Abstract
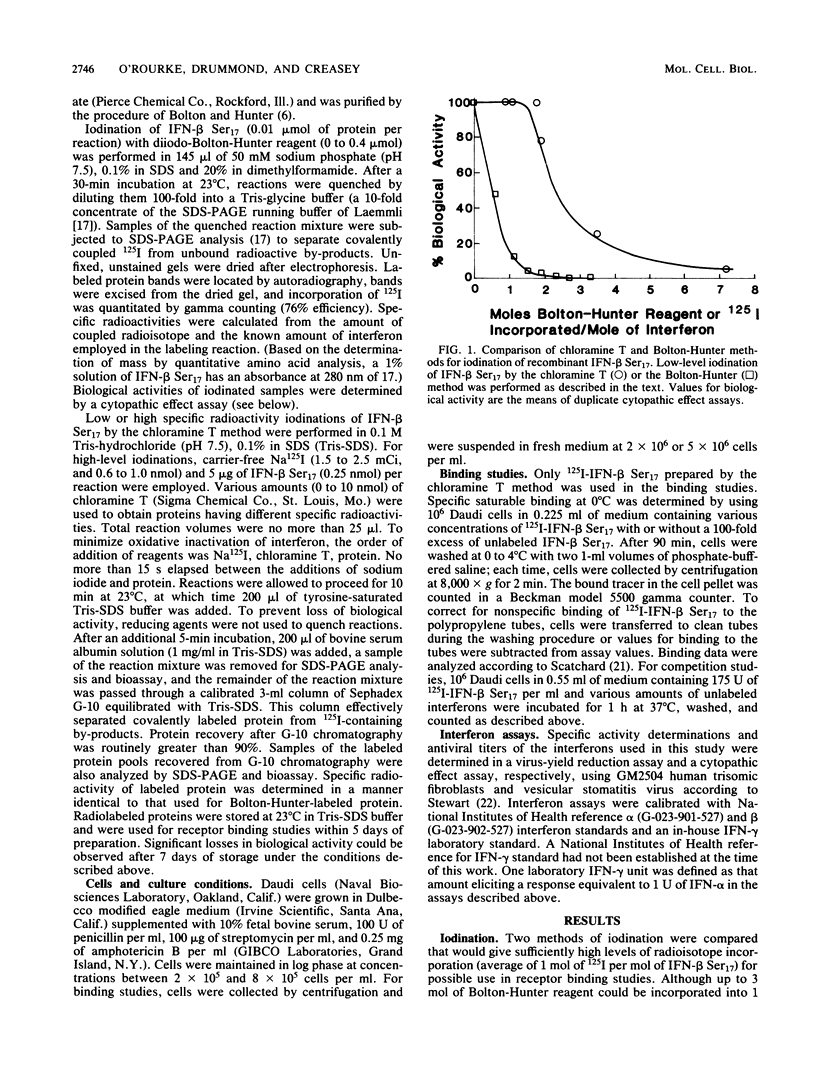
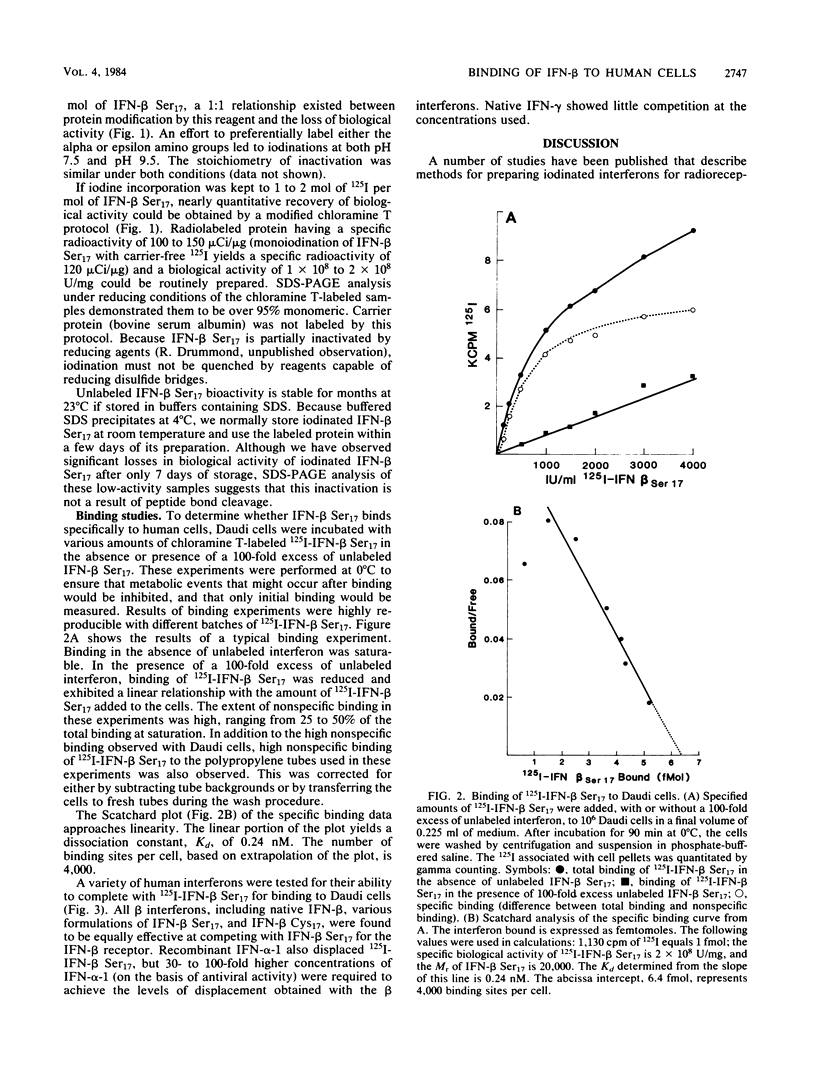
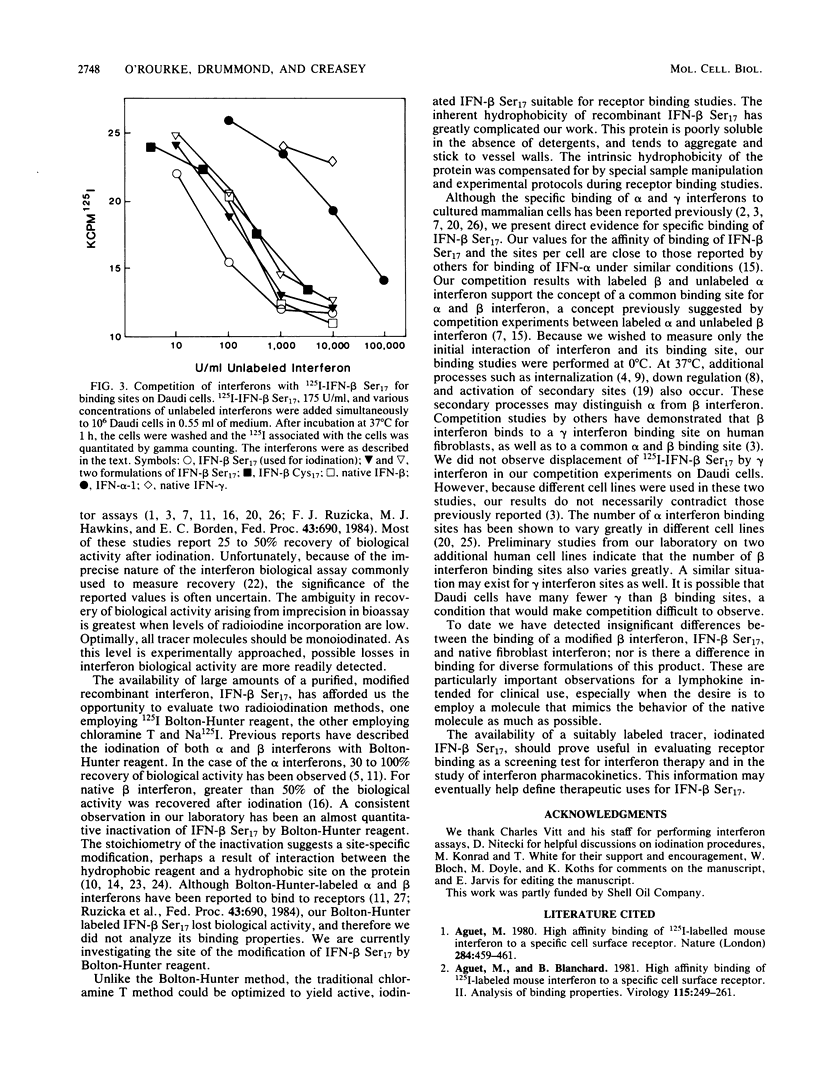
We investigated the binding of 125I-labeled beta interferon (IFN-beta Ser17), a nonglycosylated recombinant human fibroblast interferon in which cysteine at position 17 is replaced by serine by site-specific mutagenesis. An optimized chloramine T radiolabeling method produced a highly labeled, fully active 125I-IFN suitable for these studies. Unlike the case with the chloramine T method, incorporation of a single mole of Bolton-Hunter reagent into a mole of IFN-beta Ser17 led to nearly complete loss of biological activity. 125I-IFN-beta Ser17, prepared by the chloramine T method, bound specifically to human lymphoblastoid cells (Daudi) with a dissociation constant of 0.24 nM. The number of binding sites per cell was 4,000. In competition assays, unlabeled beta interferons (native, recombinant IFN-beta Cys17, and various preparations of IFN-beta Ser17) equally displaced labeled IFN-beta Ser17 on Daudi cells. Recombinant IFN-alpha-1 displaced 125I-IFN-beta binding to Daudi cells less efficiently than did unlabeled native or recombinant beta interferon. However, at the concentrations tested, native gamma interferon showed no competition with 125I-IFN. Our results indicate that IFN-beta Ser17 and native IFN-beta posses similar binding properties.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Blanchard B. High affinity binding of 125I-Labeled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. II. Analysis of binding properties. