Abstract
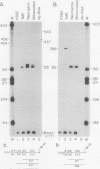
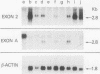
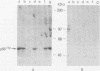
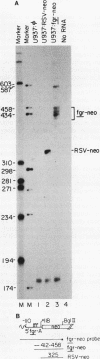
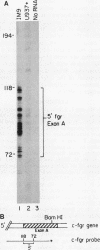
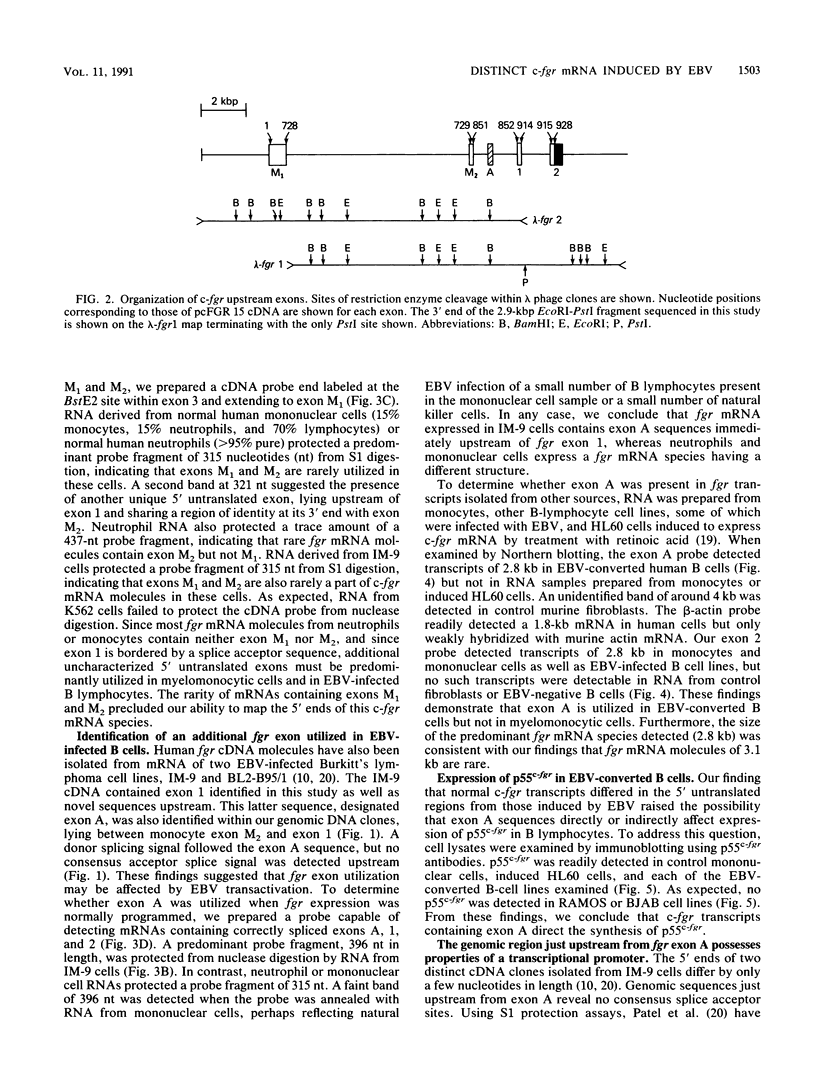
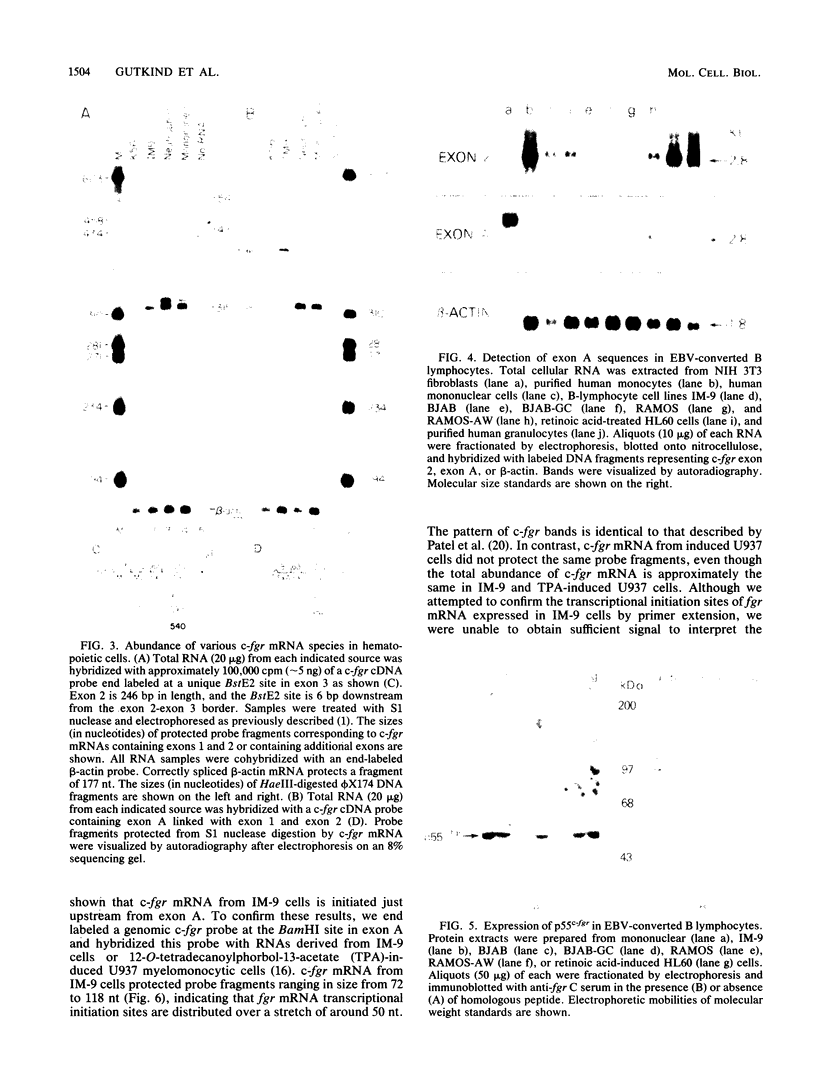
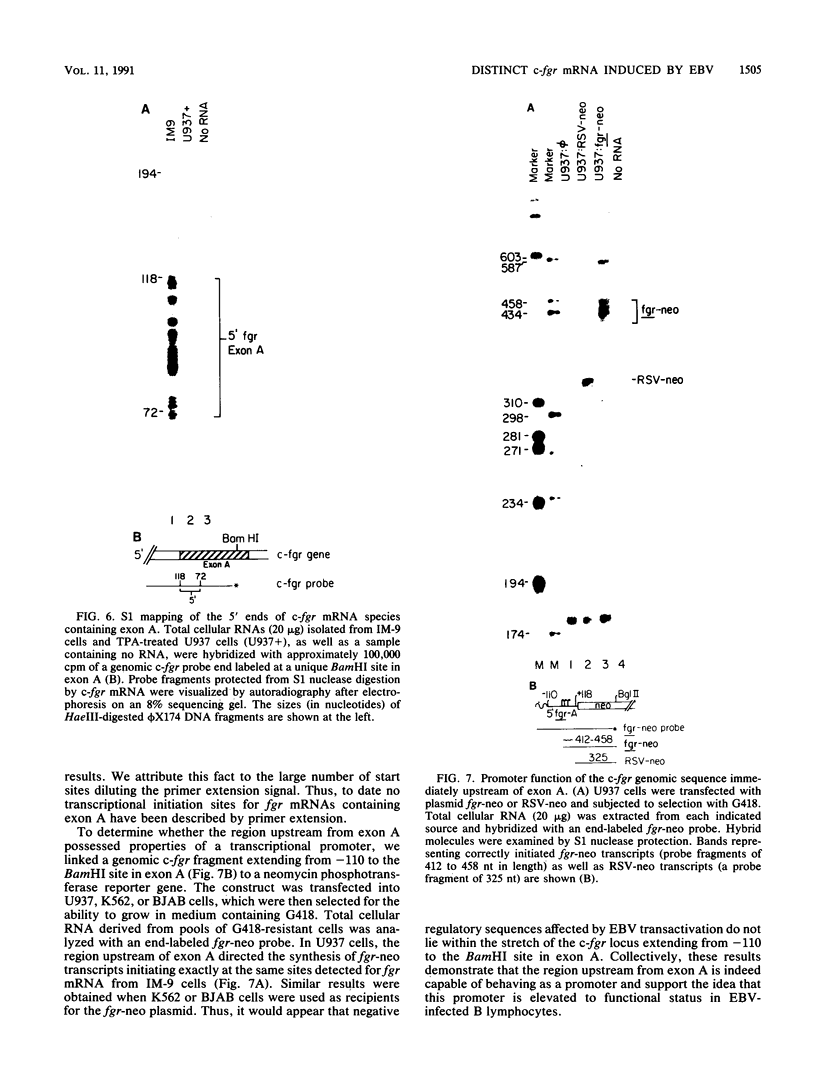
The fgr proto-oncogene encodes a nonreceptor protein-tyrosine kinase, designated p55c-fgr. In this study, we have isolated human fgr cDNA molecules from normal monocyte mRNA templates. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the longest fgr cDNA revealed a 5' untranslated region of 927 bp which included two Alu-like repeats as well as three translation stop codons immediately upstream of the initiator for p55c-fgr synthesis. Within genomic DNA, these sequences were distributed over 13 kbp as three distinct 5' untranslated exons. Previous studies have shown that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) increases c-fgr mRNA levels in B lymphocytes. By comparing the nucleotide sequence reported for transcripts isolated from EBV-infected B lymphocytes with those of our monocyte cDNA as well as genomic DNA, we identified a novel untranslated exon utilized only in EBV-infected cells. The transcriptional initiation sites of fgr mRNA expressed in EBV-converted cells were mapped and shown to reside within a region identified as an intron for fgr mRNA that is expressed in normal myelomonocytic cells. Furthermore, the region of the fgr locus upstream of the novel exon displayed properties of a transcriptional promoter when transfected into heterologous cells. We conclude from all of these findings that activation of the fgr gene by EBV is achieved by mechanisms distinct from those normally regulating its programmed expression in myelomonocytic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodine D. M., Ley T. J. An enhancer element lies 3' to the human A gamma globin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2997–3004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah M. S., Ley T. J., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C. fgr proto-oncogene mRNA induced in B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus infection. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):238–240. doi: 10.1038/319238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. B., Klein G., Povey S. Production by EBV infection of an EBNA-positive subline from an EBNA-negative human lymphoma cell line without detectable EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):125–133. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Schmid C. W. A study of the evolution of repeated DNA sequences in primates and the existence of a new class of repetitive sequences in primates. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):437–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Buell D. N., Sox H. C. Proliferation and differentiation of lymphoid cells: studies with human lymphoid cell lines and immunoglobulin synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:221–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C. Translocation of the FGR protein-tyrosine kinase as a consequence of neutrophil activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8783–8787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Ikawa S., Semba K., Sukegawa J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones homologous to the v-fgr oncogene from a human B lymphocyte cell line, IM-9. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Specific expression of human c-fgr in natural immunity effector cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1789–1792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katamine S., Notario V., Rao C. D., Miki T., Cheah M. S., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C. Primary structure of the human fgr proto-oncogene product p55c-fgr. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Connolly N. L., Katamine S., Cheah M. S., Senior R. M., Robbins K. C. Tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of the human fgr proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Matsui T., Heidaran M. A., Aaronson S. A. An efficient directional cloning system to construct cDNA libraries containing full-length inserts at high frequency. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naharro G., Robbins K. C., Reddy E. P. Gene product of v-fgr onc: hybrid protein containing a portion of actin and a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):63–66. doi: 10.1126/science.6318314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notario V., Gutkind J. S., Imaizumi M., Katamine S., Robbins K. C. Expression of the fgr protooncogene product as a function of myelomonocytic cell maturation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3129–3136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M., Leevers S. J., Brickell P. M. Structure of the complete human c-fgr proto-oncogene and identification of multiple transcriptional start sites. Oncogene. 1990 Feb;5(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Barbacid M., Aaronson S., Gardner M. B. Origin and biological properties of a new feline sarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. J., Lesley J., Trotter J., Schulte R., Hyman R., Sefton B. M. Changes in the relative abundance of type I and type II lck mRNA transcripts suggest differential promoter usage during T-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4266–4270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor O., Gregory F. S., Templeton N. S., Pawar S., Perlmutter R. M., Rosen N. Selective expression of alternative lck mRNAs in human malignant cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2983–2988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Gutkind J. S., Katamine S., Kawakami T., Robbins K. C. The actin domain of Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma virus inhibits kinase and transforming activities. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1715–1720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1715-1720.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takadera T., Leung S., Gernone A., Koga Y., Takihara Y., Miyamoto N. G., Mak T. W. Structure of the two promoters of the human lck gene: differential accumulation of two classes of lck transcripts in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2173–2180. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. J., Ley T. J. Function of normal and mutated gamma-globin gene promoters in electroporated K562 erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1990 Feb 15;75(4):990–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Adler H. T., Sefton B. M. Two lck transcripts containing different 5' untranslated regions are present in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4407–4413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]