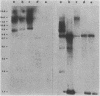
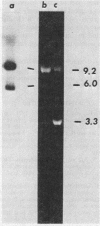
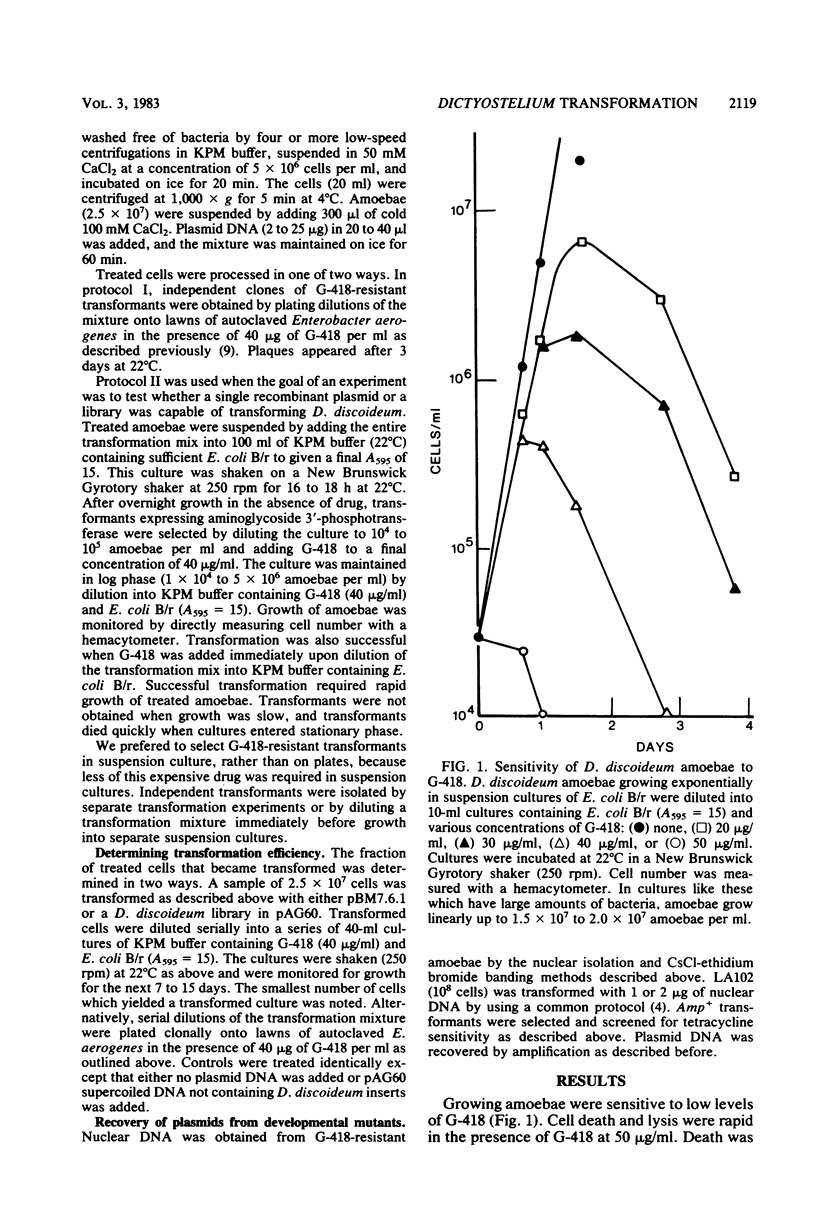
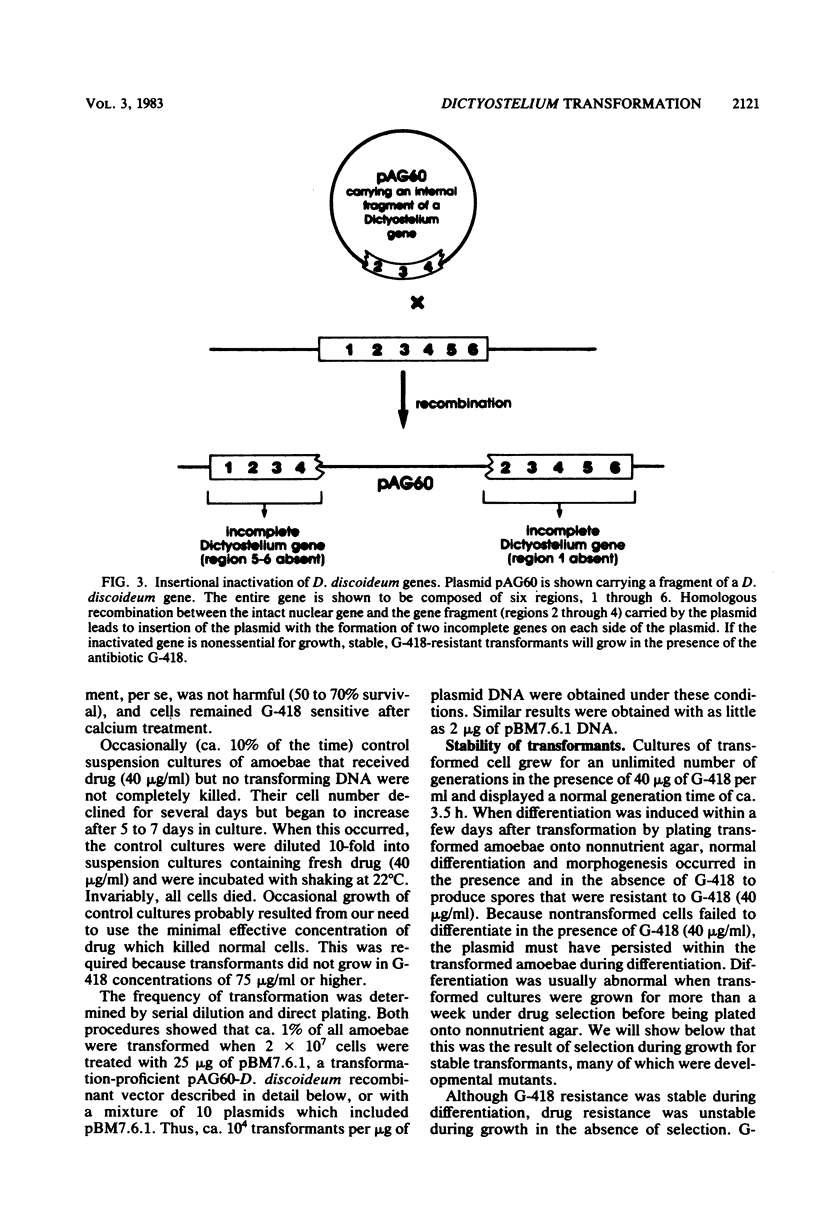
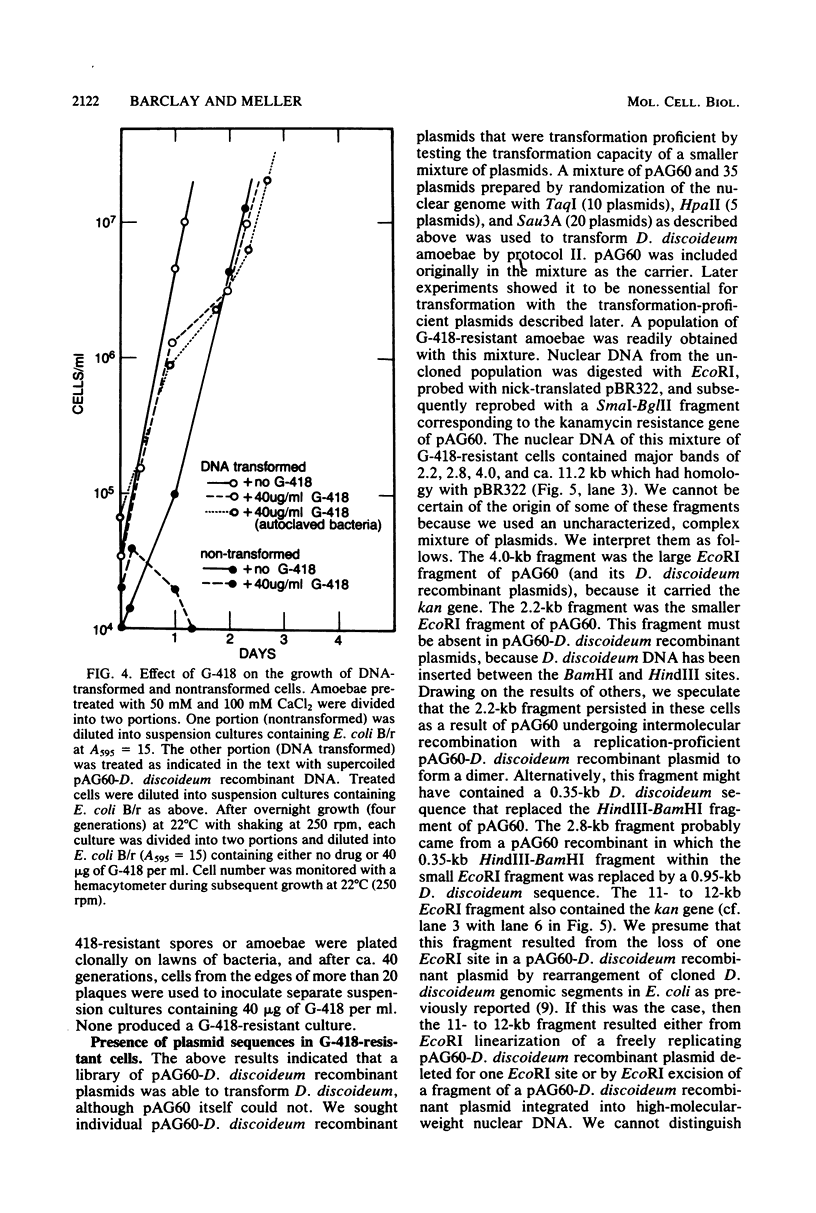
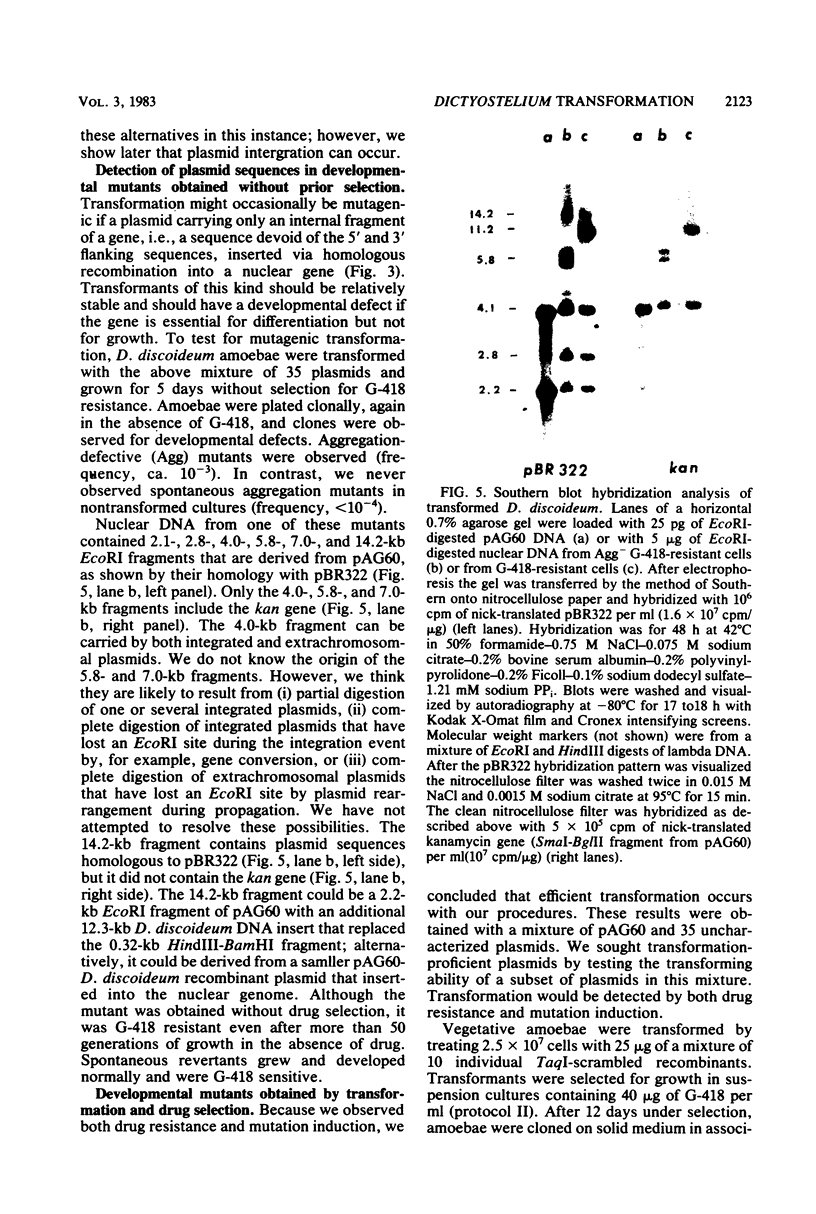
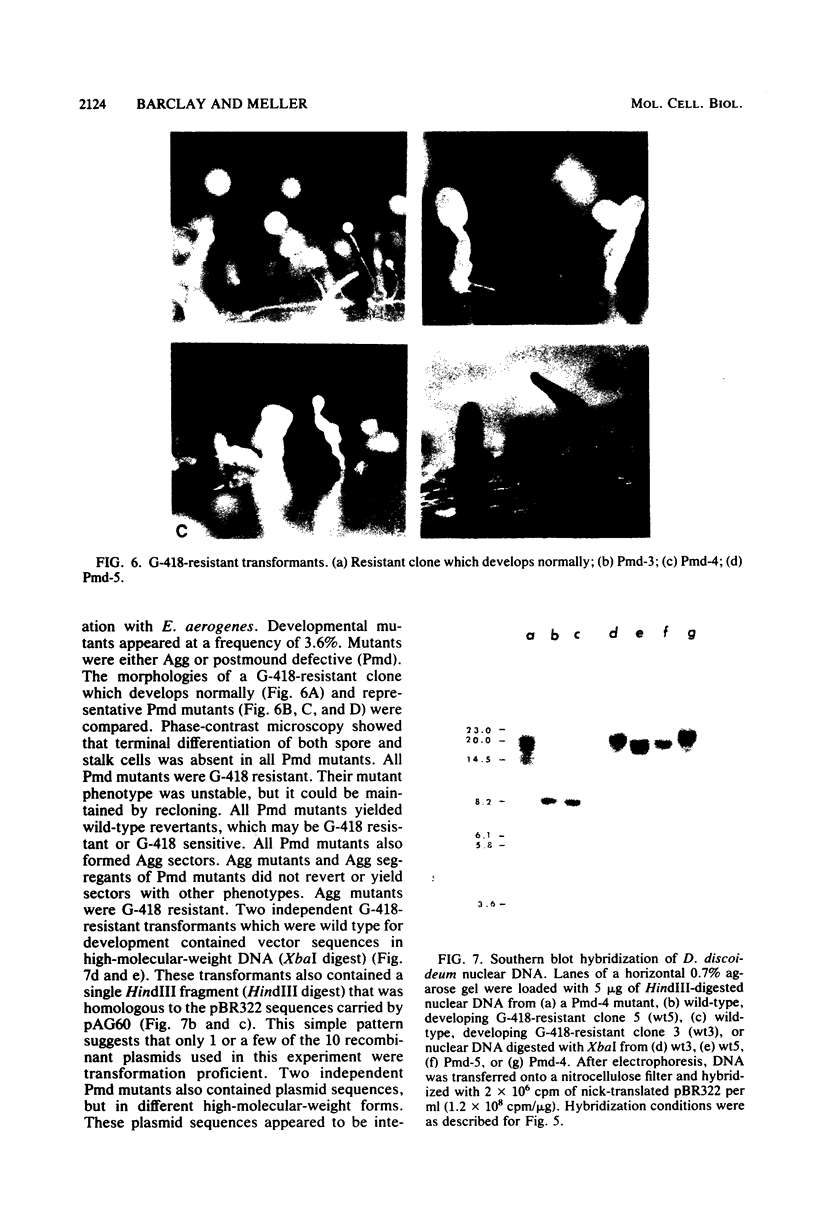
Abstract
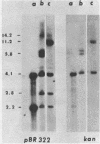
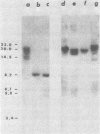
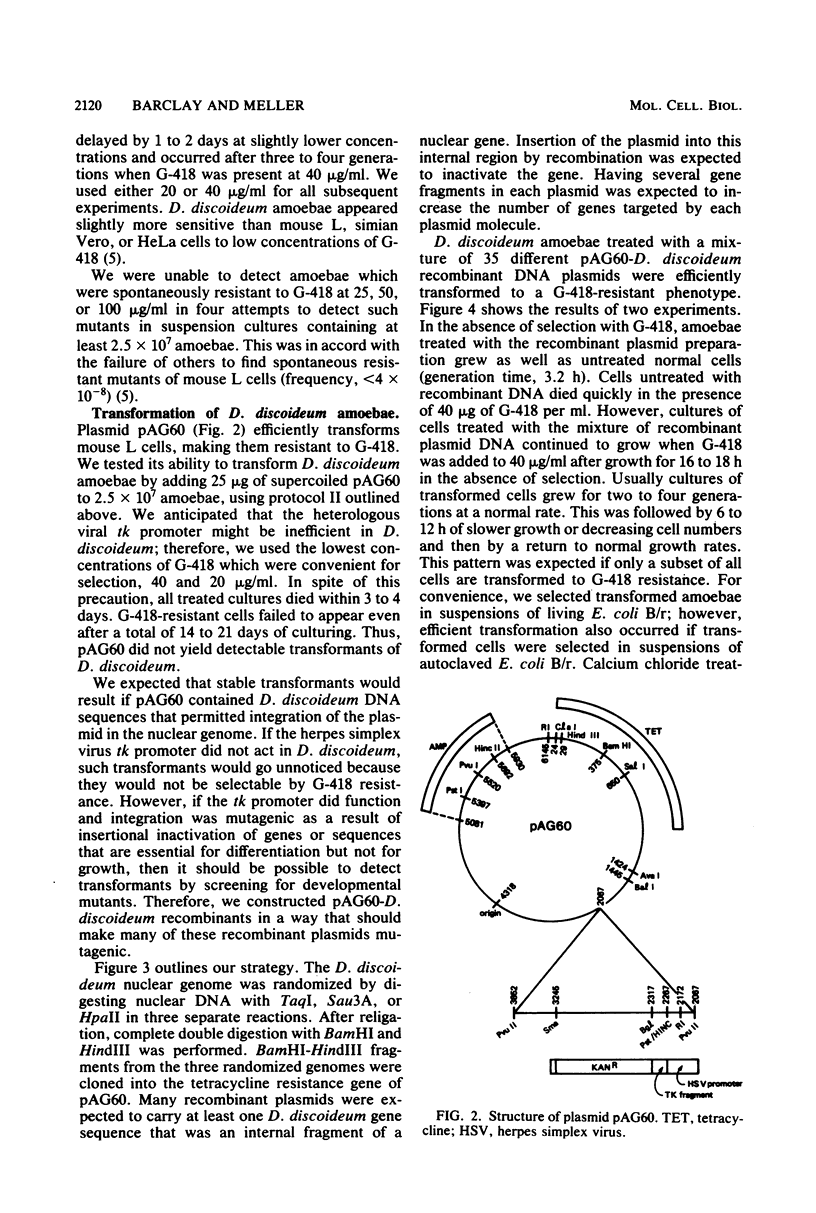
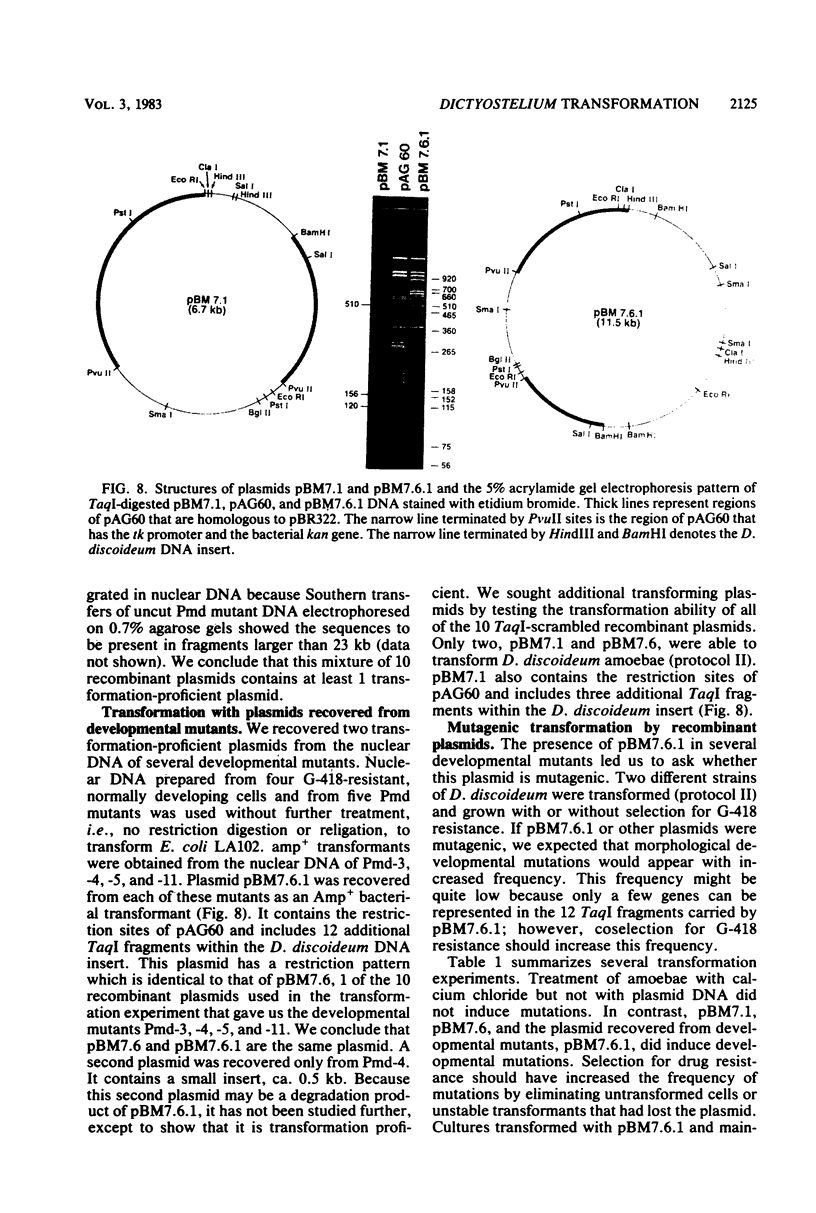
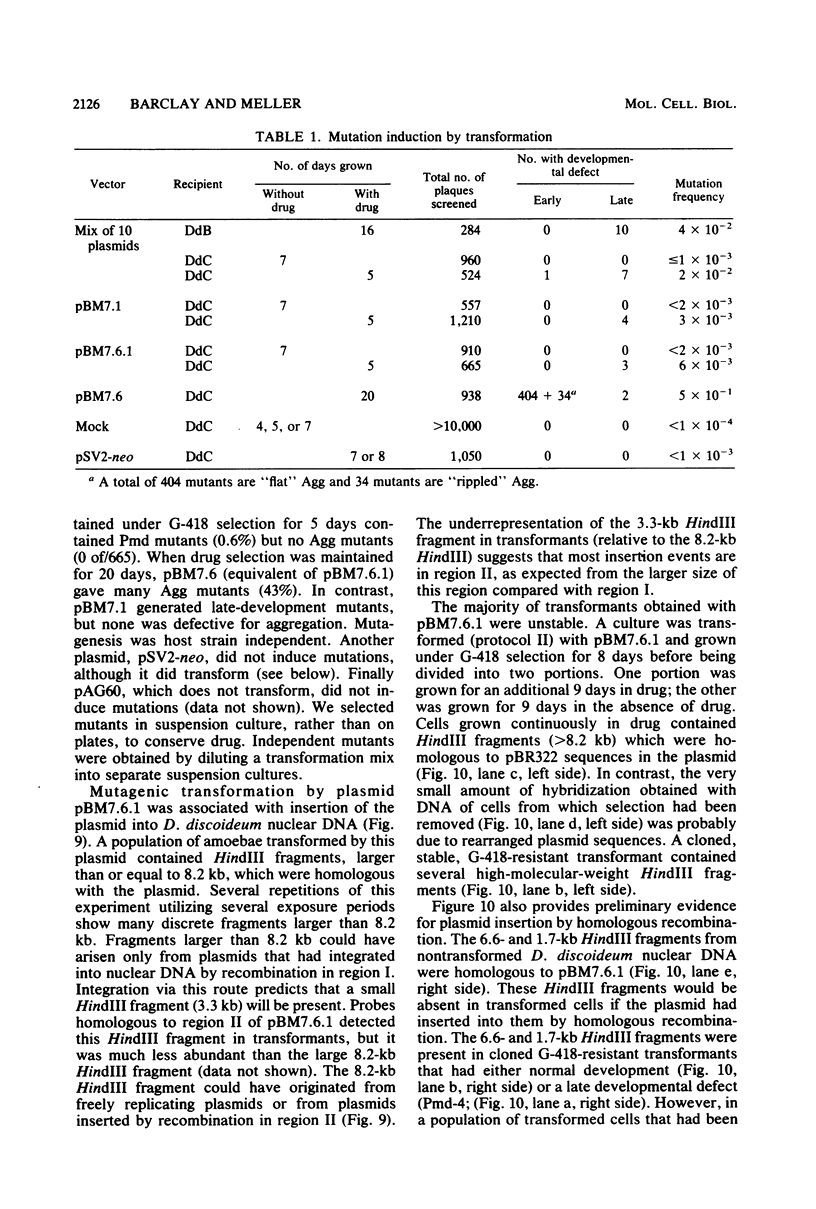
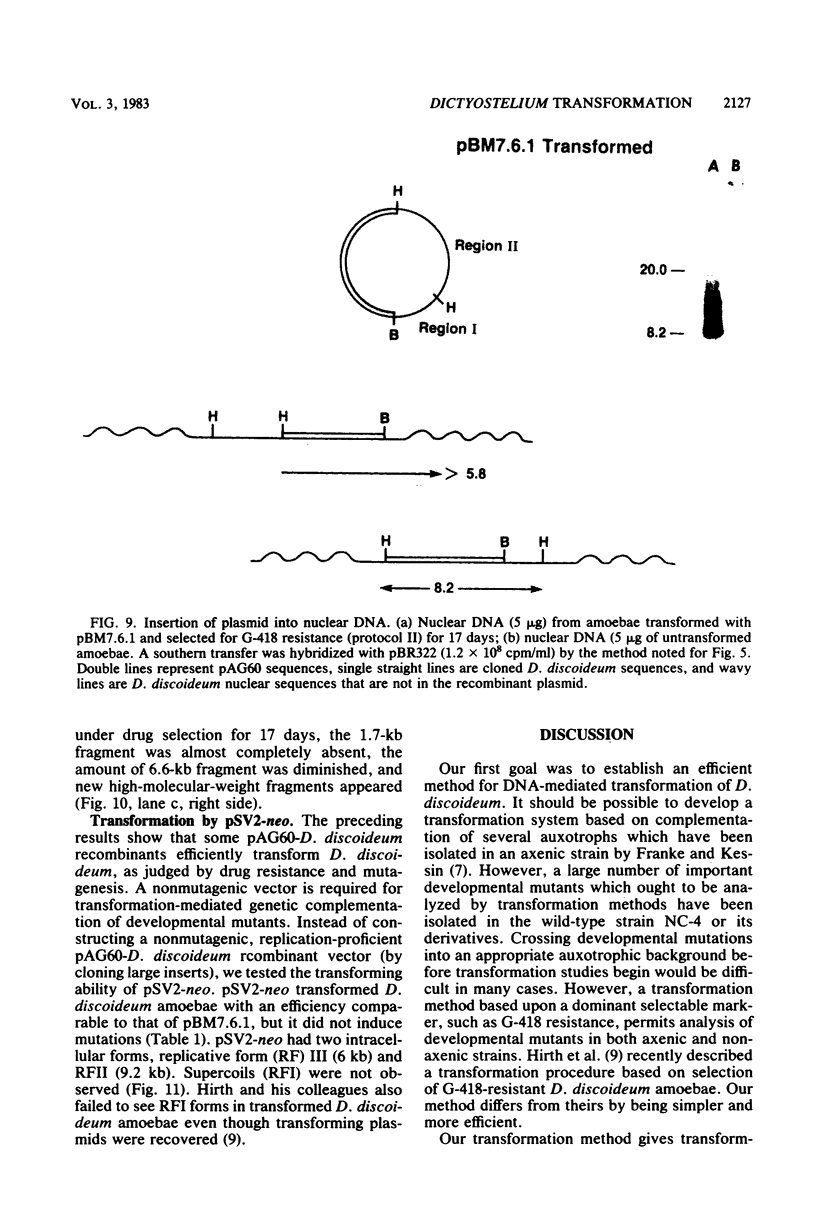
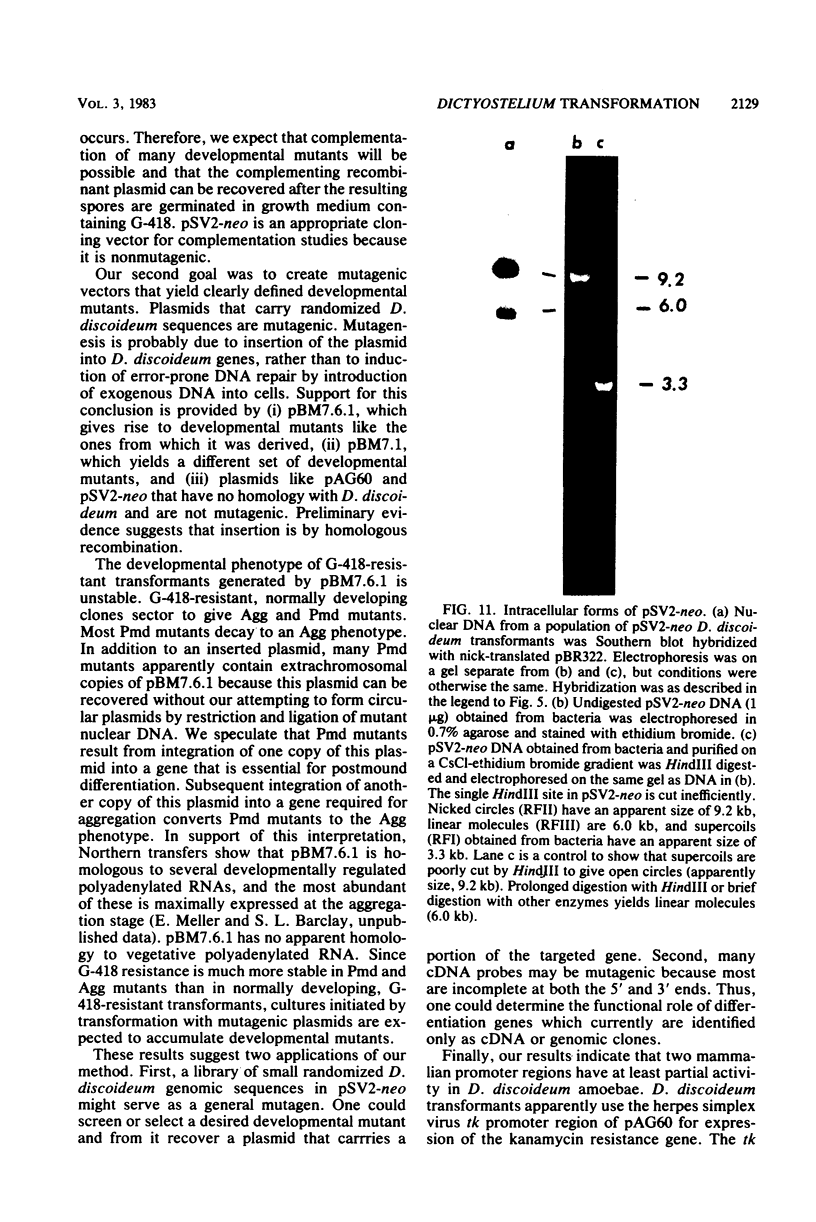
We have transformed Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae by using derivatives of a plasmid, pAG60, which was designed for