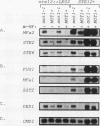
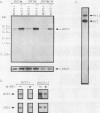
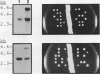
Abstract
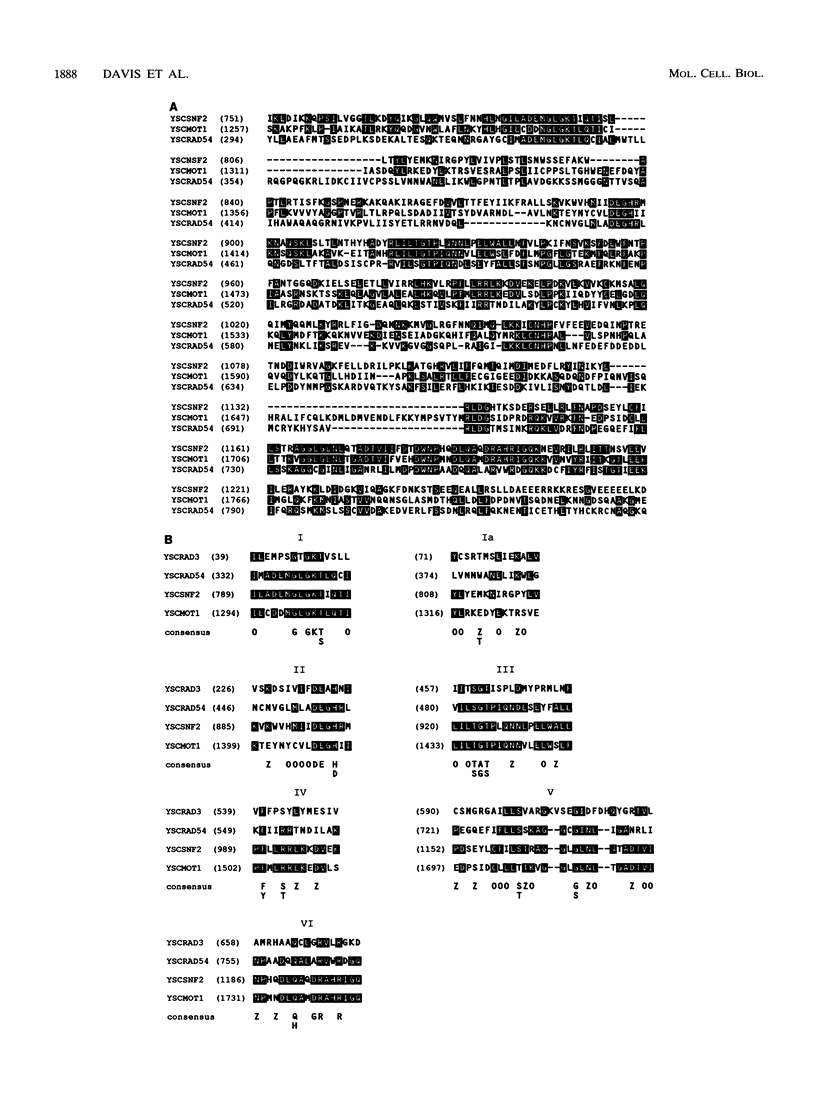
Exposure of a haploid yeast cell to mating pheromone induces transcription of a set of genes. Induction is mediated through a cis-acting DNA sequence found upstream of all pheromone-responsive genes. Although the STE12 gene product binds specifically to this sequence element and is required for maximum levels of both basal and induced transcription, not all pheromone-responsive genes are regulated in an identical manner. To investigate whether additional factors may play a role in transcription of these genes, a genetic screen was used to identify mutants able to express pheromone-responsive genes constitutively in the absence of Ste12. In this way, we identified a recessive, single gene mutation (mot1, for modifier of transcription) which increases the basal level of expression of several, but not all, pheromone-responsive genes. The mot1-1 allele also relaxes the requirement for at least one other class of upstream activating sequence and enhances the expression of another gene not previously thought to be involved in the mating pathway. Cells carrying mot1-1 grow slowly at 30 degrees C and are inviable at 38 degrees C. The MOT1 gene was cloned by complementation of this temperature-sensitive lethality. Construction of a null allele confirmed that MOT1 is an essential gene. MOT1 residues on chromosome XVI and encodes a large protein of 1,867 amino acids which contains all seven of the conserved domains found in known and putative helicases. The product of MOT1 is strikingly homologous to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF2/SW12 and RAD54 gene products over the entire helicase region.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Thach R. E., Merrick W. C. The ATP-dependent interaction of eukaryotic initiation factors with mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3826–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Stillman B. Yeast replication factor-A functions in the unwinding of the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):92–95. doi: 10.1038/342092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Dautricourt J. P., Maulik S., Relph J. Improved sensitivity of biological sequence database searches. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):237–245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Miller R. H. A rapid and convenient method for the preparation and storage of competent bacterial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3580–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N., Urdea M. S., Masiarz F. R., Thorner J. Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene: calmodulin is an essential protein. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. Pheromonal regulation and sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SST2 gene: a model for desensitization to pheromone. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4169–4177. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Fields S. Overproduction of the yeast STE12 protein leads to constitutive transcriptional induction. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Kirkman C., Fields S. The yeast STE12 protein binds to the DNA sequence mediating pheromone induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery H. S., Schild D., Kellogg D. E., Mortimer R. K. Sequence of RAD54, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in recombination and repair. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90473-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Ammerer G. STE12, a protein involved in cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast, is part of protein-DNA complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1349–1361. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estruch F., Carlson M. SNF6 encodes a nuclear protein that is required for expression of many genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2544–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassler J. S., Gray W., Lee J. P., Yu G. Y., Gingerich G. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT14 gene is essential for normal expression of the yeast transposon, Ty, as well as for expression of the HIS4 gene and several genes in the mating pathway. