Abstract
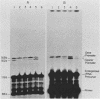
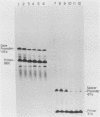
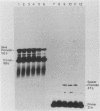
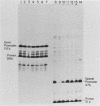
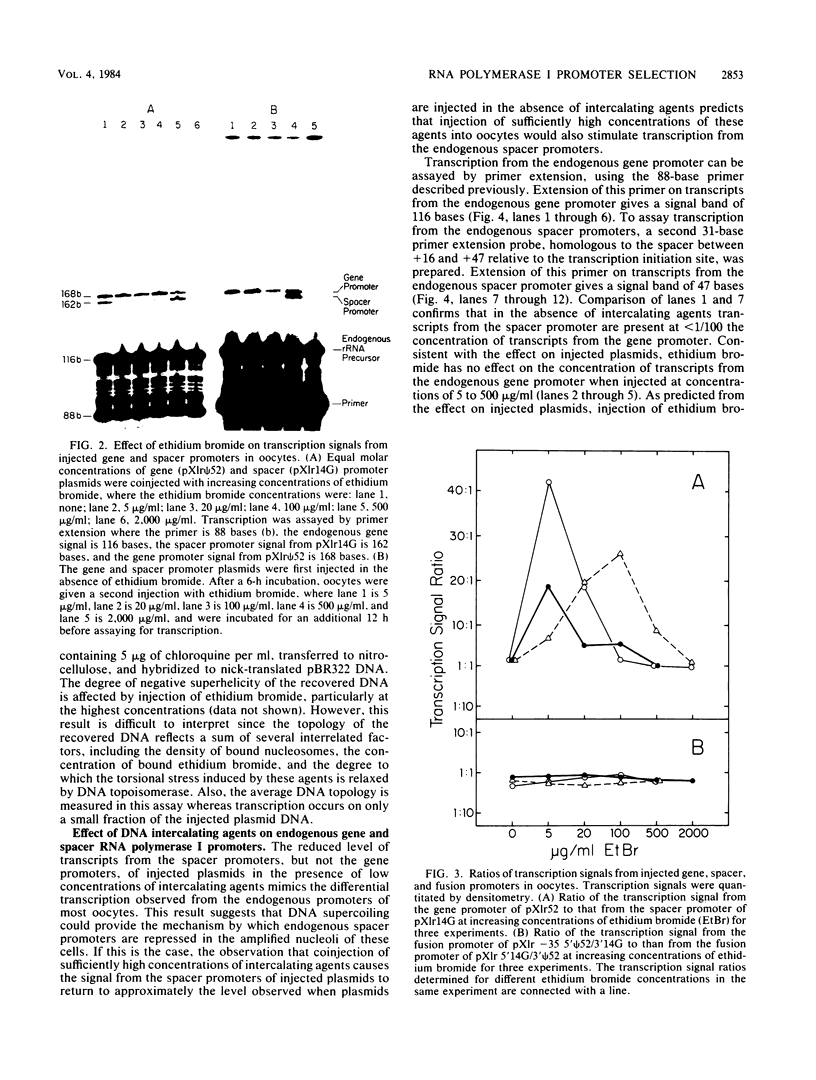
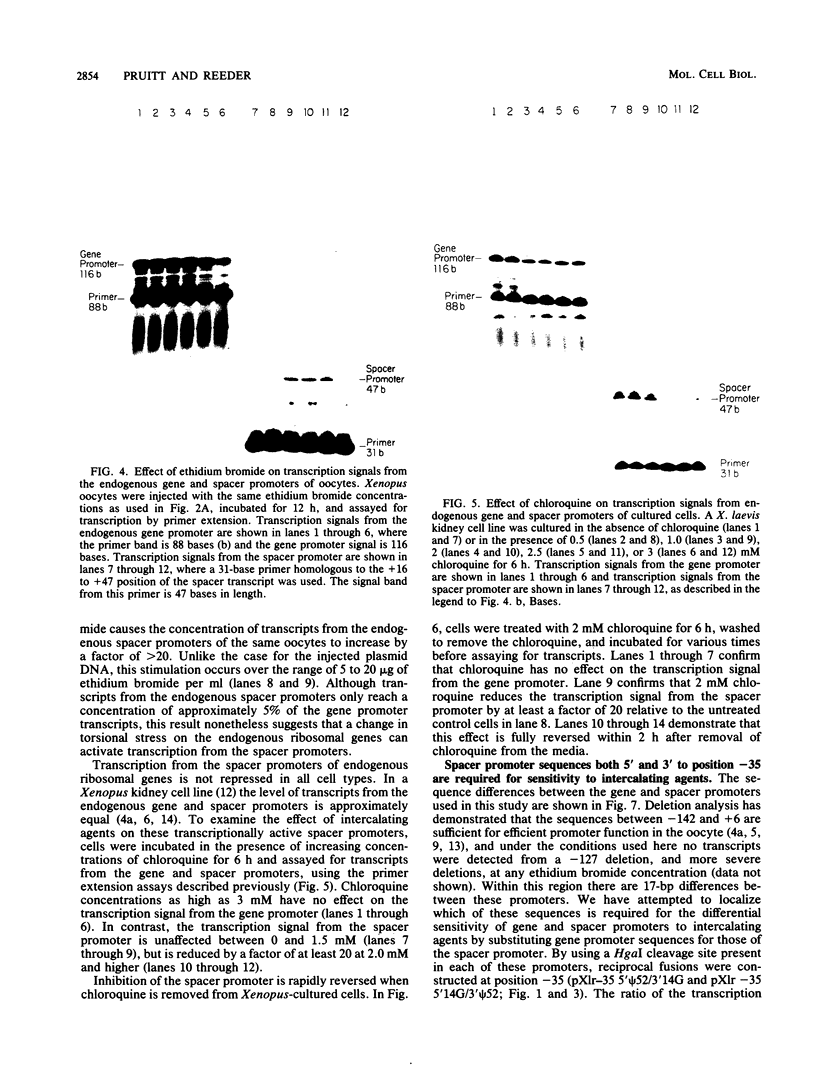
We have analyzed the effect of DNA intercalating agents on the transcription signals from two different Xenopus laevis RNA polymerase I promoters. The transcription signal from the promoter for the 7.5-kilobase rRNA precursor (the gene promoter) is unaffected over a large range of intercalating agent concentrations regardless of whether the template is injected plasmid DNA in oocytes, the amplified endogenous nucleoli of oocytes, or the endogenous chromosomes of cultured Xenopus kidney cells. The transcription signal from a closely related promoter located in the spacer DNA between genes (the spacer promoter) ranges between undetectable to equivalent to the gene promoter signal on different templates. The transcription signal from the spacer promoter is also differentially affected by intercalating agents relative to the gene promoter. Depending on the template, these agents can either increase or decrease the transcription signal from the spacer promoter. Fusions between the gene and spacer promoters demonstrate that intercalating agents affect transcription initiation. One explanation for these results is that the degree of supercoiling of the template DNA can differentially inhibit transcription from the spacer promoters. The different effects of intercalating agents on transcription from the spacer promoters of various templates could then be explained as differences in the degree of supercoiling present on these templates initially.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gurdon J. B., Brown D. D. The transcription of 5 S DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Gellert M. Regulation of the genes for E. coli DNA gyrase: homeostatic control of DNA supercoiling. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Roan J. G., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Variations in transcriptional activity of rDNA spacer promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6043–6052. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Boseley P. G., Birnstiel M. L. More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):467–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock D. G., Reeder R. H. In vitro methylation of HpaII sites in Xenopus laevis rDNA does not affect its transcription in oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2225–2232. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Grainger R. M. A mosaicism in the higher order structure of Xenopus oocyte nucleolar chromatin prior to and during ribosomal gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Reeder R. H. Effect of topological constraint on transcription of ribosomal DNA in Xenopus oocytes. Comparison of plasmid and endogenous genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):121–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Achermann H., Crippa M. Transcription of spacer sequences in genes coding for ribosomal RNA in Xenopus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Trendelenburg M. F., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Lengths and patterns of transcriptional units in the amplified nucleoli of oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma. 1977 Mar 16;60(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00288462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M., Reddy B. S., Bhandary K. K., Jain S. C., Sakore T. D., Seshadri T. P. Conformational flexibility in DNA structure as revealed by structural studies of drug intercalation and its broader implications in understanding the organization of DNA in chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):87–102. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., McKnight S. L. Accurate transcription of cloned Xenopus rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: demonstration by S1 nuclease mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3391–3405. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Wilkinson J. A., Roan J., Reeder R. H. Nested control regions promote Xenopus ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. The degree of unwinding of the DNA helix by ethidium. I. Titration of twisted PM2 DNA molecules in alkaline cesium chloride density gradients. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):783–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]