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Human interferon-gamma is internalized and degraded by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6497–6502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Specific binding of 125I-human interferon-gamma to high affinity receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11301–11304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Ohno M., Smith M., Gutte B., Zoon K. C. Orientation of a human leukocyte interferon molecule on its cell surface receptor: carboxyl terminus remains accessible to a monoclonal antibody made against a synthetic interferon fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2539–2543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Down-regulation of the interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13197–13200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human, mouse, and rabbit interferons with immobilized hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7620–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Branca A. A., McCandless S., Baglioni C. Characterization of an interferon receptor on human lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3269–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., von Muenchhausen W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Binding of human interferons to immobolized Cibacron Blue F3GA: The nature of molecular interaction. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5182–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. R., Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Interferon receptors. Cross-linking of human leukocyte interferon alpha-2 to its receptor on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13884–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E. Preparation of 125iodine-labelled human fibroblast interferon. J Gen Virol. 1978 Sep;40(3):681–684. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-3-681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Bandu M. T. Kinetic evidence for an activation step following binding of human interferon alpha 2 to the membrane receptors of Daudi cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Bandu M. T., Vignaux F., Aguet M., Gressner I. Binding of 125I-labelled human alpha interferon to human lymphoid cells. Int J Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;28(5):575–582. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Davey M. W., Carter W. A. Interaction of human interferons with immobilized hydrophobic amino acids and dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5381–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara S., Yonehara-Takahashi M., Ishii A. Binding of human interferon alpha to cells of different sensitivities: studies with internally radiolabeled interferon retaining full biological activity. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1168–1171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1168-1171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H., Zur Nedden D., Fitzgerald D. J., Willingham M. C. Human interferon alpha enters cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K., Zur Nedden D., Arnheiter H. Specific binding of human alpha interferon to a high affinity cell surface binding site on bovine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4695–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