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):310–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00290682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. Regulation by the yeast mating-type locus of STE12, a gene required for cell-type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3818–3821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. The yeast STE12 product is required for expression of two sets of cell-type specific genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. J., Anton I. A., Lane D. P. Nuclear protein with sequence homology to translation initiation factor eIF-4A. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):736–738. doi: 10.1038/332736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A conserved NTP-motif in putative helicases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–22. doi: 10.1038/333022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Induction of the yeast alpha-specific STE3 gene by the peptide pheromone a-factor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):835–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Grunstein M. Nucleosome loss activates yeast downstream promoters in vivo. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Jensen R. E. Putting the HO gene to work: practical uses for mating-type switching. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:132–146. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94011-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kinoshita N., Morikawa K., Yanagida M. Snap helix with knob and hole: essential repeats in S. pombe nuclear protein nuc2+. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90746-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. J., Rahe B., Pringle J., Beggs J. D. A suppressor of a yeast splicing mutation (prp8-1) encodes a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):715–717. doi: 10.1038/349715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Proteinase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1977 Jan;85(1):23–33. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodadek T., Alberts B. M. Stimulation of protein-directed strand exchange by a DNA helicase. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):312–314. doi: 10.1038/326312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Holly J. A., MacKay V. L. A yeast operator overlaps an upstream activation site. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3973–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahaye A., Stahl H., Thines-Sempoux D., Foury F. PIF1: a DNA helicase in yeast mitochondria. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):997–1007. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. Functional interdependence of the yeast SNF2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins in transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Fields F. O., Kunisawa R., Bishop J. M., Thorner J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90360-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Morel-Deville F., Hershey J. W., Leighton T., Schnier J. An eIF-4A-like protein is a suppressor of an Escherichia coli mutant defective in 50S ribosomal subunit assembly. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):496–498. doi: 10.1038/336496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Casadaban M. J., Botstein D. Yeast genes fused to beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli can be expressed normally in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Jensen R., Zoller M. J., Burke J., Errede B., Smith M., Herskowitz I. Structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae HO gene and analysis of its upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4281–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The N-terminal TPR region is the functional domain of SSN6, a nuclear phosphoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4744–4756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boguski M. S., Goebl M., Hieter P. A repeating amino acid motif in CDC23 defines a family of proteins and a new relationship among genes required for mitosis and RNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90745-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Signal transduction in yeast mating: receptors, transcription factors, and the kinase connection. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):393–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler G. L., Thorner J. Molecular cloning of hormone-responsive genes from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1144–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Matson S. W., Prakash S. RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8951–8955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Connelly C., Hieter P. Physical mapping of large DNA by chromosome fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6027–6031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]