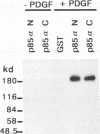
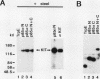
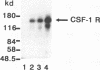
Abstract
The binding of cytoplasmic signaling proteins such as phospholipase C-gamma 1 and Ras GTPase-activating protein to autophosphorylated growth factor receptors is directed by their noncatalytic Src homology region 2 (SH2) domains. The p85 alpha regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase, which associates with several receptor protein-tyrosine kinases, also contains two SH2 domains. Both p85 alpha SH2 domains, when expressed individually as fusion proteins in bacteria, bound stably to the activated beta receptor for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Complex formation required PDGF stimulation and was dependent on receptor tyrosine kinase activity. The bacterial p85 alpha SH2 domains recognized activated beta PDGF receptor which had been immobilized on a filter, indicating that SH2 domains contact autophosphorylated receptors directly. Several receptor tyrosine kinases within the PDGF receptor subfamily, including the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor and the Steel factor receptor (Kit), also associate with PI 3-kinase in vivo. Bacterially expressed SH2 domains derived from the p85 alpha subunit of PI 3-kinase bound in vitro to the activated colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor and to Kit. We infer that the SH2 domains of p85 alpha bind to high-affinity sites on these receptors, whose creation is dependent on receptor autophosphorylation. The SH2 domains of p85 are therefore primarily responsible for the binding of PI 3-kinase to activated growth factor receptors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Lyman S. D., Baird A., Wignall J. M., Eisenman J., Rauch C., March C. J., Boswell H. S., Gimpel S. D., Cosman D. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90304-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Margolis B. L., Zilberstein A., Ashmun R. A., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J., Schlessinger J. Phospholipase C-gamma, a substrate for PDGF receptor kinase, is not phosphorylated on tyrosine during the mitogenic response to CSF-1. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Wang H. C., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. The SH2 and SH3 domains of pp60src direct stable association with tyrosine phosphorylated proteins p130 and p110. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1689–1698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. vav, a novel human oncogene derived from a locus ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2283–2290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor beta subunit creates a tight binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3279–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Riethmüller G., Johnson J. P. Nck, a melanoma cDNA encoding a cytoplasmic protein consisting of the src homology units SH2 and SH3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1048–1048. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Givol D., Yarden Y. A specific combination of substrates is involved in signal transduction by the kit-encoded receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):647–654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Pawson T. The epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylates GTPase-activating protein (GAP) at Tyr-460, adjacent to the GAP SH2 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Polakis P., McCormick F., Pawson T., Ellis C. Protein-tyrosine kinases regulate the phosphorylation, protein interactions, subcellular distribution, and activity of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan S. J., Smith A. D., Parker P. J. Purification and characterization of bovine brain type I phosphatidylinositol kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 17;191(3):761–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Havlik M. H., Maru Y., Witte O. N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X. Q., Pawson T. Interactions of phosphatidylinositol kinase, GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and GAP-associated proteins with the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5601–5608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell V. M., Rohrschneider L. R. Murine c-fms cDNA: cloning, sequence analysis and retroviral expression. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):311–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottapel R., Reedijk M., Williams D. E., Lyman S. D., Anderson D. M., Pawson T., Bernstein A. The Steel/W transduction pathway: kit autophosphorylation and its association with a unique subset of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is induced by the Steel factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3043–3051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Rock C. O., Hawkins S. A., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Structural features of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor that affect its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzman L., Ellis C., Lin L. L., Pawson T., Knopf J. Platelet-derived growth factor increases the in vivo activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phospholipase C-gamma 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2018–2025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J. C., Heidaran M. A., Pierce J. H., Gutkind J. S., Lombardi D., Ruggiero M., Aaronson S. A. Tyrosine mutations within the alpha platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinase insert domain abrogate receptor-associated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity without affecting mitogenic or chemotactic signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3780–3785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]