Abstract
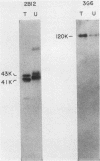
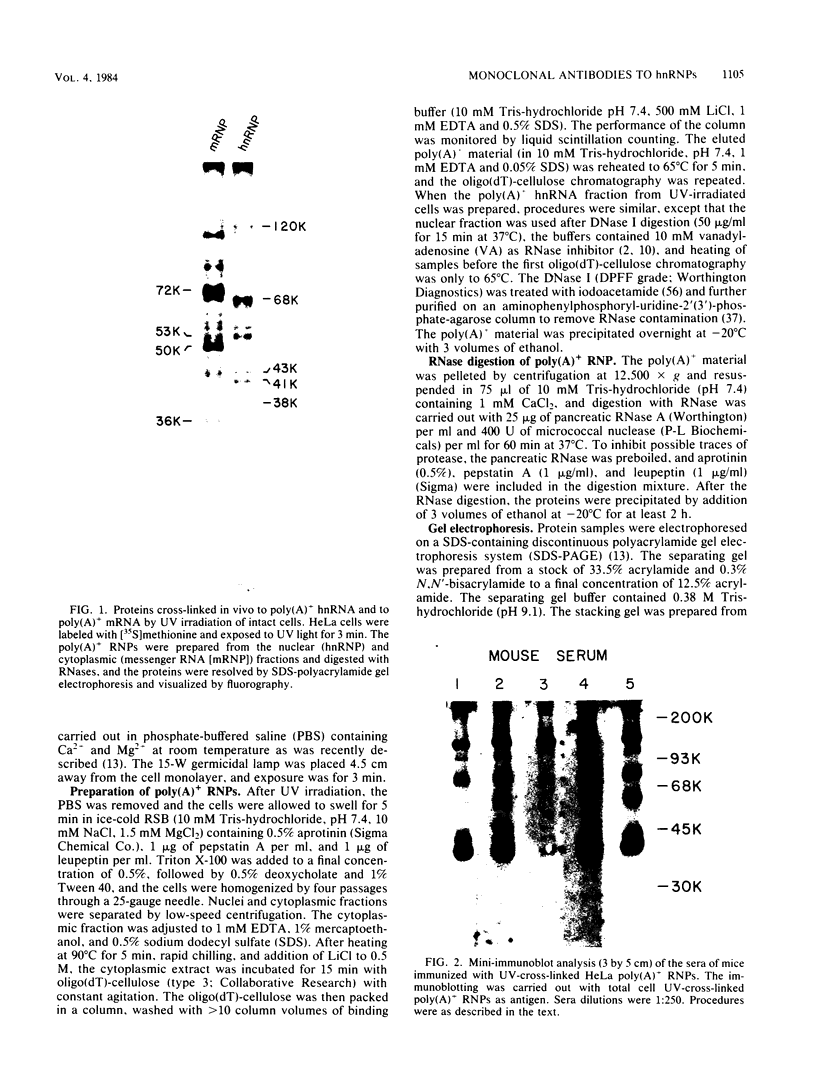
Exposure of cells to UV light of sufficient intensity brings about cross-linking of RNA to proteins which are in direct contact with it in vivo. The major [35S]methionine-labeled proteins which become cross-linked to polyadenylated heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells have molecular weights of 120,000 (120K), 68K, 53K, 43K, 41K, 38K, and 36K. Purified complexes of polyadenylated RNA with proteins obtained by UV cross-linking in intact cells were used to immunize mice and generate monoclonal antibodies to several of these proteins. Some properties of three of the proteins, 41K, 43K, and 120K, were characterized with these antibodies. The 41K and 43K polypeptides are highly related. They were recognized by the same antibody (2B12) and have identical isoelectric points (pl = 6.0 +/- 0.2) but different partial peptide maps. The 41K and 43K polypeptides were part of the 40S heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle and appear to correspond to the previously described C proteins (Beyer et al., Cell II:127-138, 1977). A different monoclonal antibody (3G6) defined a new major heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein of 120K. The 41K, 43K, and 120K polypeptides were associated in vivo with both polyadenylated and non-polyadenylated nuclear RNA, and all three proteins were phosphorylated. The monoclonal antibodies recognized similar proteins in human and monkey cells but not in several other vertebrates. Immunofluorescence microscopy demonstrated that these proteins are segregated to the nucleus, where they are part of a fine particulate nonnucleolar structure. In cells extracted in situ with nonionic detergent, all of the 41K and 43K polypeptides were associated with the nucleus at salt concentrations up to 0.5 M NaCl, whereas the 120K polypeptide was completely extracted at this NaCl concentration. A substantial fraction of the 41K and 43K polypeptides (up to 40%) was retained with a nuclear matrix--a structure which is resistant to digestion with DNase I and to extraction by 2 M NaCl, but the 41K and 43K polypeptides were quantitatively removed at 0.5 M NaCl after digestion with RNase.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Interaction of HeLa cell proteins with RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. Biological properties of the nuclear matrix: steroid hormone binding. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1982;38:133–195. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571138-8.50009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Identification of a nuclear protein matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1410–1417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Bouton A. H., Hodge L. D., Miller O. L., Jr Visualization of the major late R strand transcription unit of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):269–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Bouton A. H., Miller O. L., Jr Correlation of hnRNP structure and nascent transcript cleavage. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Miller O. L., Jr, McKnight S. L. Ribonucleoprotein structure in nascent hnRNA is nonrandom and sequence-dependent. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen M. E., LeStourgeon W. M., Jamrich M., Howard G. C., Serunian L. A., Silver L. M., Elgin S. C. Distribution studies on polytene chromosomes using antibodies directed against hnRNP. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):18–24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidis I. V., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: heterogeneous nuclear RNA is complexed with a major sextet of proteins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1599–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Wilkinson L. E., Laird C. D. Comparative organization of active transcription units in Oncopeltus fasciatus. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Stevenin J., Devilliers G., Jacob M. Size heterogeneity of monoparticles from nuclear ribonucleoproteins containing premessenger RNA. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80395-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Baltimore D. The effect of HeLa cell cytoplasm on the rate of sedimentation of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):999–1002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. The polyribosomal mRNA--protein complex is a dynamic structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2923–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Chelm B. K., Gray P. W., Orozco E. M., Jr Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., Okamura C. S., Martin T. E. Immunofluorescent localization of the proteins of nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):235–243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Allfrey V. G. Characterization of the non-histone nuclear proteins associated with rapidly labeled heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7307–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Coffey D. S., Shaper J. H. Considerations in the isolation of rat liver nuclear matrix, nuclear envelope, and pore complex lamina. