Abstract
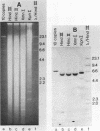
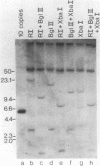
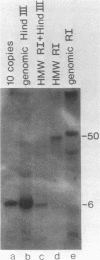
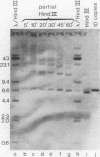
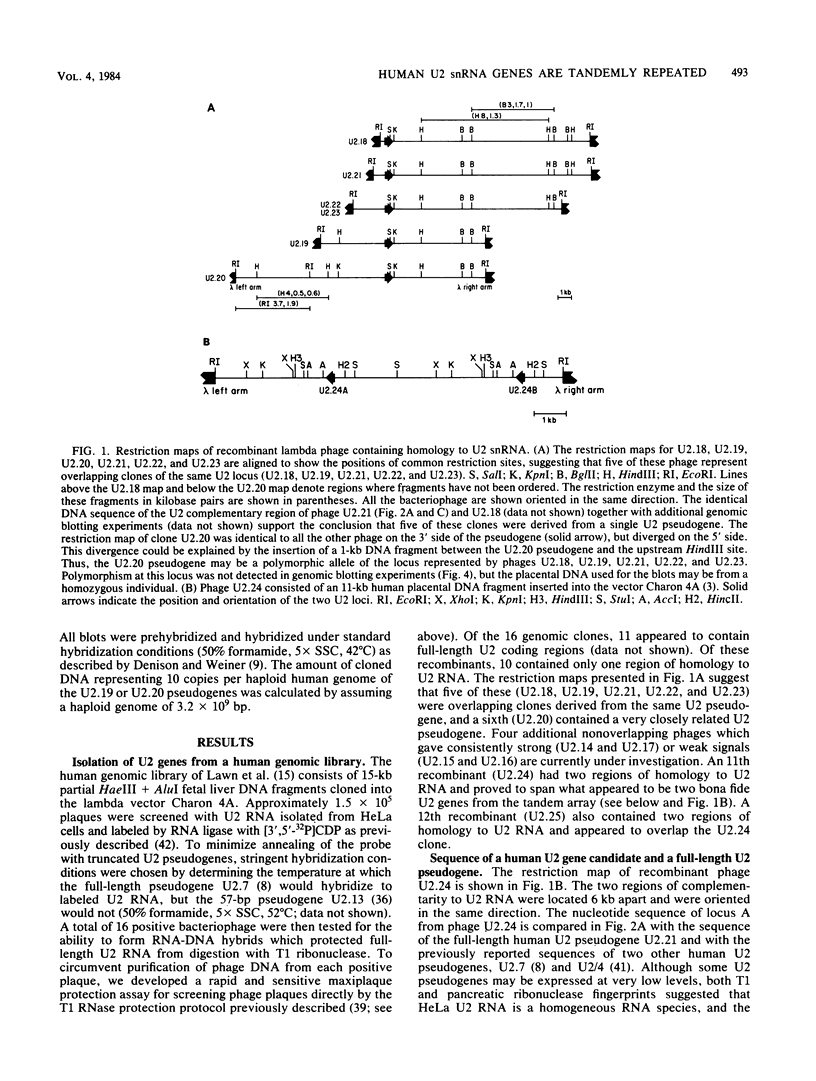
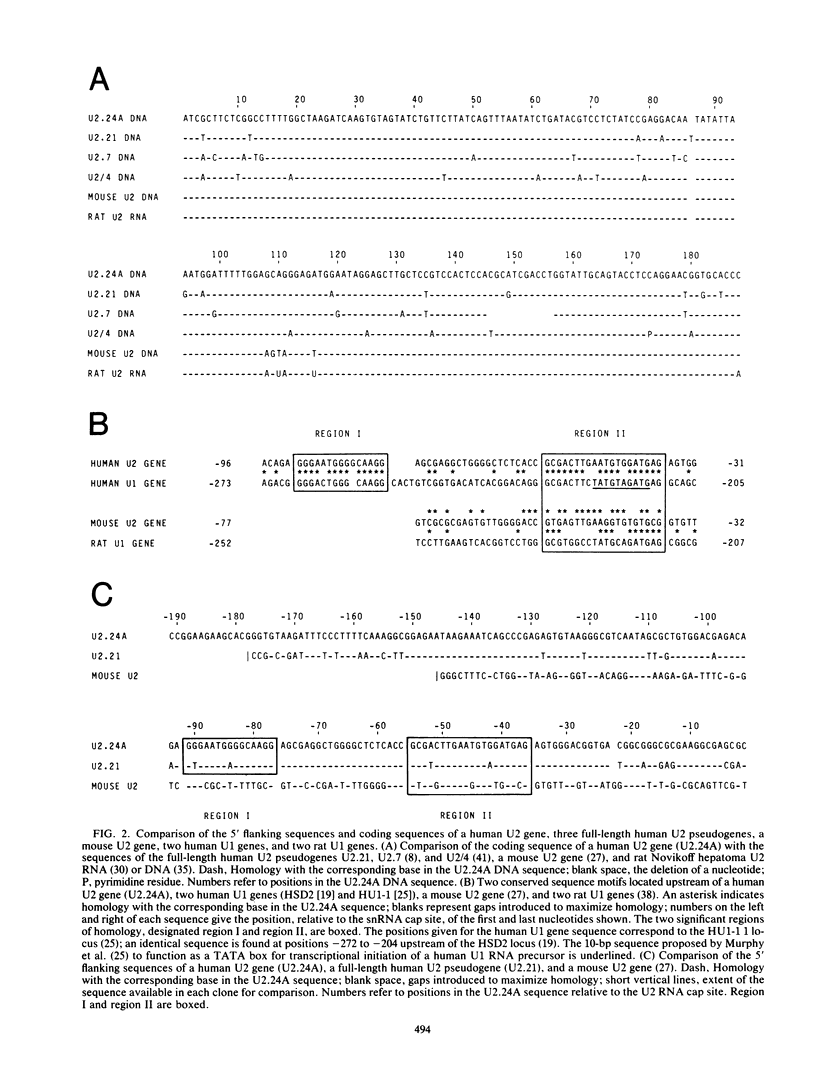
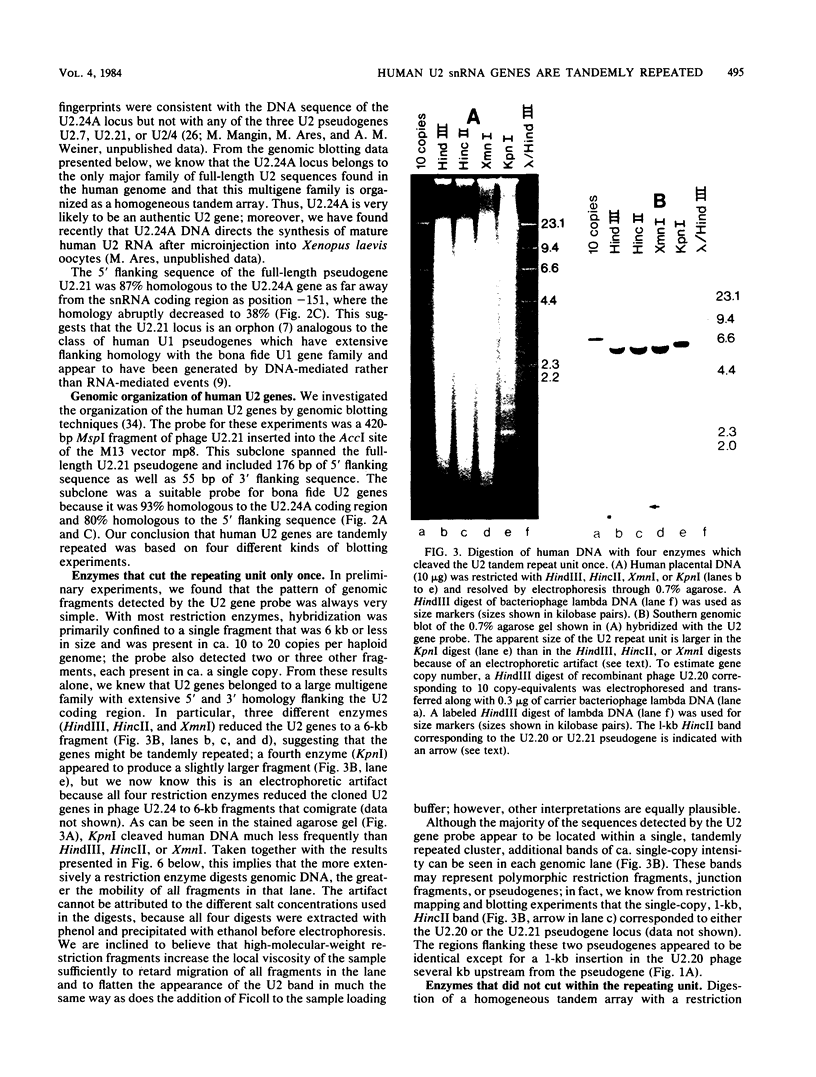
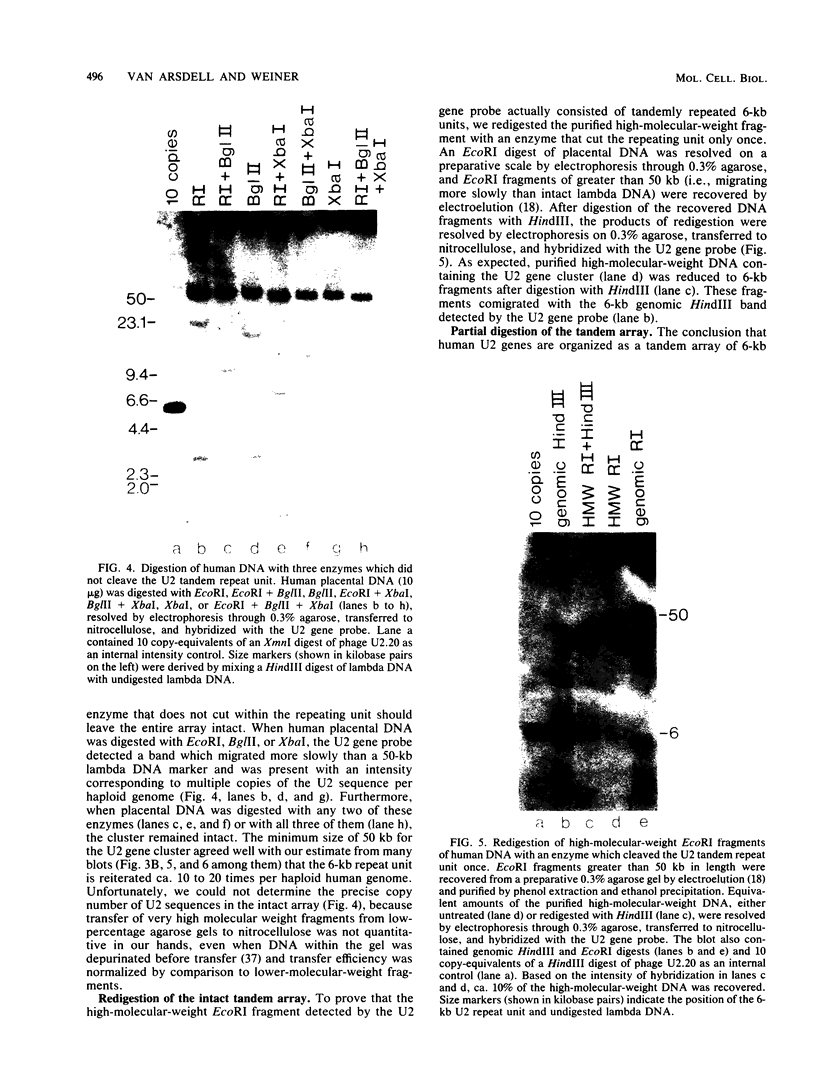
We found that the genes for human U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) are organized as a nearly perfect tandem array of 10 to 20 copies per haploid genome. Although the coding region for the mature form of U2 RNA was only 188 base pairs (bp) long, the basic repeating unit of the tandem array was 6 kilobase pairs in length. Comparison of DNA sequences immediately upstream from human U1 and U2 genes revealed two regions of strong homology: region I (15 bp long) lay upstream of region II (20 bp long) and was separated from it by about the same distance in U1 genes (25 bp) as in U2 genes (21 bp); however, region I and region II were located 174 bp further upstream from the 5' end of the snRNA coding sequence in U1 genes than in U2 genes. Homologs of region II were also found upstream of the snRNA coding region in a mouse U2 gene and two rat U1 genes. Murphy et al. (Cell 29:265-274, 1982) have found that sequences within region II may function as the equivalent of a TATA box for initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro at a position 183 bp upstream from the 5' end of the human U1 snRNA coding region. In light of the data reported here, this result suggests that region II does indeed play a role in transcription but that its position relative to the actual initiation site can vary.