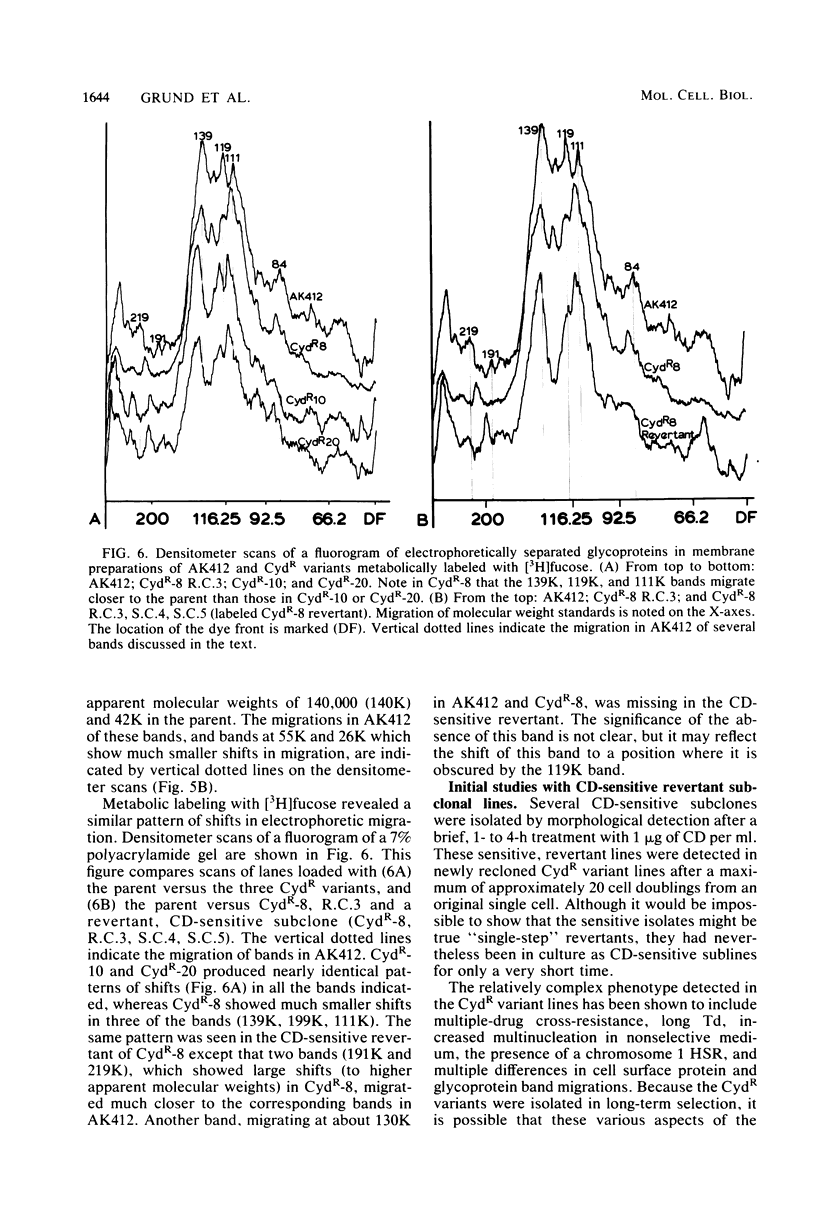
Abstract
An enrichment selection method using repeated pulses of low drug concentration (1 microgram/ml) was used to isolate CHO (AK412) variants that are 20-fold more resistant to cytochalasin D (CD). CD-resistant (CydR) variants possess a unique unstable phenotype, including a longer doubling time in nonselective medium, a higher frequency of multinucleate cells in the population (probably due to a defect in cytokinesis), an altered morphology, and increased resistance or sensitivity to a number of unrelated drugs. In each of two variant lines examined cytologically, this multiple phenotype is associated with a small homogeneously staining region on chromosome 1. The homogeneously staining region is present in the CydR variants, but absent both in the CD-sensitive parent and in a CD-sensitive revertant subpopulation. Studies of CD-displaceable binding of [3H]cytochalasin B show a fourfold reduction in CD binding or uptake when whole cells of the variant line were examined. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination and metabolic labeling with [H3]fucose of cell surface proteins of the CydR variants showed multiple differences in electrophoretic band migration when compared with parental proteins.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban-Malenbaum G., Gilbert F. Double minute chromosomes and the homogeneously staining regions in chromosomes of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Science. 1977 Nov 18;198(4318):739–741. doi: 10.1126/science.71759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin F., Rosenberg R. N., Dev V. Correlation of double-minute chromosomes with unstable multidrug cross-resistance in uptake mutants of neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach L. R., Palmiter R. D. Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium-resistant mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A. The effect of ploidy on chemical mutagenesis in cultured Chinese hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Oct;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debenham P. G., Kartner N., Siminovitch L., Riordan J. R., Ling V. DNA-mediated transfer of multiple drug resistance and plasma membrane glycoprotein expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):881–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godman G. C., Miranda A. F. Cellular contractility and the visible effects of cytochalasin. Front Biol. 1978;46:277–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Schimke R. T. Unstable amplification of an altered dihydrofolate reductase gene associated with double-minute chromosomes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in unstably methotrexate-resistant cells are associated with double minute chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T. Amplification and loss of dihydrofolate reductase genes in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1069–1076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopnin B. P. Specific karyotypic alterations in colchicine-resistant cells. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;30(1):11–14. doi: 10.1159/000131582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Kuzik B. A., Wright J. A. Assay of ribonucleotide reduction in nucleotide-permeable hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Mar;94(3):287–298. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040940306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D. C., Lin S. A rapid assay for actin-associated high-affinity cytochalasin binding sites based on isoelectric precipitation of soluble protein. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):316–322. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90617-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V., Thompson L. H. Reduced permeability in CHO cells as a mechanism of resistance to colchicine. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Feb;83(1):103–116. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters J., Keeley B., Gay H., Attardi G. Variable content of double minute chromosomes is not correlated with degree of phenotype instability in methotrexate-resistant human cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):498–507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melera P. W., Lewis J. A., Biedler J. L., Hession C. Antifolate-resistant Chinese hamster cells. Evidence for dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification among independently derived sublines overproducing different dihydrofolate reductases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):7024–7028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M., Green H. Alterations leading to increased ribonucleotide reductase in cells selected for resistance to deoxynucleosides. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes are localized to a homogeneously staining region of a single chromosome in a methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5553–5556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauw P. G., David J. D. Alterations in surface proteins during myogenesis of a rat myoblast cell line. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Hardeman E. C., Endo A., Simoni R. D. Isolation and characterization of cells resistant to ML236B (compactin) with increased levels of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6762–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Brown P. C., Kaufman R. J., McGrogan M., Slate D. L. Chromosomal and extrachromosomal localization of amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):785–797. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Shows T. B. Genetics of cell fusion: human chromosome 10 assignment of a gene (FUSE) that promotes polykaryocyte formation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jul;5(4):503–517. doi: 10.1007/BF01538884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]