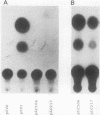
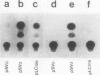
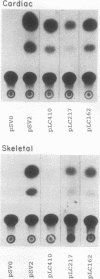
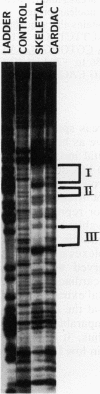
Abstract
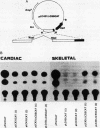
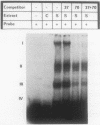
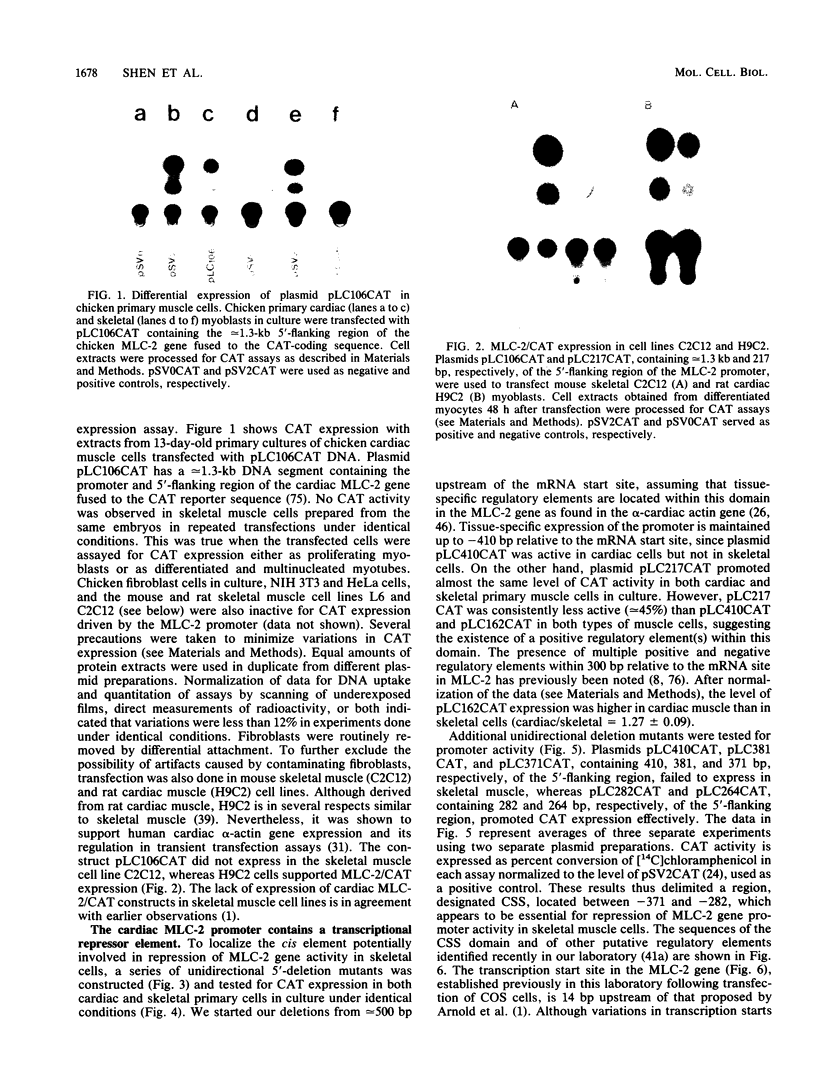
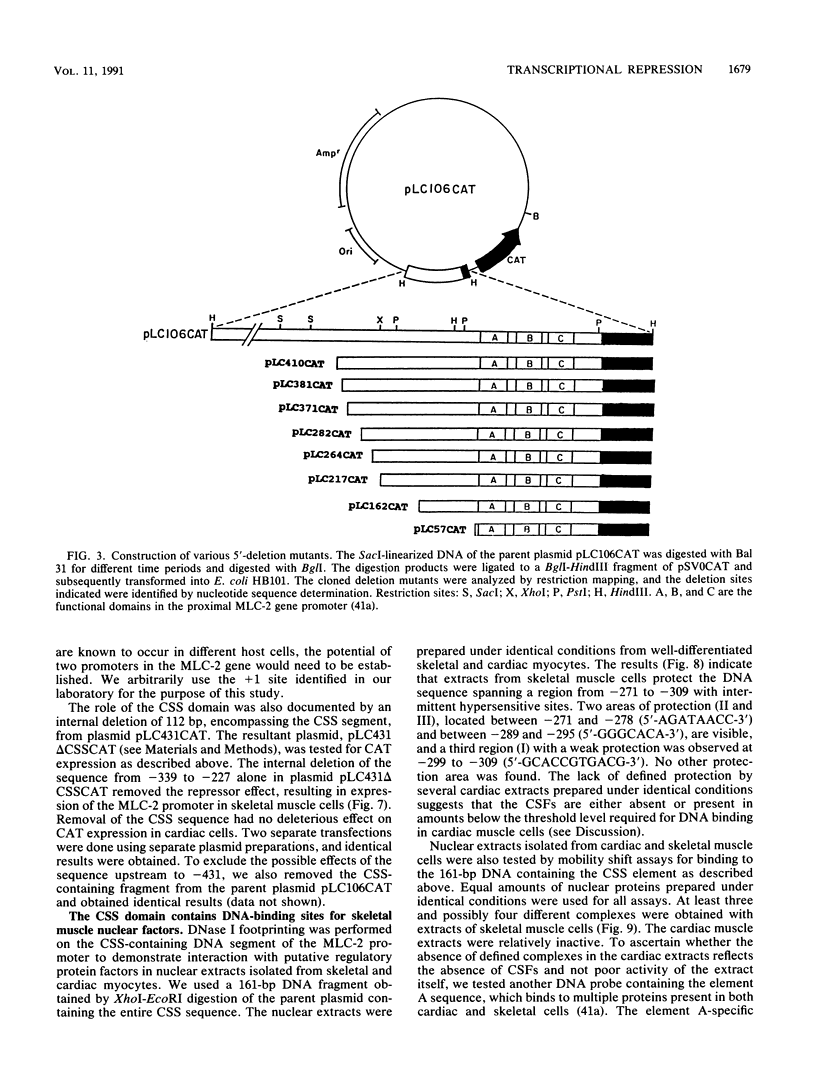
Physiological expression of the cardiac muscle myosin light-chain 2 (MLC-2) gene in chickens is restricted to cardiac muscle tissue only, at least during the late embryonic to adult stages of development. The mechanism by which cardiac MLC-2 gene expression is repressed in differentiated noncardiac muscle tissues is unknown. Using sequential 5'-deletion mutants of the cardiac MLC-2 promoter introduced into primary skeletal muscle cells in culture, we have demonstrated that a 89-bp region, designated the cardiac-specific sequence (CSS), is essential for repression of cardiac MLC-2 expression in skeletal muscle. Removal of the CSS sequence alone allows transcription in skeletal muscle cells without affecting the transcriptional activity of the promoter in cardiac muscle cells. DNase I footprinting and gel shift assays indicate that protein binding to sequences in the CSS domain occurs readily in nuclear extracts obtained from skeletal muscle but not in extracts isolated under identical conditions from cardiac muscle. Thus, it appears that a negative regulatory mechanism accounts for the lack of expression of the cardiac MLC-2 gene in skeletal muscle and that the CSS element and its binding proteins are important functional components of the regulatory apparatus which ensures the developmental program for cardiac tissue-specific gene expression.
