Abstract
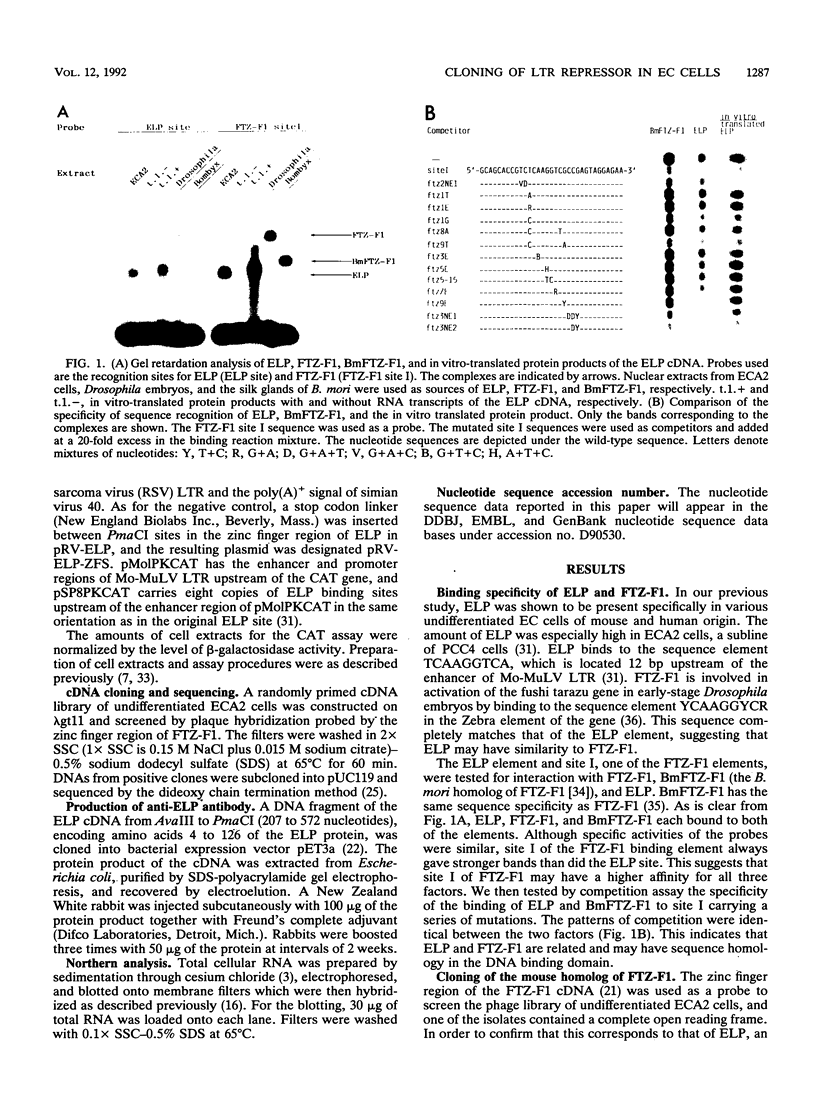
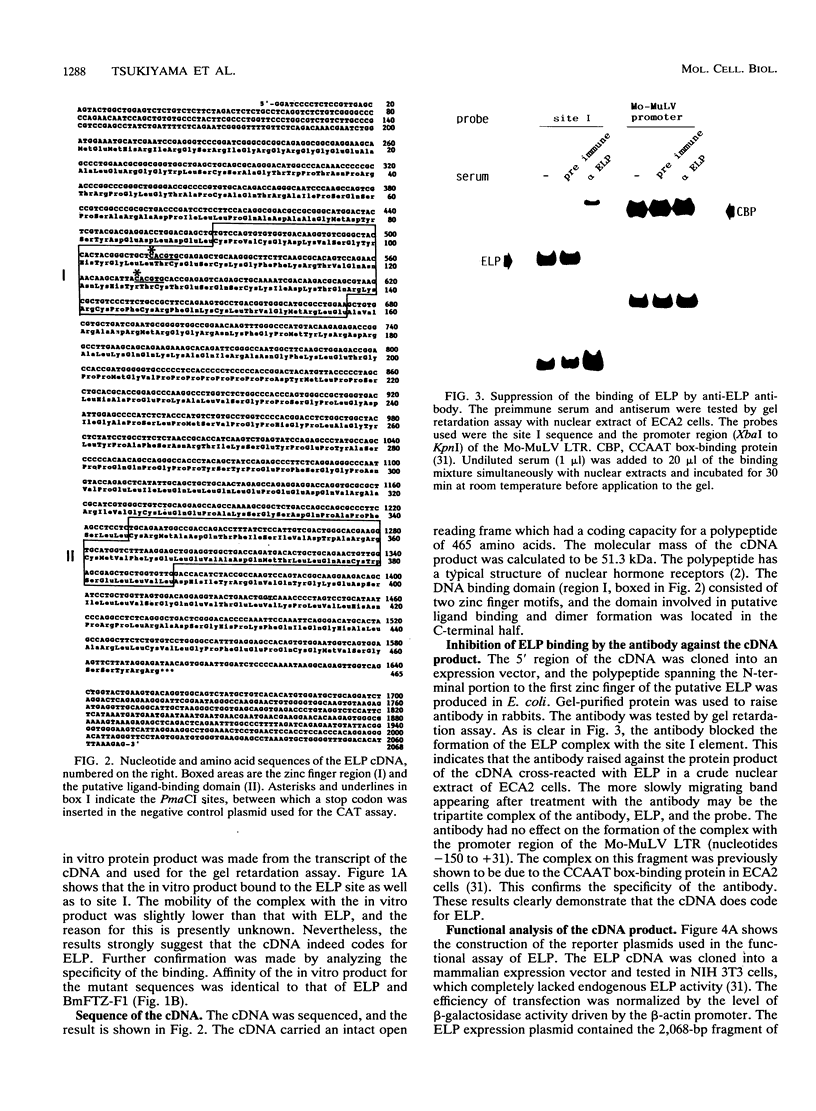
The embryonal long terminal repeat-binding protein, ELP, is present in undifferentiated mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. It binds to and suppresses transcription of the Moloney leukemia virus long terminal repeat in undifferentiated murine embryonal carcinoma cells. We report here that ELP is a mouse homolog of Drosophila FTZ-F1, which positively regulates transcription of the fushi tarazu gene in blastoderm-stage embryos of the fly. As members of the steroid receptor superfamily, ELP and FTZ-F1 have both DNA binding and putative ligand binding domains which are well conserved between the two. ELP and FTZ-F1 function in cells in the extremely early stage of development. A high degree of conservation between the two transcription factors during the evolution of these species indicates the importance of their functions in early-stage embryogenesis. In addition, the sequence elements they recognize do not contain repeat units, in contrast to other steroid receptors, which usually bind to either palindromic or direct repeat sequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Hinck L., Ringold G. M. Two amino acids within the knuckle of the first zinc finger specify DNA response element activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1131–1138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wilson M. C. Delayed de novo methylation in teratocarcinoma suggests additional tissue-specific mechanisms for controlling gene expression. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):32–37. doi: 10.1038/301032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Yang N., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):91–94. doi: 10.1038/331091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Zörnig M., Nowock J., Ziegler M. A single point mutation activates the Moloney murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat in embryonal stem cells. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4691–4698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4691-4698.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilberg F., Stocking C., Ostertag W., Grez M. Functional analysis of a retroviral host-range mutant: altered long terminal repeat sequences allow expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna G., Ueda H., Clos J., Wu C. FTZ-F1, a steroid hormone receptor-like protein implicated in the activation of fushi tarazu. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.1709303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh T. P., Sievert L. L., Scott R. W. Evidence for a stem cell-specific repressor of Moloney murine leukemia virus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4045–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Kumar V., de Verneuil H., Chambon P. Three amino acids of the oestrogen receptor are essential to its ability to distinguish an oestrogen from a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):271–274. doi: 10.1038/338271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima N., Kadowaki Y., Fukushige S., Shimizu S., Semba K., Yamanashi Y., Matsubara K., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Identification of two novel members of erbA superfamily by molecular cloning: the gene products of the two are highly related to each other. