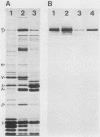
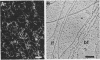
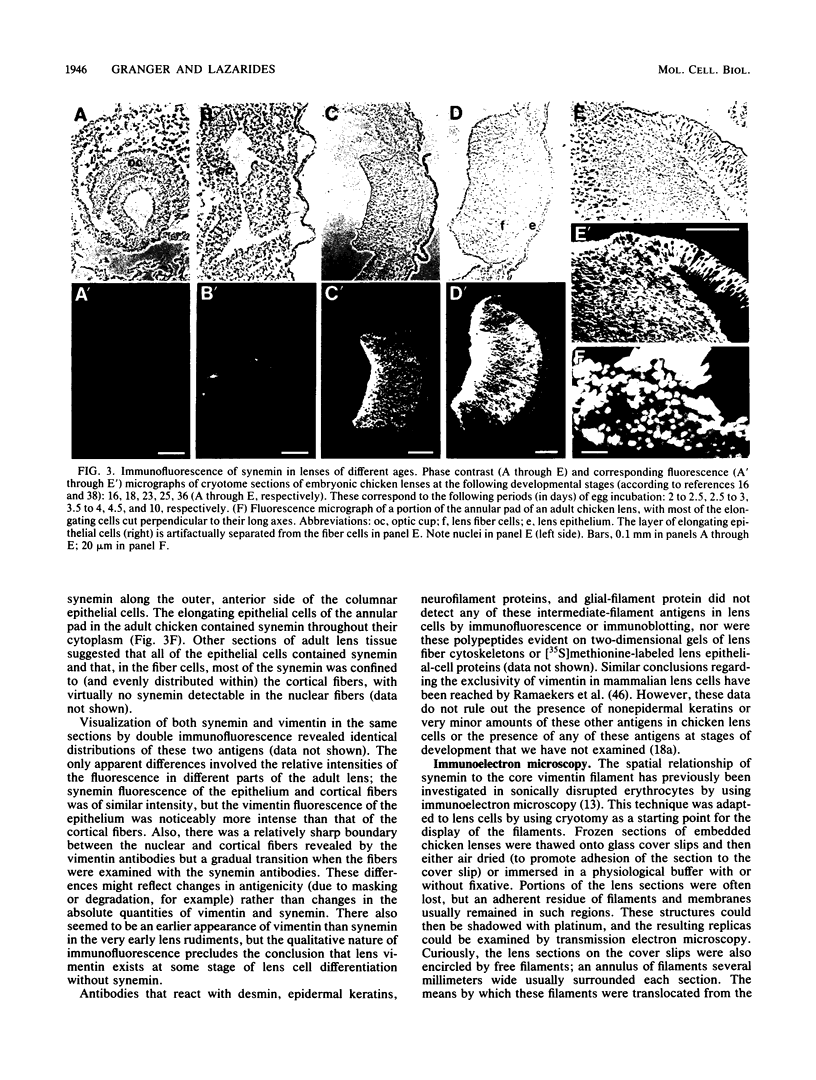
Abstract
Synemin, a 230-kilodalton polypeptide component of avian muscle and erythrocyte intermediate filaments, is also found in association with the vimentin filaments of lens tissue. In chicken lens cells, synemin is bound to the core vimentin polymer with the same 180-nm periodicity that it exhibits in erythrocytes. Its solubility properties are characteristic of those of intermediate filaments in general and similar to those of synemin in muscle cells and erythrocytes. Synemin appears at an early stage of lens development and undergoes a dramatic accumulation as the epithelial cells elongate and differentiate into fiber cells. In contrast to synemin in cultured skeletal muscle, lens synemin is not confined to postmitotic, terminally differentiating cells but is present in proliferative cells as well. It is lost from the fibers near the center of the lens, as are many other cellular structures including intermediate filaments. These findings provide new information about the occurrence and expression of avian synemin and new insight regarding its presumptive role as a modulator of intermediate-filament function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):127–138. doi: 10.1126/science.877544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. H., Ireland M., Maisel H. The cytoskeleton of chick lens cells. Exp Eye Res. 1979 Apr;28(4):441–453. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(79)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G. A., Ingram V. M. The erythroid cells and haemoglobins of the chick embryo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Oct 25;266(877):225–305. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. Direct identification of specific glycoproteins and antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:54–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. H., Chase R. H. Potassium chloride-insoluble myofilaments in vertebrate smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drochmans P., Freudenstein C., Wanson J. C., Laurent L., Keenan T. W., Stadler J., Leloup R., Franke W. W. Structure and biochemical composition of desmosomes and tonofilaments isolated from calf muzzle epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):427–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M., Alousi S., Lawniczak J., Maisel H., Welsh M. Studies on lens vimentin. Exp Eye Res. 1984 Feb;38(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(84)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C. Intermyofibrillar and nuclear-myofibrillar connections in human and canine myocardium. An ultrastructural study. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1973 Jun;5(3):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(73)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garadi R., Katar M., Maisel H. Two-dimensional gel analysis of chick lens proteins. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Jun;36(6):859–869. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Expression of the major neurofilament subunit in chicken erythrocytes. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.6346488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Membrane skeletal protein 4.1 of avian erythrocytes is composed of multiple variants that exhibit tissue-specific expression. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):595–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Structural associations of synemin and vimentin filaments in avian erythrocytes revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Synemin: a new high molecular weight protein associated with desmin and vimentin filaments in muscle. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Repasky E. A., Lazarides E. Synemin and vimentin are components of intermediate filaments in avian erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. J., Dilley K. J. Structural proteins of the mammalian lens: a review with emphasis on changes in development, aging and cataract. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Jan;22(1):1–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield J. S., Skoff R. P., Maisel H., Eng L. Glial fibrillary acidic protein is localized in the lens epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1895–1898. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland M., Maisel H. Identification of native actin filaments in chick lens fiber cells. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Apr;36(4):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Davidson R. S., McNamee K. C., Russell G., Goodwin D., Holborow E. J. Fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy: a study of the phenomenon and its remedy. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Franke W. W., Moser J. G., Stoffels U. Specific attachment of desmin filaments to desmosomal plaques in cardiac myocytes. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):735–742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibbelaar M. A., Selten-Versteegen A. M., Dunia I., Benedetti E. L., Bloemendal H. Actin in mammalian lens. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):543–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Granger B. L. Preparation and assay of the intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):488–508. