Abstract
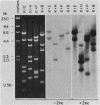
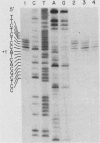
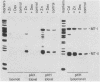
The mouse metallothionein II (MT-II) gene is located approximately 6 kilobases upstream of the MT-I gene. A comparison of the sequences of mouse MT-I and MT-II genes (as well as those of other mammals) reveals that the coding regions are highly conserved even at "silent" positions but that the noncoding regions and introns are extremely divergent between primates and rodents. There are four blocks of conserved sequences in the promoters of mouse MT-I, mouse MT-II, and human MT-IIA genes; one includes the TATAAA sequence, and another has been implicated in regulation by heavy metals. Mouse MT-I and MT-II mRNAs are induced to approximately the same extent in vivo in response to cadmium, dexamethasone, or lipopolysaccharide. Mouse MT-I and MT-II genes are regulated by metals but not by glucocorticoids after transfection into HeLa cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Birren B. W., Ganz T., Piletz J. E., Herschman H. R. Molecular cloning of the rat metallothionein 1 (MT-1) mRNA sequence. DNA. 1983;2(1):15–22. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Leslie A. G., Ratliff R. L. Left-handed DNA helices. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):743–745. doi: 10.1038/283743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach L. R., Palmiter R. D. Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium-resistant mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compere S. J., Palmiter R. D. DNA methylation controls the inducibility of the mouse metallothionein-I gene lymphoid cells. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Palmiter R. D. The metallothionein-I gene maps to mouse chromosome 8: implications for human Menkes' disease. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00289481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Hoffman J. S., Quaife C. J., Benditt E. P., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Induction of mouse metallothionein-I mRNA by bacterial endotoxin is independent of metals and glucocorticoid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1053–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. A practical approach for quantitating specific mRNAs by solution hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Induction of metallothionein-I mRNA in cultured cells by heavy metals and iodoacetate: evidence for gratuitous inducers. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):484–491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the mouse metallothionein-I gene by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5712–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Palmiter R. D. Isolation and characterization of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick G. G., McCarty K. S., Sr Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium- and zinc-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9049–9053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. B., Walters R. A., Enger M. D., Hildebrand C. E., Griffith J. K. cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence comparison of Chinese hamster metallothionein I and II mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):901–910. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Wu R. New rapid methods for DNA sequencing based in exonuclease III digestion followed by repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2065–2084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager L. J., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of mouse liver metallothionein-I gene by glucocorticoids. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):340–342. doi: 10.1038/291340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Walling M. Regulation in vivo of a cloned mammalian gene: cadmium induces the transcription of a mouse metallothionein gene in SV40 vectors. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):273–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Tsunoo H., Kimura M., Nakashima H., Yoshida A. Primary structure of mouse liver metallothionein -I and -II. Experientia Suppl. 1979;34:169–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6493-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Ghosh P. K. Initiation and regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):449–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.449-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. W., Beach L. R., Palmiter R. D. Ultraviolet radiation-induced metallothionein-I gene activation is associated with extensive DNA demethylation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse metallothionein I gene is selectively lost following amplification of the gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3061–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. The mouse metallothionein-I gene is transcriptionally regulated by cadmium following transfection into human or mouse cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Hamer D. H. Regulation of a metallothionein-growth hormone hybrid gene in bovine papilloma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):397–401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Molecular biology. CACA sequences - the ends and the means? Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):101–102. doi: 10.1038/305101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Cloning and sequence analysis of two monkey metallothionein cDNAs. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]