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11057–11074. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mélin F., Kemler R., Kress C., Pinon H., Blangy D. Host range specificity of polyomavirus EC mutants in mouse embryonal carcinoma and embryonal stem cells and preimplantation embryos. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3029–3043. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3029-3043.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Yokota Y., Ishida H., Sugahara T. Independent mechanisms involved in suppression of the Moloney leukemia virus genome during differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1105–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H., Shibata R., Sakuragi J., Kiyomasu T., Kawamura M., Hayami M., Ishimoto A., Adachi A. Compatibility of rev gene activity in the four groups of primate lentiviruses. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., Wilson J. D., McPhaul M. J. Characterization and expression of a cDNA encoding the human androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):327–331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Analysis of the binding proteins and activity of the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine leukemia virus during differentiation of mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2979–2986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2979-2986.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Characterization of the negative regulatory element of the 5' noncoding region of Moloney murine leukemia virus in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):772–776. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90547-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Niwa O., Yokoro K. Mechanism of suppression of the long terminal repeat of Moloney leukemia virus in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4670–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Hirose S. Defining the sequence recognized with BmFTZ-F1, a sequence specific DNA binding factor in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, as revealed by direct sequencing of bound oligonucleotides and gel mobility shift competition analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3689–3693. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Hirose S. Identification and purification of a Bombyx mori homologue of FTZ-F1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7229–7234. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Sonoda S., Brown J. L., Scott M. P., Wu C. A sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that activates fushi tarazu segmentation gene expression. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):624–635. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Barklis E., Ostertag W., Jaenisch R. Two distinct sequence elements mediate retroviral gene expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2742–2746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2742-2746.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