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Mar;132(1):105–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kish V. M., Pederson T. Ribonucleoprotein organization of polyadenylate sequences in HeLa cell heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 25;95(2):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Pederson T. Comparison of proteins bound to heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D., Wilkinson L. E., Foe V. E., Chooi W. Y. Analysis of chromatin-associated fiber arrays. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 28;58(2):169–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00701357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Setyono B., Spindler E., Köhler K. Comparison of proteins bound to the different functional classes of messenger RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukanidin E. M., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Antigenic difference between informofers and protein bound to polyribosomal mRNA from rat liver. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):90–92. doi: 10.1038/newbio240090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T., Billings P., Levey A., Ozarslan S., Quinlan T., Swift H., Urbas L. Some properties of RNA:protein complexes from the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:921–932. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T., Billings P., Pullman J., Stevens B., Kinniburgh A. Substructure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):899–909. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Scherrer K. Characterization of pre-messenger-RNA-containing nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles from avian erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):225–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell I. H., Maxwell F., Hahn W. E. Removal of RNase activity from DNase by affinity chromatography on agarose coupled aminophenylphosphoryl-uridine-2' (3')-phosphate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):241–246. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Pederson T. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles probed in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2208–2212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Setyono B., Greenberg J. R., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: identification of proteins in contact with poly(A)+ heterogeneous nuclear RNA in living HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):380–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Miller O. L., Jr Ultrastructural patterns of RNA synthesis during early embryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Symmons P., Saumweber H., Frasch M. Nonpackaging and packaging proteins of hnRNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarina O. P., Lukanidin E. M., Molnar J., Georgiev G. P. Structural organization of nuclear complexes containing DNA-like RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Greenberg J. R. Proteins associated with poly(A) and other regions of mRNA and hnRNA molecules as investigated by crosslinking. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Kamen R. Arrangement of 30S heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein on polyoma virus late nuclear transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenin J., Gallinaro-Matringe H., Gattoni R., Jacob M. Complexity of the structure of particles containing heterogeneous nuclear RNA as demonstrated by ribonuclease treatment. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):589–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomcsányi T., Molnár J., Tigyi A. Structural characterization of nuclear poly(A)-protein particles in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eekelen C. A., Mariman E. C., Reinders R. J., Van Venrooij W. J. Adenoviral heterogeneous nuclear RNA is associated with host cell proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):461–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenmakers A. J., Reinders R. J., van Venrooij W. J. Cross-linking of mRNA to proteins by irradiation of intact cells with ultraviolet light. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. W., Lothstein L., Baker C. L., LeStourgeon W. M. The release of 40S hnRNP particles by brief digestion of HeLa nuclei with micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3639–3657. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Sandeen D. The ribonuclease activity of crystallized pancreatic deoxyribonuclease. Anal Biochem. 1966 Feb;14(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., van Venrooij W. J. hnRNA and its attachment to a nuclear protein matrix. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):554–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., Riemen T., van Eekelen C. A. Host proteins are associated with adenovirus specific mRNA in the cytoplasm. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 16;145(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]