Abstract
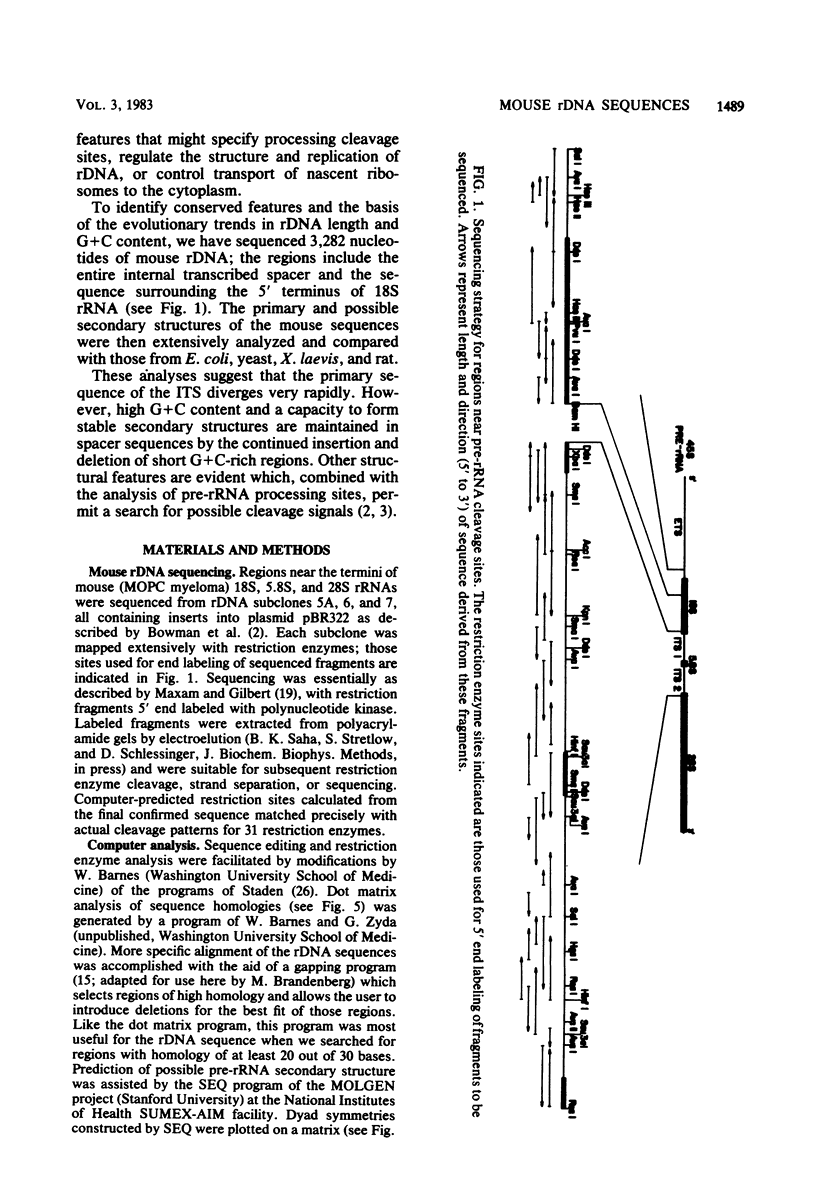
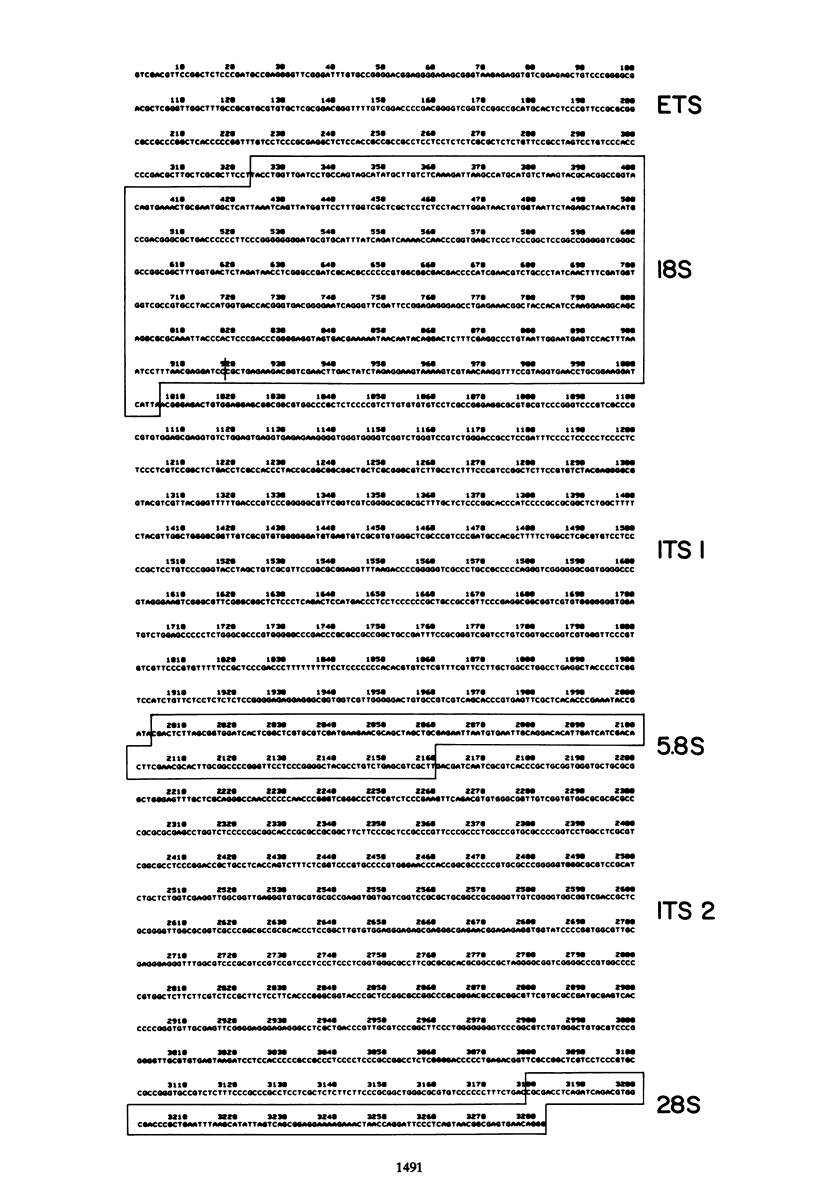
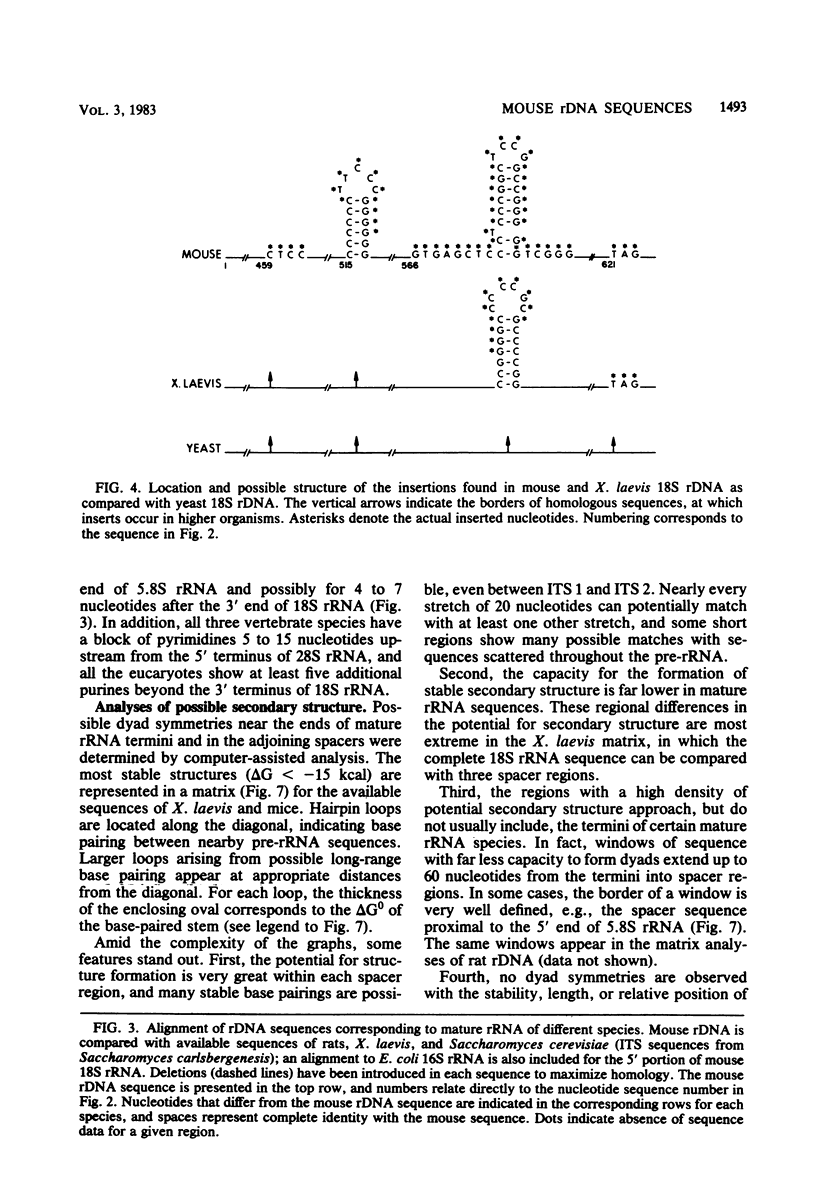
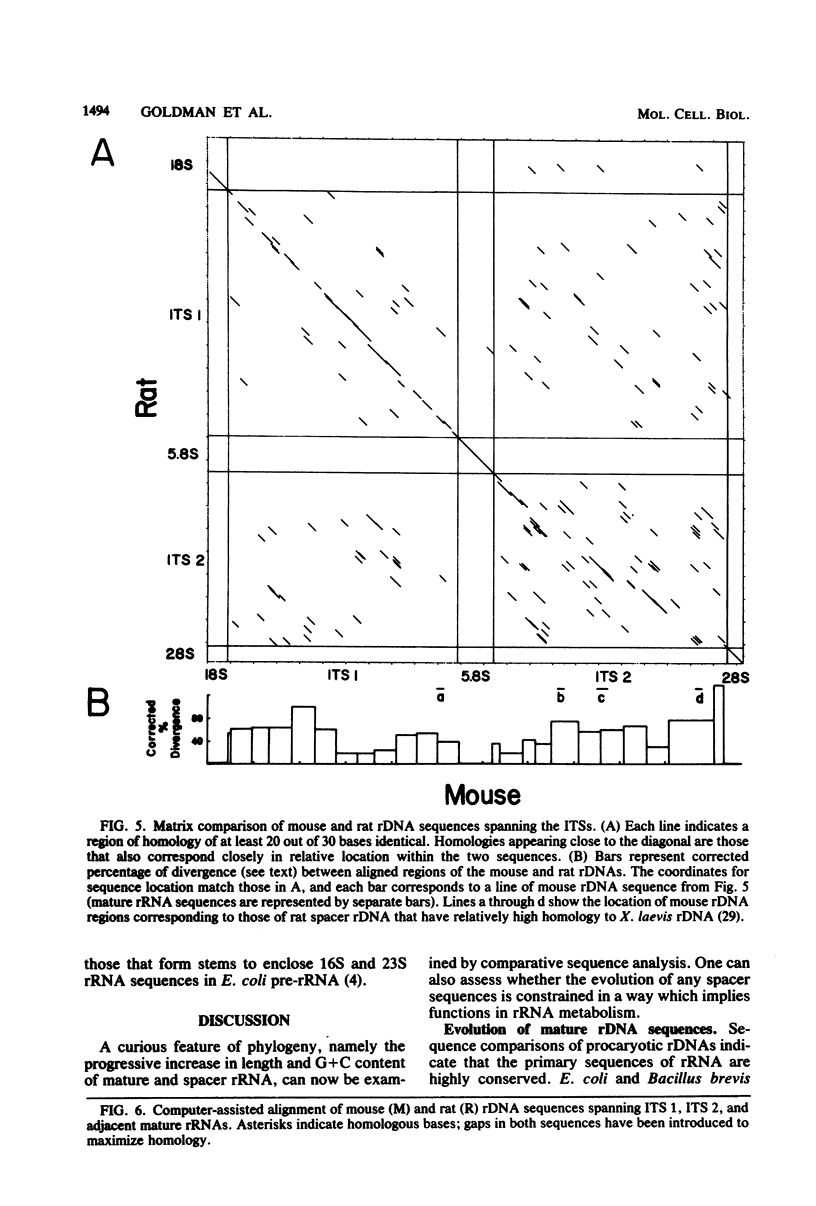
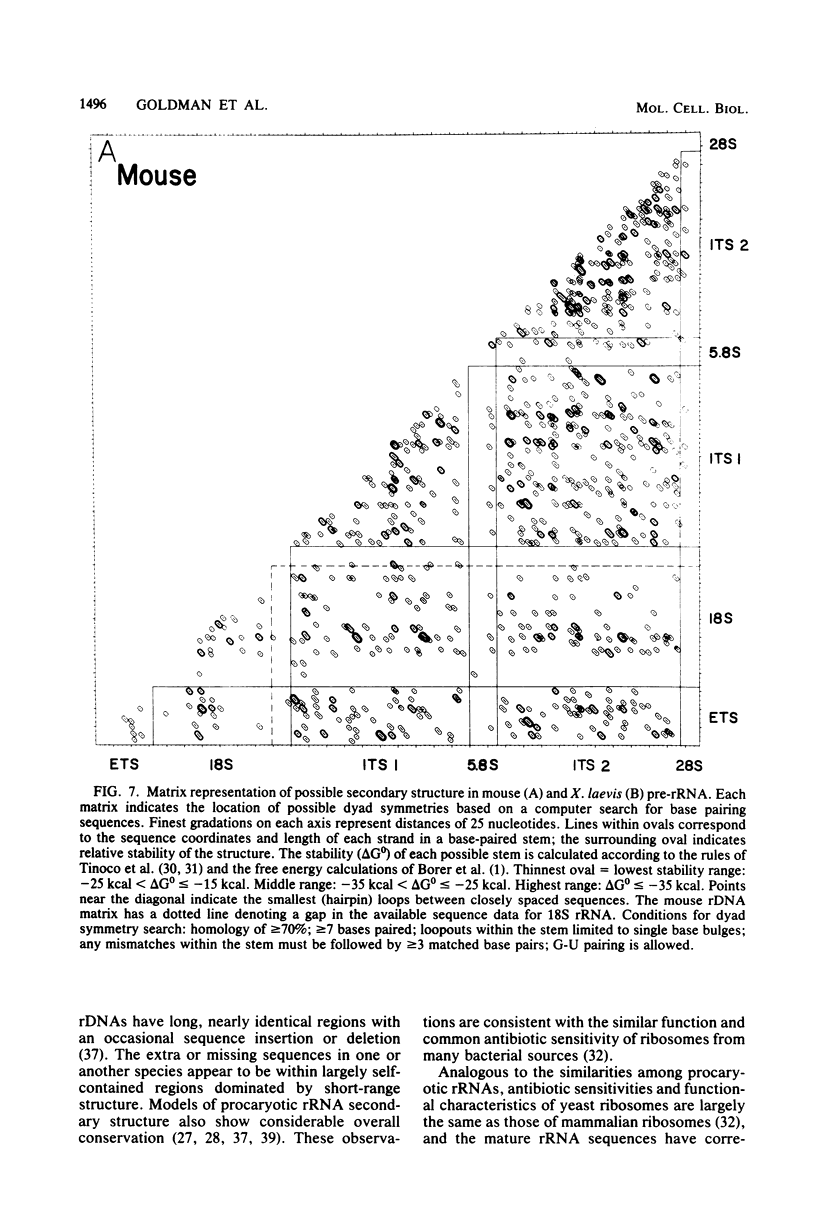
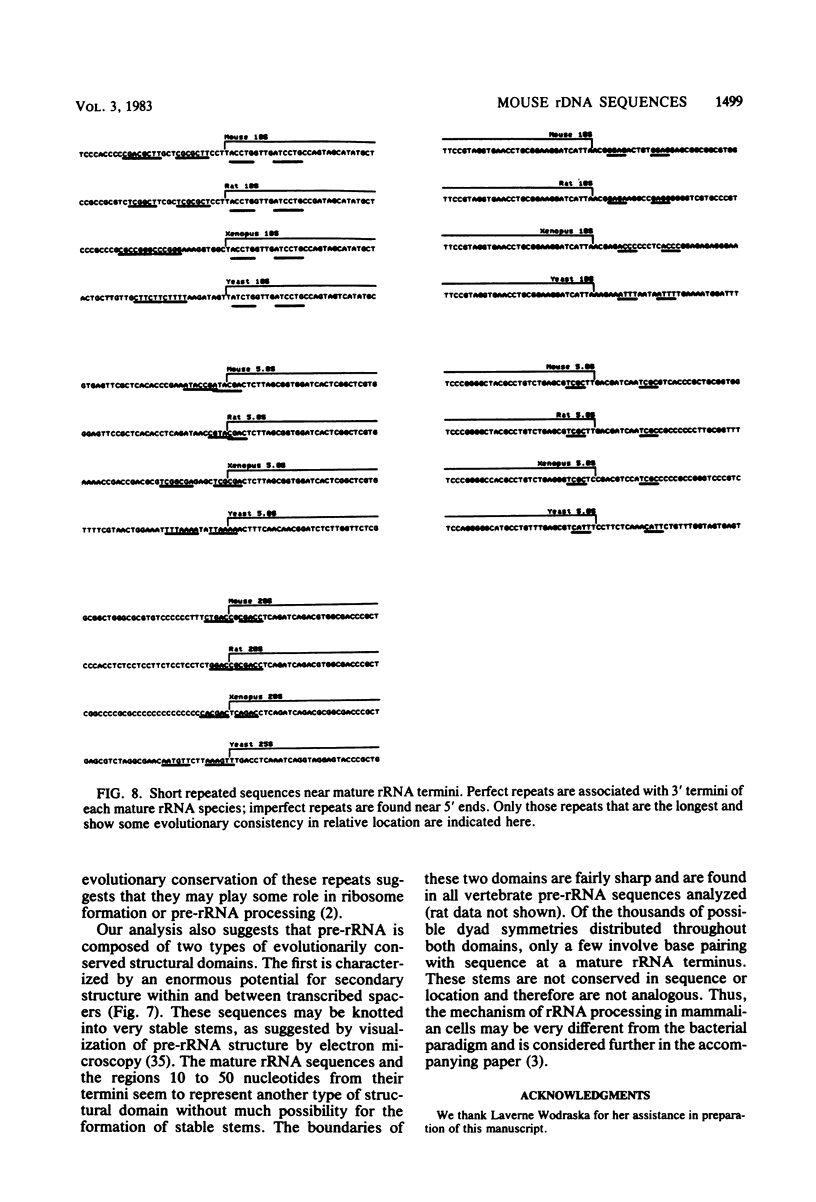
Two regions of mouse rDNA were sequenced. One contained the last 323 nucleotides of the external transcribed spacer and the first 595 nucleotides of 18S rRNA; the other spanned the entire internal transcribed spacer and included the 3' end of 18S rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, and the 5' end of 28S rRNA. The mature rRNA sequences are very highly conserved from yeast to mouse (unit evolutionary period, the time required for a 1% divergence of sequence, was 30 X 10(6) to 100 X 10(6) years). In 18S rRNA, at least some of the evolutionary expansion and increase in G + C content is due to a progressive accretion of discrete G + C-rich insertions. Spacer sequence comparisons between mouse and rat rRNA reveal much more extensive and frequent insertions and substitutions of G + C-rich segments. As a result, spacers conserve overall G + C richness but not sequence (UEP, 