Abstract
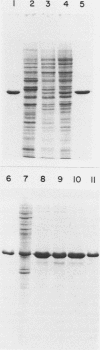
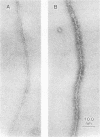
Inhibition of DNase I activity has been used as an assay to purify actin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast actin). The final fraction, obtained after a 300-fold purification, is approximately 97% pure as judged by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis. Like rabbit skeletal muscle actin, yeast actin has a molecular weight of about 43,000, forms 7-nm-diameter filaments when polymerization is induced by KCl or Mg2+, and can be decorated with a proteolytic fragment of muscle myosin (heavy meromyosin). Although heavy meromyosin ATPase activity is stimulated by rabbit muscle and yeast actins to approximately the same Vmax (2 mmol of Pi per min per mumol of heavy meromyosin), half-maximal activation (Kapp) is obtained with 14 micro M muscle actin, but requires approximately 135 micro M yeast actin. This difference suggests a low affinity of yeast actin for muscle myosin. Yeast and muscle filamentous actin respond similarly to cytochalasin and phalloidin, although the drugs have no effect on S. cerevisiae cell growth.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawley S. H., Quatrano R. S. Sulfation of fucoidin in Fucus embryos. IV. Autoradiographic investigations of fucoidin sulfation and secretion during differentiation and the effect of cytochalasin treatment. Dev Biol. 1979 Dec;73(2):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. A highly ordered ring of membrane-associated filaments in budding yeast. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):717–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Lindberg U., Kannan K. K., Cid-Dresdner H., Lövgren S. Crystallization of a non-muscle actin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 15;105(3):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Elzinga M. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Completion and analysis of the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Boyer J. L., Korn E. D. Comparative biochemistry of non-muscle actins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8300–8309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Eisenberg E., Korn E. D. Characterization of cytoplasmic actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii by a new method. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C., Schekman R. Calcium control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae actin assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1279–1286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Zubenko G. S., Hasilik A., Jones E. W. Mutant defective in processing of an enzyme located in the lysosome-like vacuole of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):435–439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock S. E., Carisson L., Lindberg U. Depolymerization of F-actin by deoxyribonuclease I. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. ATP binding to a protease-resistant core of actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koteliansky V. E., Glukhova M. A., Bejanian M. V., Surguchov A. P., Smirnov V. N. Isolation and characterization of actin-like protein from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80927-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Lindberg U. Actin is the naturally occurring inhibitor of deoxyribonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4742–4746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu R. C., Elzinga M. Partial amino acid sequence of brain actin and its homology with muscle actin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5801–5806. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH B. B. The estimation of inorganic phosphate in the presence of adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:357–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90607-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer H. H., Morré D. J. Cytochalasin B, but not colchicine, inhibits migration of secretory vesicles in root tips of maize. Protoplasma. 1976;87(1-3):39–48. doi: 10.1007/BF01623957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T., Huxley H. E. Electron microscope observations on actomyosin and actin preparations from Physarum polycephalum, and on their interaction with heavy meromyosin subfragment I from muscle myosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund R. E., Leung J. T., Kipnis D. M. Muscle actin filaments bind pituitary secretory granules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):78–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees M. K., Young M. Studies on the isolation and molecular properties of homogeneous globular actin. Evidence for a single polypeptide chain structure. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4449–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Lin S. Cytochalasin B, its interaction with actin and actomyosin from muscle (cell movement-microfilaments-rabbit striated muscle). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Schwarz R. P., Jr, Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence that adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis can occur without dissociation of the actomyosin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3895–3909. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Appel P., Morales M. On the molecular weight of myosin. II. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):515–521. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyemura D. G., Brown S. S., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural characterization of actin from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9088–9096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin amino-acid sequences. Comparison of actins from calf thymus, bovine brain, and SV40-transformed mouse 3T3 cells with rabbit skeletal muscle actin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of Physarum actin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):720–721. doi: 10.1038/276720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of actins from bovine aorta, bovine heart, bovine fast skeletal muscle, and rabbit slow skeletal muscle. A protein-chemical analysis of muscle actin differentiation. Differentiation. 1979;14(3):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Water R. D., Pringle J. R., Kleinsmith L. J. Identification of an actin-like protein and of its messenger ribonucleic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1143–1151. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1143-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H. Amatoxins, phallotoxins, phallolysin, and antamanide: the biologically active components of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978 Dec;5(3):185–260. doi: 10.3109/10409237809149870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Wolff J. Cytochalasin B inhibits thyroid secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):422–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90617-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]