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieska N., Chen J., Maisel H., Romero-Herrera A. E. Subunit characterization of lens intermediate filaments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):136–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel H., Lieska N., Bradley R. Isolation of filaments of the chick lens. Experientia. 1978 Mar 15;34(3):352–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01923029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel H., Perry M. M. Electron microscope observations on some structural proteins of the chick lens. Exp Eye Res. 1972 Jul;14(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(72)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAvoy J. W. Induction of the eye lens. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):137–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Lazarides E. Synthesis and post-translational assembly of intermediate filaments in avian erythroid cells: vimentin assembly limits the rate of synemin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Brown M., Degenstein L., Fox L., Soh B. M. Transformation of retinal glia cells into lens phenotype: expression of MP26, a lens plasma membrane antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7239–7243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Avian lens spectrin: subunit composition compared with erythrocyte and brain spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1271–1276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Expression of the beta subunit of spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):363–367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Balzer D. R., Jr, Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of subunit proteins of intermediate filaments from chicken muscle and nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'RAHILLY R., MEYER D. B. The early development of the eye in the chick Gallus domesticus (stages 8 to 25). Acta Anat (Basel) 1959;36(1-2):20–58. doi: 10.1159/000141425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou J. Molecular aspects of lens cell differentiation. Science. 1967 Apr 21;156(3773):338–346. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3773.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 1981;19(3):134–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. G., Lazarides E. Expression of intermediate filament-associated proteins paranemin and synemin in chicken development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1860–1874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty N. S., Goossens W. Cytoplasmic filaments in the crystalline lens of various species: functional correlations. Exp Eye Res. 1978 Feb;26(2):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(78)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Boomkens T. R., Bloemendal H. Cytoskeletal and contractile structures in bovine lens cell differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Dunia I., Dodemont H. J., Benedetti E. L., Bloemendal H. Lenticular intermediate-sized filaments: biosynthesis and interaction with plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Osborn M., Schimid E., Weber K., Bloemendal H., Franke W. W. Identification of the cytoskeletal proteins in lens-forming cells, a special epitheloid cell type. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jun;127(2):309–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90437-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Poels L. G., Jap P. H., Bloemendal H. Simultaneous demonstration of microfilaments and intermediate-sized filaments in the lens by double immunofluorescence. Exp Eye Res. 1982 Oct;35(4):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(82)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repasky E. A., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Widespread occurrence of avian spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):821–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roessmann U., Velasco M. E., Sindely S. D., Gambetti P. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in ependymal cells during development. An immunocytochemical study. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 27;200(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval I. V., Colaco C. A., Lazarides E. Purification of the intermediate filament-associated protein, synemin, from chicken smooth muscle. Studies on its physicochemical properties, interaction with desmin, and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2568–2576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A. Structure and function of intercellular junctions. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:191–283. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60940-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Campbell G. R., Burnstock G. Cytoplasmic filaments in developing and adult vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):484–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gomer R. H., Lazarides E. Heat shock proteins are methylated in avian and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Antibody decoration of neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):198–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaan J., Ikeda A. Macromolecular events during differentiation of the chicken lens. Exp Eye Res. 1968 Apr;7(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(68)80081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]