0.3 X 10(6) years) or specific base-paired stems. Although no stems analogous to those bracketing 16S and 23S rRNA in Escherichia coli pre-rRNA are evident, certain features of the spacer regions flanking eucaryotic mature rRNAs are conserved and could be involved in rRNA processing or ribosome formation. These conserved regions include some short homologous sequence patterns and closely spaced direct repeats.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borer P. N., Dengler B., Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Goldman W. E., Goldberg G. I., Hebert M. B., Schlessinger D. Location of the initial cleavage sites in mouse pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1501–1510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Rabin B., Schlessinger D. Multiple ribosomal RNA cleavage pathways in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4951–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Subrahmanyan C. S., Rothblum L. I. The nucleotide sequence of the 5' region of rat 18S rDNA and adjoining spacer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1571–1576. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Structure and function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1977;32(3):193–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structures of cytochrome c and the rates of molecular evolution. J Mol Evol. 1971;1(1):26–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01659392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K., Kössel H. The rRNA operon from Zea mays chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of 23S rDNA and its homology with E.coli 23S rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2853–2869. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eladari M. E., Galibert F. Sequence determination of 5'-terminal and 3'-terminal T1 oligonucleotides of 18-S ribosomal RNA of a mouse cell line (L 5178 Y). Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):r29–r44. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.419-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Vanin E. F., Zrolka A. M., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the gene for the constant region of the mu chain of Balb/c mouse immunoglobulin. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Nikolaev N. Maturation of ribosomal ribonucleic acids and the biogenesis of ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1976;31(2):95–144. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(78)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence through the 18S-28S intergene region of a vertebrate ribosomal transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5993–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence encoding the 5' end of Xenopus laevis 18S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2871–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Sequence data handling by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):4037–4051. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Zuker M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Structural organization of the 16S ribosomal RNA from E. coli. Topography and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2153–2172. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Nucleotide sequence of the region between the 18S rRNA sequence and the 28S rRNA sequence of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3667–3680. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiulenev V. I., Masiuk A. I. Nervnaia reguliatsiia sinteza RNK v iadrakh pecheni krys. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1979;247(5):1278–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Brand R. C., Klootwijk J., Planta R. Some characteristics of processing sites in ribosomal precursor RNA of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2907–2920. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. The nucleotide sequence of the intergenic region between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes of the yeast ribosomal RNA operon. Possible implications for the interaction between 5.8S and 26S rRNA and the processing of the primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4847–4862. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA. II. Processing of mouse L-cell ribosomal RNA and variations in the processing pathway. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., Carlson S. S., White T. J. Biochemical evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:573–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



