Abstract
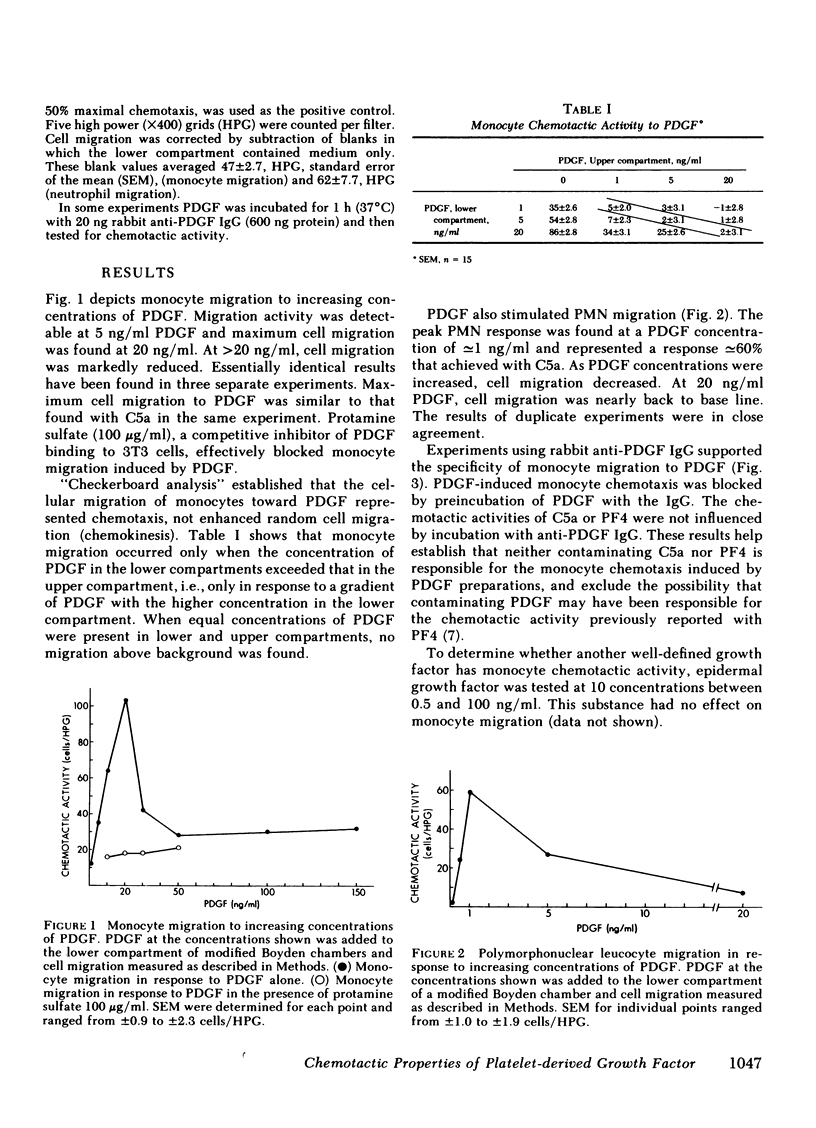
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is shown to be chemotactic for monocytes and neutrophils. Maximum monocyte chemotaxis to PDGF is fully equal to that achieved with C5a and occurs at congruent to 20 ng/ml (congruent to 0.7 nM). Maximum neutrophil chemotaxis is congruent to 60% that achieved with C5A but occurs at congruent to 1 ng/ml (congruent to 32 pM). The chemotactic activity of PDGF is blocked by specific antisera to PDGF and by protamine sulfate, a competitive inhibitor of PDGF binding to cell surfaces. In contrast to PDGF, epidermal growth factor shows no chemotactic activity for inflammatory cells at 0.5-100 ng/ml. The high level of chemotactic activity of PDGF suggests that in addition to its role as a mitogen for smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts, PDGF may be involved in attracting inflammatory cells to sites of platelet release.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braunstein P. W., Cuénoud H. F., Joris I., Majno G. Platelets, fibroblasts, and inflammation: tissue reactions to platelets injected subcutaneously. Am J Pathol. 1980 Apr;99(1):53–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Proffitt R. T., Baenziger J. U., Chang D., Kennedy B. B. Human platelet-derived growth factor. Purification and resolution into two active protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8896–8899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Keim P. S., Farmer M., Heinrikson R. L. Amino acid sequence of human platelet factor 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2256–2258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Chang D., Griffin G. L., Heinrikson R. L., Kaiser E. T. Platelet factor 4 is chemotactic for neutrophils and monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4584–4587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantone J., Senior R. M., Kreutzer D. L., Jones M., Ward P. A. Biochemical quantitation of the chemotactic factor inactivator activity in human serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jan;93(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Niewiarowski S., Rucinski B., Salganicoff L. Subcellular localization of human platelet antiheparin proteins. Thromb Res. 1979 Feb-Mar;14(2-3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Woods J. M., Gorman R. R. Stimulation of human eosinophil and neutrophil polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis and random migration by 12-L-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1172/JCI108617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. D., Stemerman M. B., Handin R. I. Vascular permeation of platelet factor 4 after endothelial injury. Science. 1980 Aug 1;209(4456):611–612. doi: 10.1126/science.6994228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Ross R., Slichter S. J., Scott C. R. Homocystine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):731–741. doi: 10.1172/JCI108520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Broekman M. J., Chernoff A., Lesznik G. R., Drillings M. Platelet alpha-granule proteins: studies on release and subcellular localization. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Movat H. Z., Macmorine D. R., Sényi A. Release of permeability factors from the blood platelet. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Aug-Sep;119(4):988–991. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Weksler B., Ferris B. Increased vascular permeability produced by human platelet granule cationic extract. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):274–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI106237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Nishizawa E. E., Mustard J. F. Response of platelets to tissue injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Butler C., Shaw J. O., Henson P. M. Intravascular aggregation and pulmonary sequestration of platelets during IgE-induced systemic anaphylaxis in the rabbit: abrogation of lethal anaphylactic shock by platelet depletion. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2185–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson G., Robertson A. L., Jr, Cowan D. H. Migration of human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Lab Invest. 1979 Jul;41(1):51–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