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. B., Mount S. M., Weiner A. M. Pseudogenes for human small nuclear RNA U3 appear to arise by integration of self-primed reverse transcripts of the RNA into new chromosomal sites. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Haendler B., Jacob M. U2 RNA shares a structural domain with U1, U4, and U5 RNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card C. O., Morris G. F., Brown D. T., Marzluff W. F. Sea urchin small nuclear RNA genes are organized in distinct tandemly repeating units. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7677–7688. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. Orphons: dispersed genetic elements derived from tandem repetitive genes of eucaryotes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison R. A., Van Arsdell S. W., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M. Abundant pseudogenes for small nuclear RNAs are dispersed in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison R. A., Weiner A. M. Human U1 RNA pseudogenes may be generated by both DNA- and RNA-mediated mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):815–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström K., Westin G., Pettersson U. A pseudogene for human U4 RNA with a remarkable structure. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):737–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K. Organization of sequences related to U6 RNA in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3379–3388. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Isolation of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins containing U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2604–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlaw C. S., Dusing-Swartz S. K., Berget S. M. Human U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins contain common and unique polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1159–1166. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Bostock C., Robertson M., Christie S., Mitchen J. L., Dahlberg J. E. U1 small nuclear RNA genes are located on human chromosome 1 and are expressed in mouse-human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2211–2220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Human U1 loci: genes for human U1 RNA have dramatically similar genomic environments. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Zeller R. Xenopus laevis U2 snRNA genes: tandemly repeated transcription units sharing 5' and 3' flanking homology with other RNA polymerase II transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monstein H. J., Westin G., Philipson L., Pettersson U. A candidate gene for human U1 RNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):133–137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Transcription of a gene for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohga K., Reddy R., Busch H. Comparison of RNase T1 fingerprints of U1, U2, and U3 small nuclear RNA's of HeLa cells, human normal fibroblasts, and Novikoff hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jun;41(6):2215–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima H., Kornberg R. D. Genes and pseudogenes for mouse U1 and U2 small nuclear RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8151–8155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Itoh M., Okada N., Miyata T. Novel models for RNA splicing that involve a small nuclear RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4471–4474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Epstein P., Busch H. Primary and secondary structure of U2 snRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5645–5658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Kristo P., Stumph W. E., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure and expression of a chicken gene coding for U1 RNA. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90430-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions: nucleotide sequence requirements for initiation by RNA polymerase II and III. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:25–46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Watanabe-Nagasu N., Okada N., Ohshima Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene for rat U2 small nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):579–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Nagasu N., Itoh Y., Tani T., Okano K., Koga N., Okada N., Ohshima Y. Structural analysis of gene loci for rat U1 small nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1791–1801. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Denison R. A. Either gene amplification or gene conversion may maintain the homogeneity of the multigene family encoding human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1141–1149. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Monstein H. J., Zabielski J., Philipson L., Pettersson U. Human DNA sequences complementary to the small nuclear RNA U2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6323–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. The small nuclear RNAs of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):956–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]