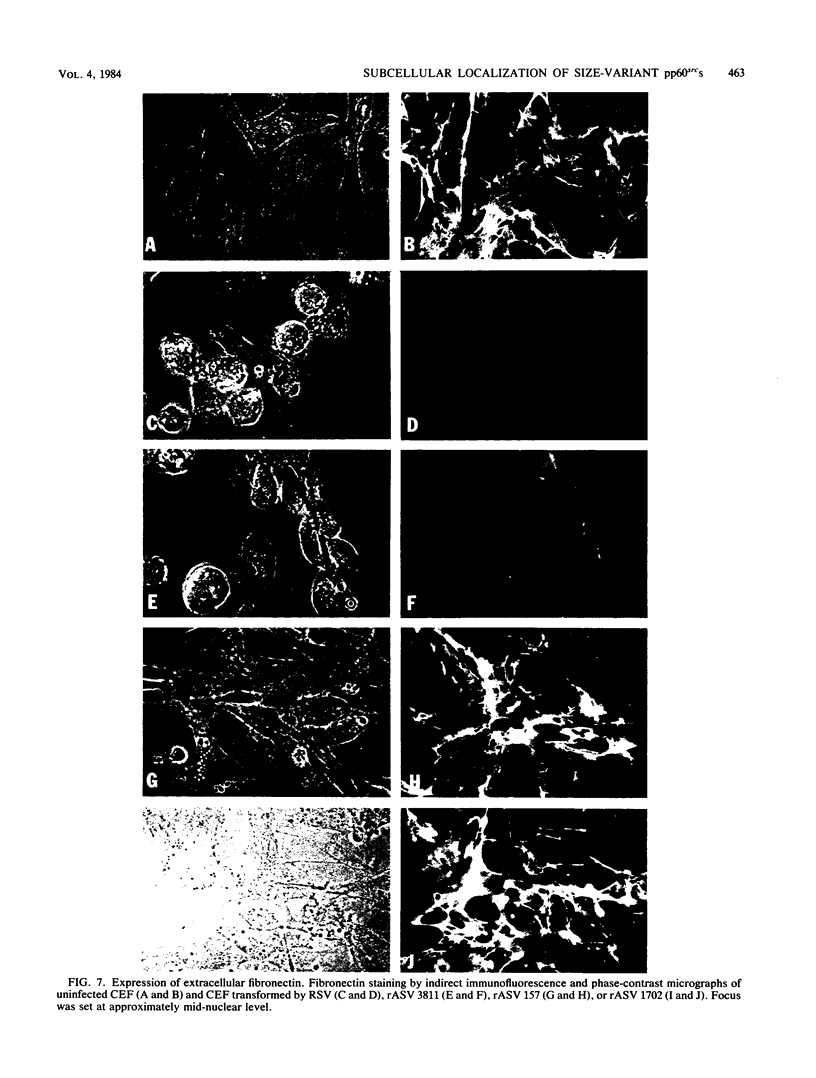
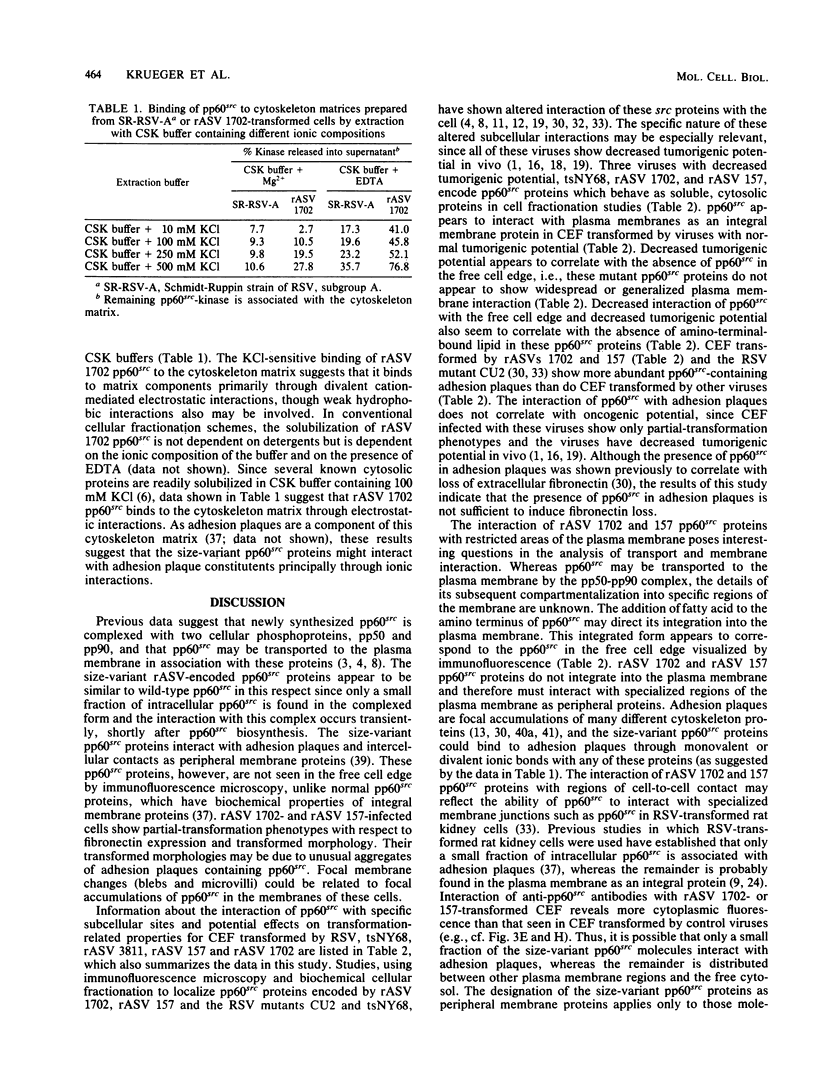
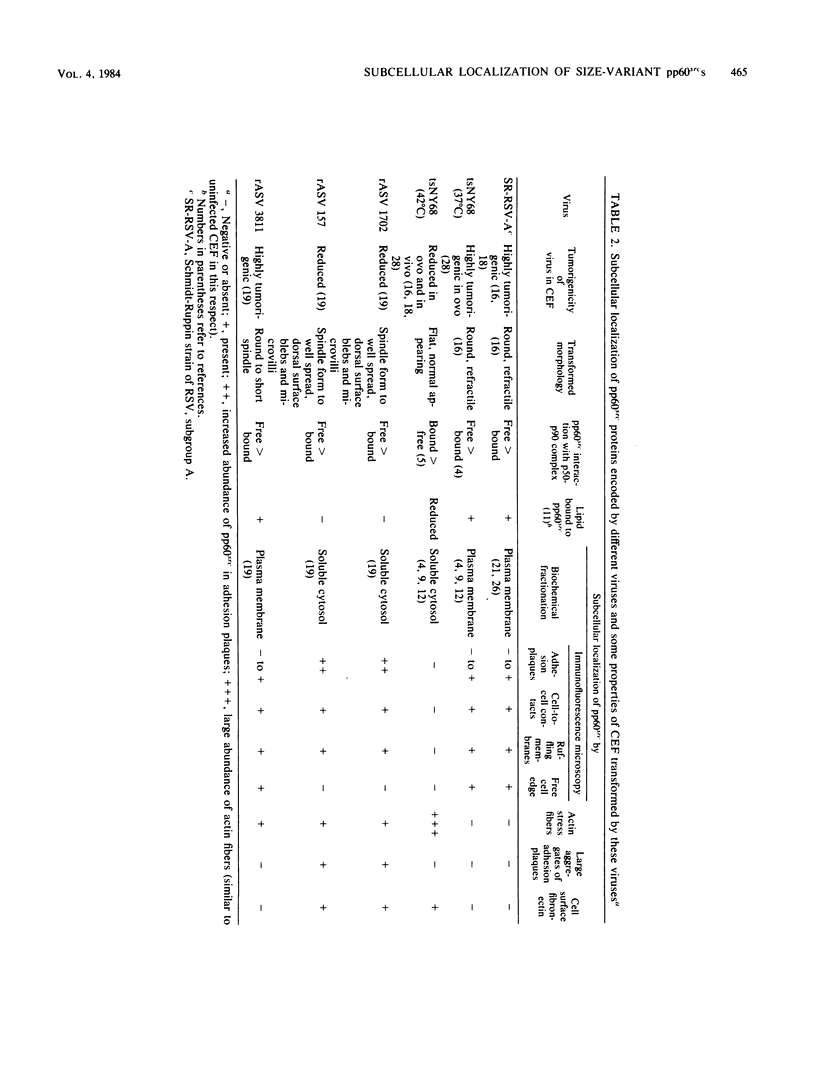
We have shown previously that the membrane association of the src proteins of recovered avian sarcoma viruses (rASVs) 1702 (56 kilodaltons) and 157 (62.5 kilodaltons), whose size variations occur within 8 kilodaltons of the amino terminus, is salt sensitive and that, in isotonic salt, these src proteins fractionate as soluble cytoplasmic proteins. In contrast, wild-type Rous sarcoma virus pp60src behaves as an integral plasma membrane protein in cellular fractionation studies and shows prominent membrane interaction by immunofluorescence microscopy. In this study we have examined the distribution of these size-variant src proteins between free and complexed forms, their subcellular localization by immunofluorescence microscopy, and their ability to effect several transformation-related cell properties. Glycerol gradient sedimentation of extracts from cells infected either with rASV 1702 or rASV 157 showed that soluble src proteins of these viruses were distributed between free and complexed forms as has been demonstrated for wild-type Rous sarcoma virus pp60src. Pulse-chase studies with rASV pp60src showed that, like wild-type Rous sarcoma virus pp60src, it was transiently found in a complexed form. Indirect immunofluorescence showed that size-variant pp60src proteins are localized in adhesion plaques and regions of cell-to-cell contact in rASV 1702- or 157-infected cells. This result is in contrast with the generalized localization of pp60src in plasma membranes of control rASV-infected cells which produce pp60src. Chicken embryo fibroblasts infected by rASVs 1702 and 157 display a partial-transformation phenotype with respect to (i) transformation-related morphology, (ii) cell surface membrane changes, and (iii) retained extracellular fibronectin. It is possible that the induction of a partial-transformation phenotype may be the result of the unique interaction of the src proteins encoded by these viruses with restricted areas of the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. D., Beckmann R. P., Harms E. H., Nakamura K., Weber M. J. Biological properties of "partial" transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus and characterization of their pp60src kinase. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):445–458. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.445-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R., Nothnagel E. A., Webb W. W. Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr J. G., Dreyfuss G., Penman S., Buchanan J. M. Association of the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus with cytoskeletal structures of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Wang E., Hanafusa H. Cytoplasmic localization of the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus: salt-sensitive association with subcellular components. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):782–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.782-791.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Temperature-sensitive membrane association of pp60src in tsNY68-infected cells correlates with increased tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. Relationships between fibronectin (LETS protein) and actin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Nakamura K., Shin S., Smith R. E., Weber M. J. Tumorigenicity of partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):602–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.602-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Viral and cellular src genes contribute to the structure of recovered avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90511-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R., Hanafusa H. Changes in amino-terminal sequences of pp60src lead to decreased membrane association and decreased in vivo tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Differences in intracellular location of pp60src in rat and chicken cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzek R. A., Mitchell R. L., Lau A. F., Faras A. J. Association of pp60src and src protein kinase activity with the plasma membrane of nonpermissive and permissive avian sarcoma virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):805–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.805-815.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific messenger RNAs in permissive cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8015–8022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Walter G., Singer S. J. Immunofluorescent localization of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus with antibodies against a synthetic src peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5322–5326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Lawrence D., Vigier P., Jullien P. A ts T mutant of Schmidt Ruppin strain of Rous sarcoma virus restricted at 39.5 degrees C for the morphological transformation and the tumorigenicity of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 1982 Jan 15;29(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Jovanovich S., Erikson R. L. Sites of synthesis of viral proteins in avian sarcoma virus-infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):629–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.629-636.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Immunofluorescence on avian sarcoma virus-transformed cells: localization of the src gene product. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L., Rosok M. J. Transformation parameters and pp60src localization in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):731–746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L., Rosok M., Shriver K. Mechanism of transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: events within adhesion plaques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):953–965. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizuta Y., Shizuta H., Gallo M., Davies P., Pastan I. Purification and properties of filamin, and actin binding protein from chicken gizzard. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6562–6567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriver K., Rohrschneider L. Organization of pp60src and selected cytoskeletal proteins within adhesion plaques and junctions of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):525–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Paradiso P. R. A transmembrane relationship between fibronectin and vinculin (130 kd protein): serum modulation in normal and transformed hamster fibroblasts. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Changes in microfilament organization and surface topogrophy upon transformation of chick embryo fibroblasts with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Yin H. L., Krueger J. G., Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Unphosphorylated gelsolin is localized in regions of cell-substratum contact or attachment in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Osborn M., Weber K. Cell-to-substratum contacts in living cells: a direct correlation between interference-reflexion and indirect-immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies against actin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:257–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]