transformation of mammalian cells. The plasmid carries the promoter region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene linked to the bacterial gene kan, which codes for the enzyme aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase. kan is derived from the Tn5 transposon. Expression of the phosphotransferase permits direct selection of transformed cells by their resistance to the antibiotic G-418. pAG60 is incapable of transforming D. discoideum but is made transformation proficient by cloning D. discoideum sequences into the tetracycline resistance gene. The majority of transformed cells grow and develop normally and differentiate to give G-418-resistant spores. These transformants are unstable and rapidly lose their G-418-resistance during growth in the absence of antibiotic selection. Southern blots show that these unstable G-418-resistant transformants carry the pBR322 and kan sequences of pAG60. The pAG60-D. discoideum recombinant plasmids used for transformation were constructed in a way that might make them mutagenic. We have isolated several developmental mutants after transformation of D. discoideum with libraries of pAG60-D. discoideum recombinant plasmids. These mutants are G-418 resistant and carry pAG60 in their nuclear DNA. We recovered a pAG60-D. discoideum recombinant plasmid from several developmental mutants. This plasmid transforms D. discoideum at an elevated frequency and integrates into the nuclear genome. We speculate that integration can result in insertional inactivation of genes that are essential for differentiation but not for growth. Mutagenic transformation occurred only if the transforming plasmid had homology with D. discoideum nuclear DNA. A mammalian cell transformation vector, pSV2-neo, carried no D. discoideum sequences and was able to transform. However, pSV2-neo transformation was not mutagenic. These results suggest that direct inactivation and recovery of genes that are essential for differentiation of D. discoideum will be possible.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Developmental changes in messenger RNAs and protein synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):180–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Translational control of protein synthesis during the early stages of differentiation of the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay S. L., Henderson E. J. Thermosensitive development and tip regulation in a mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Changes in the expression of single-copy DNA during development of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):363–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90420-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. Auxotrophic mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):537–538. doi: 10.1038/272537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirth K. P., Edwards C. A., Firtel R. A. A DNA-mediated transformation system for Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez A., Davies J. Expression of a transposable antibiotic resistance element in Saccharomyces. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):869–871. doi: 10.1038/287869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss G. B., Pearlman R. E., Cornish K. V., Friesen J. D., Chan V. L. The herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene is not transcribed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):542–547. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.542-547.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacWilliams H. K., Bonner J. T. The prestalk-prespore pattern in cellular slime molds. Differentiation. 1979;14(1-2):1–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Chung S., Zuker C., Lodish H. F. Selection and analysis of cloned developmentally-regulated Dictyostelium discoideum genes by hybridization-competition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):947–963. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Kutter E., Nakanishi M. A restriction map of the bacteriophage T4 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):421–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00425473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel C., Marchal C., Louise A., Fritsch A., Tiollais P. Bacteriophage lambda-E. coli K12 vector-host system for gene cloning and expression under lactose promoter control: I. DNA fragment insertion at the lacZ EcoRI restriction site. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 26;170(2):161–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00337792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Firtel R. A. Isolation of developmentally regulated genes from Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Lloyd M. M. Changes in the abundance of polyadenylated RNA during slime mould development measured using cloned molecular hybridization probes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):19–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]