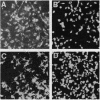
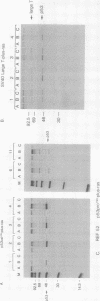
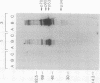
Abstract
Overexpression of an activated ras gene in the rat embryo fibroblast line REF52 results in growth arrest at either the G1/S or G2/M boundary of the cell cycle. Both the DNA tumor virus proteins simian virus 40 large T antigen and adenovirus 5 E1a are able to rescue ras induced lethality and cooperate with ras to fully transform REF52 cells. In this report, we present evidence that the wild-type activity of the tumor suppressor gene p53 is involved in the negative growth regulation of this model system. p53 genes encoding either a p53Val-135 or p53Pro-193 mutation express a highly stable p53 protein with a conformation-dependent loss of wild-type activity and the ability to eliminate any endogenous wild-type p53 activity in a dominant negative manner. In cotransfection assays, these mutant p53 genes are able to rescue REF52 cells from ras-induced growth arrest, resulting in established cell lines which express elevated levels of the ras oncoprotein and show morphological transformation. Full transformation, as assayed by tumor formation in nude mice, is found only in the p53Pro-193-plus-ras transfectants. These cells express higher levels of the ras protein than do the p53Val-135-plus-ras-transfected cells. Transfection of REF52 cells with ras alone or a full-length genomic wild-type p53 plus ras results in growth arrest and lethality. Therefore, the selective event for p53 inactivation or loss during tumor progression may be to overcome a cell cycle restriction induced by oncogene overexpression (ras). These results suggest that a normal function of p53 may be to mediate negative growth regulation in response to ras or other proliferative inducing signals.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Jenkins J. R., Stürzbecher H. W. The p53 nuclear localisation signal is structurally linked to a p34cdc2 kinase motif. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Bastin M. Sequences from polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T genes capable of immortalizing primary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):958–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.958-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben David Y., Prideaux V. R., Chow V., Benchimol S., Bernstein A. Inactivation of the p53 oncogene by internal deletion or retroviral integration in erythroleukemic cell lines induced by Friend leukemia virus. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Friedman P. N., Marshak D. R., Prives C., Beach D. Human p53 is phosphorylated by p60-cdc2 and cyclin B-cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner R., Balmain A. Genetic changes in skin tumor progression: correlation between presence of a mutant ras gene and loss of heterozygosity on mouse chromosome 7. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90523-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Cheng K., Frey A. B., Stein R., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. Purification of complexes of nuclear oncogene p53 with rat and Escherichia coli heat shock proteins: in vitro dissociation of hsc70 and dnaK from murine p53 by ATP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., McClarty G. A., Jarolim L., Wright J. A., Spiro I., Hager G., Greenberg A. H. Expression of H-ras correlates with metastatic potential: evidence for direct regulation of the metastatic phenotype in 10T1/2 and NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):830–837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Overproduction of p53 antigen makes established cells highly tumorigenic. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):158–160. doi: 10.1038/316158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Maruyama K., Garrels J. I., Ruley H. E. In vitro establishment is not a sufficient prerequisite for transformation by activated ras oncogenes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks G. G., Mowat M. Integration of Friend murine leukemia virus into both alleles of the p53 oncogene in an erythroleukemic cell line. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4752–4755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4752-4755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakawa T., Ruley H. E. Rescue of cells from ras oncogene-induced growth arrest by a second, complementing, oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1519–1523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Gray D., Mowat M., Benchimol S. Expression of wild-type p53 is not compatible with continued growth of p53-negative tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Tumorigenicity of fibroblast lines expressing the adenovirus E1a, cellular p53, or normal c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Ruley H. E. Role of c-myc in the transformation of REF52 cells by viral and cellular oncogenes. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiss S., Quaiser A., Oren M., Montenarh M. Oligomerization of oncoprotein p53. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4737–4744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4737-4744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Sukumar S., Barbacid M. Activation of ras oncogenes preceding the onset of neoplasia. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1101–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2188364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J. Tumor suppressor genes: the p53 and retinoblastoma sensitivity genes and gene products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90015-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Cook A. The cellular tumour antigen p53: evidence for transformation-related, immunological variants of p53. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Milner S. SV40-53K antigen: a possible role for 53K in normal cells. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):785–788. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Cheng A., Kimura N., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Rearrangements of the cellular p53 gene in erythroleukaemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):633–636. doi: 10.1038/314633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D. G., Peacock J. W., Benchimol S. Inactivation of the cellular p53 gene is a common feature of Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia: relationship of inactivation to dominant transforming alleles. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3307–3313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H., Reeves B., Brown R., Hall A., Furth M., Bos J., Jones P., Marshall C. Activated N-ras controls the transformed phenotype of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Noble M., Land H. Ras-mediated cell cycle arrest is altered by nuclear oncogenes to induce Schwann cell transformation. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1635–1645. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Benchimol S. Immortalization of rat embryo fibroblasts by the cellular p53 oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Munroe D., Peacock J., Mowat M., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Deletion of 5'-coding sequences of the cellular p53 gene in mouse erythroleukemia: a novel mechanism of oncogene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):847–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Chumakov P., Welch W. J., Jenkins J. R. Mutant p53 proteins bind hsp 72/73 cellular heat shock-related proteins in SV40-transformed monkey cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):201–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Maimets T., Chumakov P., Brain R., Addison C., Simanis V., Rudge K., Philp R., Grimaldi M., Court W. p53 interacts with p34cdc2 in mammalian cells: implications for cell cycle control and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):795–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuck S. P., Crawford L. Overexpression of normal human p53 in established fibroblasts leads to their tumorigenic conversion. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(2):81–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a ras cooperation activity is separate from its positive and negative transcription regulatory functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2177–2183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Admon S., Oren M., Rotter V. Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed cells that lack p53 protein synthesis express aberrant p53 mRNA species. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):552–558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Major deletions in the gene encoding the p53 tumor antigen cause lack of p53 expression in HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):790–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]