Full text
PDF

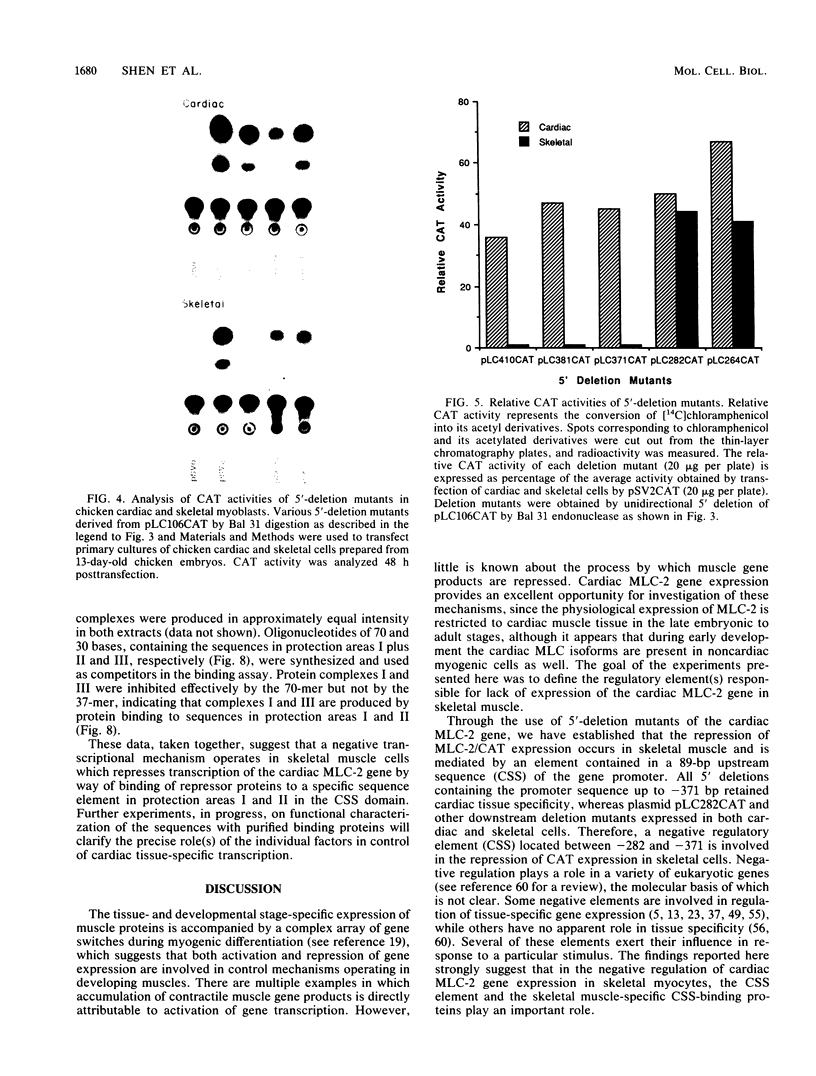
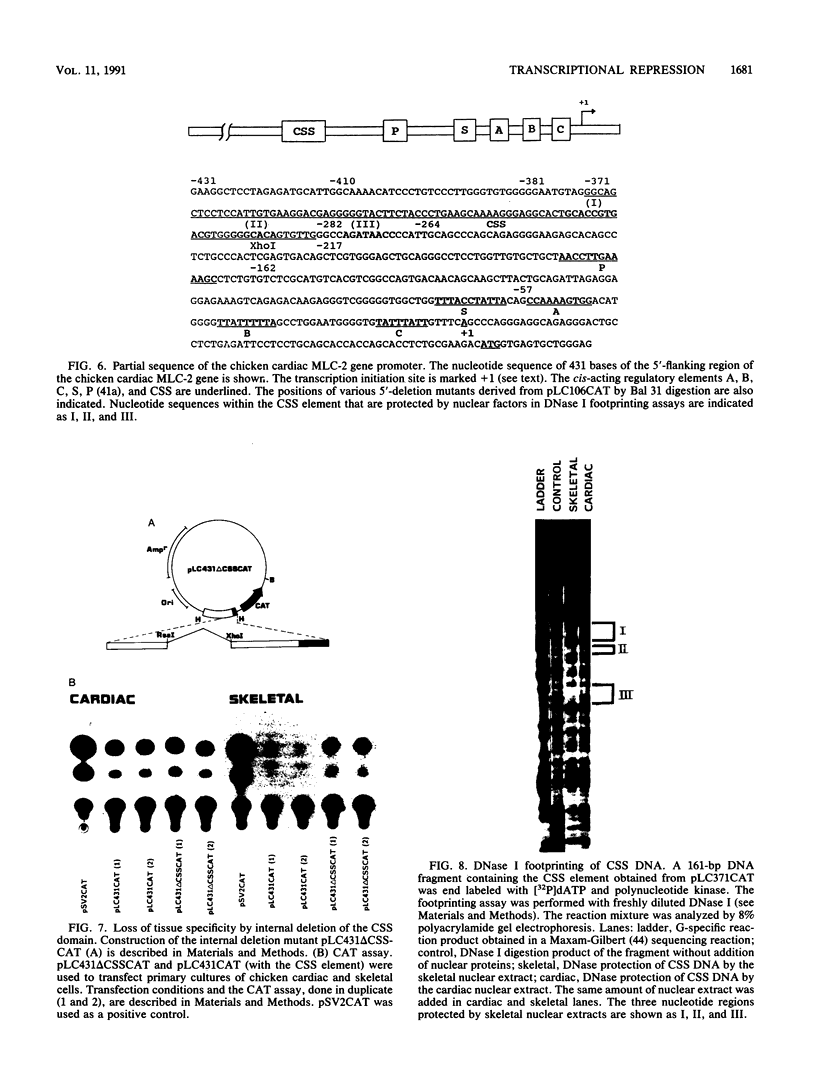




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold H. H., Tannich E., Paterson B. M. The promoter of the chicken cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene shows cell-specific expression in transfected primary cultures of chicken muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2411–2429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bains W., Ponte P., Blau H., Kedes L. Cardiac actin is the major actin gene product in skeletal muscle cell differentiation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1449–1453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Burden S. J. Isolation and characterization of the mouse acetylcholine receptor delta subunit gene: identification of a 148-bp cis-acting region that confers myotube-specific expression. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2271–2279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás T., Peterson C. A., Piatigorsky J. Evidence for positive and negative regulation in the promoter of the chicken delta 1-crystallin gene. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Kohtz S., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H., Kotz S. Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivation by the Myf gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3617–3625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Tannich E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Arnold H. H. Promoter upstream elements of the chicken cardiac myosin light-chain 2-A gene interact with trans-acting regulatory factors for muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2513–2525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher E. A., Maisonpierre P. C., Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Expression of the troponin complex genes: transcriptional coactivation during myoblast differentiation and independent control in heart and skeletal muscles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4134–4142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. L., Schwartz R. J. A combination of closely associated positive and negative cis-acting promoter elements regulates transcription of the skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):528–538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Bernstein S. I. Molecular genetics of myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., Bergsma D. J., Schwartz R. J. Tissue restricted and stage specific transcription is maintained within 411 nucleotides flanking the 5' end of the chicken alpha-skeletal actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1683–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., French B. A., Schwartz R. J. The chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene promoter region exhibits partial dyad symmetry and a capacity to drive bidirectional transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4587–4597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. Interaction of nuclear proteins with muscle-specific regulatory sequences of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4110–4119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardeman E. C., Minty A., Benton-Vosman P., Kedes L., Blau H. M. In vivo system for characterizing clonal variation and tissue-specific gene regulatory factors based on function. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1027–1034. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Spencer M., Sen A., Kumar C., Siddiqui M. A., Chien K. R. Structure, organization, and expression of the rat cardiac myosin light chain-2 gene. Identification of a 250-base pair fragment which confers cardiac-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18142–18148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Benfield P. A. The upstream muscle-specific enhancer of the rat muscle creatine kinase gene is composed of multiple elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2396–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Identification of factors that interact with the E1A-inducible adenovirus E3 promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1132–1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Johnson J. E., Buskin J. N., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D. The muscle creatine kinase gene is regulated by multiple upstream elements, including a muscle-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimes B. W., Brandt B. L. Properties of a clonal muscle cell line from rat heart. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):367–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Complex regulation of the muscle-specific contractile protein (troponin I) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3065–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikovits W., Jr, Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. Muscle-specific activity of the skeletal troponin I promoter requires interaction between upstream regulatory sequences and elements contained within the first transcribed exon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3468–3482. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B. A negative transcriptional control element located upstream of the murine c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidapet C., Khandekar P., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue specificity of 3'-untranslated sequence of myosin light chain gene: unexpected interspecies homology with repetitive DNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguin C., Hamer D. H. Regulation in vitro of metallothionein gene binding factors. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1383–1387. doi: 10.1126/science.3103216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific expression of rat myosin light-chain 2 gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):283–286. doi: 10.1038/314283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Melián A., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene is regulated by multiple positive and negative elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8300–8308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry M. E., Olson E. N. A ras-dependent pathway abolishes activity of a muscle-specific enhancer upstream from the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):594–601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry W. M., Vizard D., Weil T., Olson E. N. Identification of upstream and intragenic regulatory elements that confer cell-type-restricted and differentiation-specific expression on the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2896–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uetsuki T., Nabeshima Y., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Nabeshima Y. Regulation of the chicken embryonic myosin light-chain (L23) gene: existence of a common regulatory element shared by myosin alkali light-chain genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2562–2569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Kline R. L., Konieczny S. F. An internal regulatory element controls troponin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1397–1405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarraga A. M., Danishefsky K., Deshpande A., Nicholson D., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Characterization of 5'-flanking region of heart myosin light chain 2A gene. Structural and functional evidence for promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13852–13860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]