Abstract
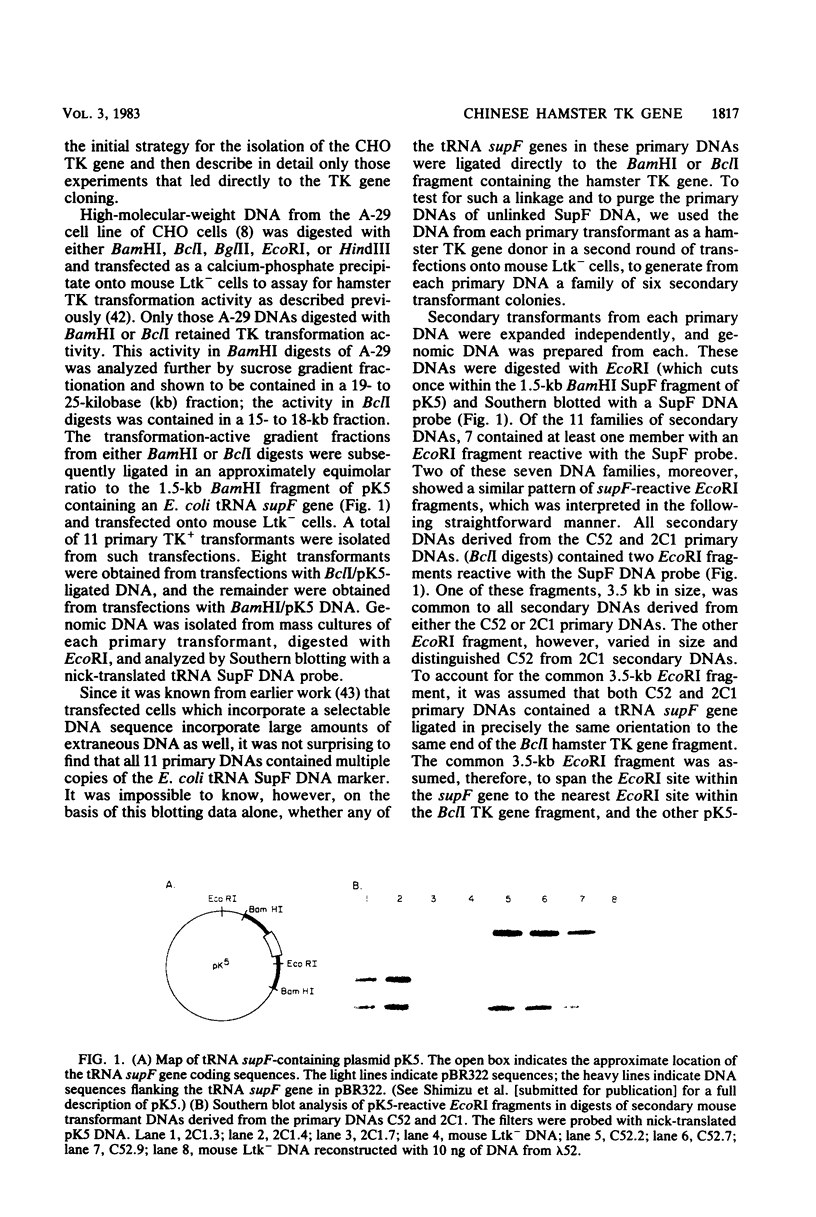
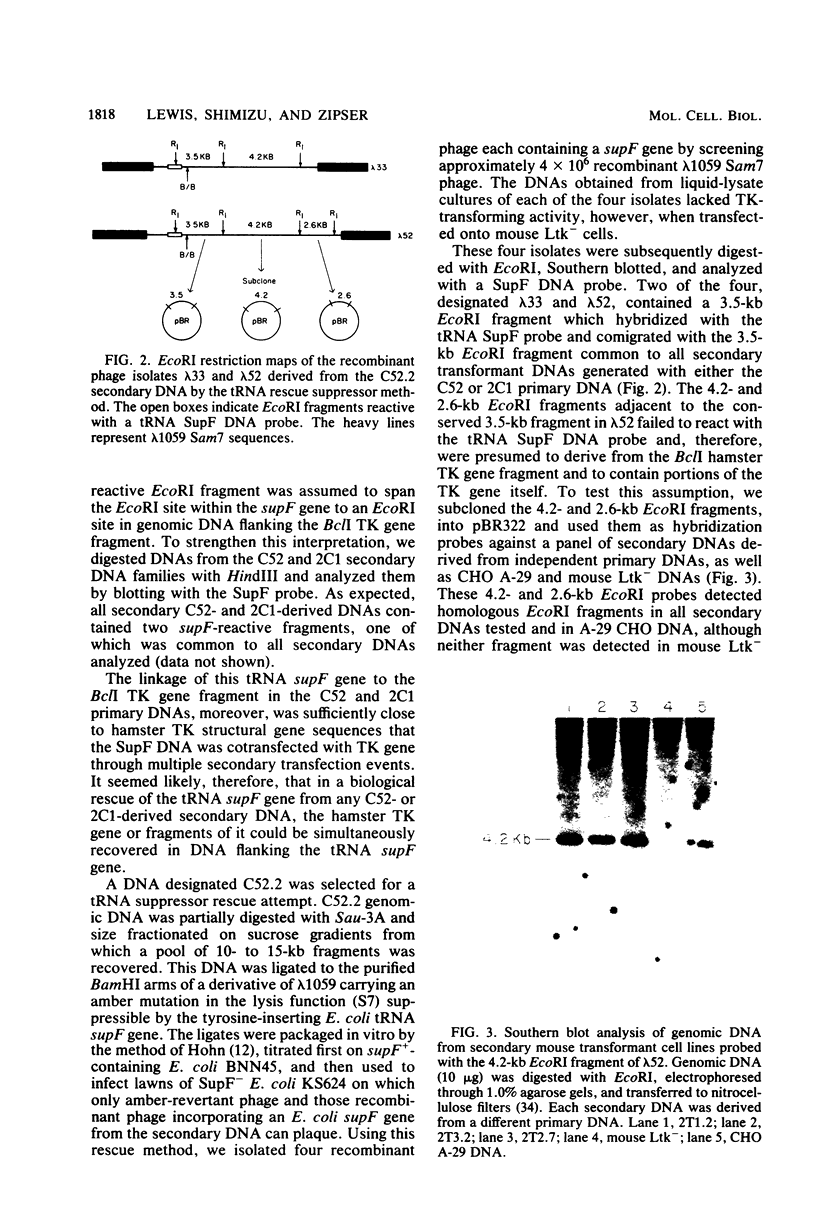
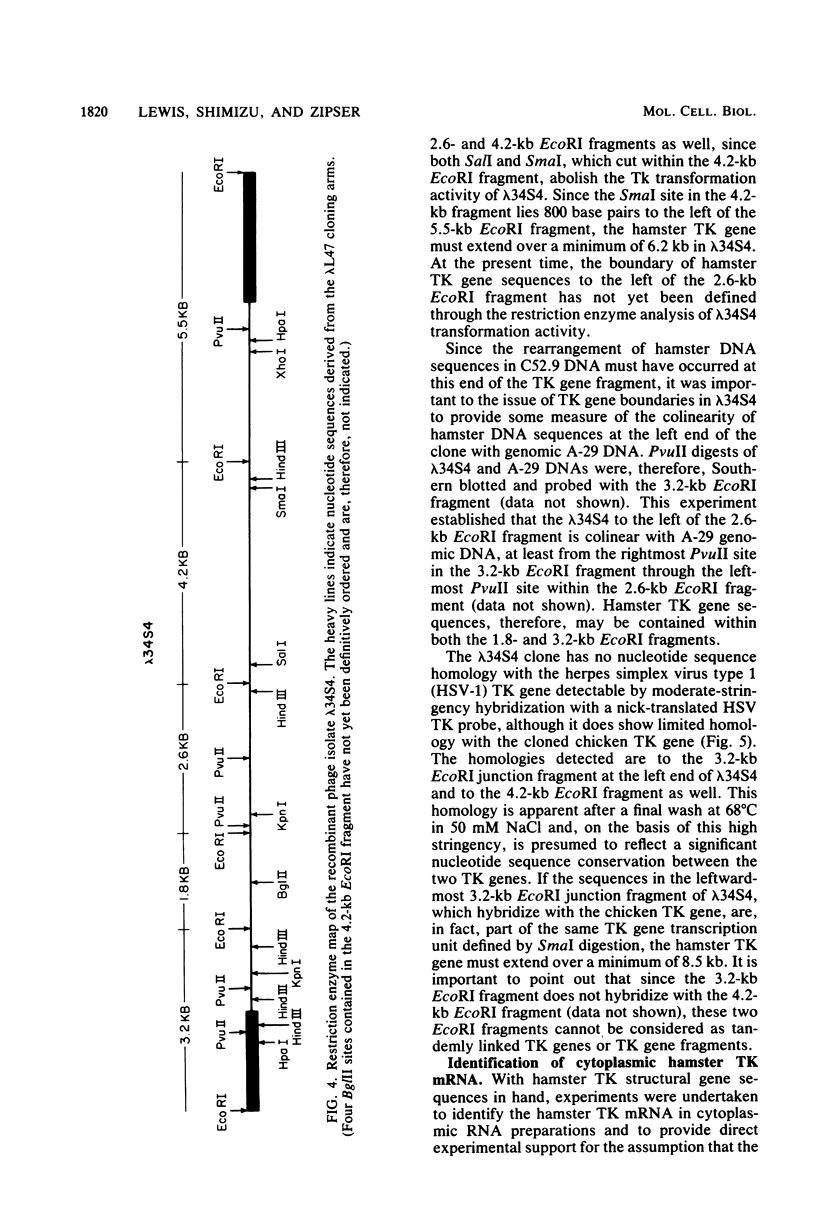
The Chinese hamster thymidine kinase (TK) gene has been isolated from a recombinant phage library constructed with genomic DNA from mouse Ltk- cells transformed to Tk+ by transfection with Chinese hamster genomic DNA. The phage library was screened by the Benton-Davis plaque hybridization technique, using as probes, subclones of recombinant phage that were isolated from mouse Ltk+ transformants by the tRNA suppressor rescue method. The Chinese hamster TK gene is contained within 13.2 kilobases of genomic DNA in the isolate designated lambda 34S4. This gene, defined by restriction enzyme sensitivity experiments, homology studies with the chicken TK gene, and mRNA blotting experiments, may extend over 8.5 kilobases. Subclones of the lambda 34S4 isolate used as hybridization probes identified a 1,400-nucleotide polyadenylated RNA as the hamster TK mRNA. The abundance of this mRNA varies dramatically in Chinese hamster cells cultured under various growth conditions, providing direct evidence that the growth dependence of TK activity may be regulated in an important way at the level of cytoplasmic TK mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOTSMA D., BUDKE L., VOS O. STUDIES ON SYNCHRONOUS DIVISION OF TISSUE CULTURE CELLS INITIATED BY EXCESS THYMIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:301–309. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent T. P., Butler J. A., Crathorn A. R. Variations in phosphokinase activities during the cell cycle in synchronous populations of HeLa cells. Nature. 1965 Jul 10;207(993):176–177. doi: 10.1038/207176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKER P. ACTIVITIES OF THYMIDINE KINASE AND THYMINE DEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATASE DURING GROWTH OF CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2607–2611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flintoff W. F., Davidson S. V., Siminovitch L. Isolation and partial characterization of three methotrexate-resistant phenotypes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):245–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01538963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudewicz T. M., Morhenn V. B., Kellems R. E. The effect of polyoma virus, serum factors, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP on dihydrofolate reductase synthesis, and the entry of quiescent cells into S phase. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jul;108(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Induction of thymidine kinase in enzyme-deficient Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson S. L., Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA metabolism in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Bonner J. Preparation, molecular weight, base composition, and secondary structure of giant nuclear ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2330–2338. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Fuhrman C. L., Wiedemann L. M. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression in mouse fibroblasts during the transition from the resting to growing state. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):397–306. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Rao L. G., Muench A. J. Regulation of thymidine kinase enzyme level in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., FREARSON P. M. DECLINE OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY IN STATIONARY PHASE MOUSE FIBROBLAST CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2565–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Jorgensen G. N. Formation of thymidine kinase and deoxycytidylate deaminase in synchronized cultures of chinese hamster cells temperature-sensitive for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. STUDIES ON THYMIDINE KINASE IN CULTURED MOUSE FIBROBLASTS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:14–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Kurtz D. T., Melera P. W. Molecular cloning of Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase-specific cDNA and the identification of multiple dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs in antifolate-resistant Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1311–1322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys E. J., Kellems R. E. Control of dihydrofolate reductase messenger ribonucleic acid production. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):961–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Yamaizumi M., Murphy P. D., Egg A., Ruddle F. H. Partial purification and characterization of the mRNA for human thymidine kinase and hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield J. W. The periodic synthesis of thymidine kinase in mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Slate D. L., Schimke R. T. S phase-specific synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4985–4989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittermayer C., Bosselmann R., Bremerskov V. Initiation of DNA synthesis in a system of synchronized L-cells: rhythmicity of thymidine kinase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):487–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalgund L. G., Rossana C., Muench A. J., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7386–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Levine A. J. Studies on the regulation of deoxypyrimidine kinases in normal, SV40-transformed and SV40- and adenovirus-infected mouse cells in culture. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):404–420. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosser C. A., Steglich C., deWet J. R., Scheffler I. E. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of thymidine kinase activity introduced into mouse LMTK- cells by DNA and chromatin-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Gallimore P. H., Flint S. J. Mapping of adenovirus 2 RNA sequences in lytically infected cells and transformed cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):457–474. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Mueller G. C. Thymidine kinase activity in synchronized HeLa cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Growth and nucleic acid synthesis in synchronously dividing populations of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Apr;30:344–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Oskarsson M., Enquist L. W., Nomura S., Sullivan M., Fischinger P. J. Cloning of integrated Moloney sarcoma proviral DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Johnson L. F. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase synthesis in an overproducing 3T6 cell line during transition from resting to growing state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2818–2822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase gene transcription in methotrexate-resistant mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):183–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- XEROS N. Deoxyriboside control and synchronization of mitosis. Nature. 1962 May 19;194:682–683. doi: 10.1038/194682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]