Abstract
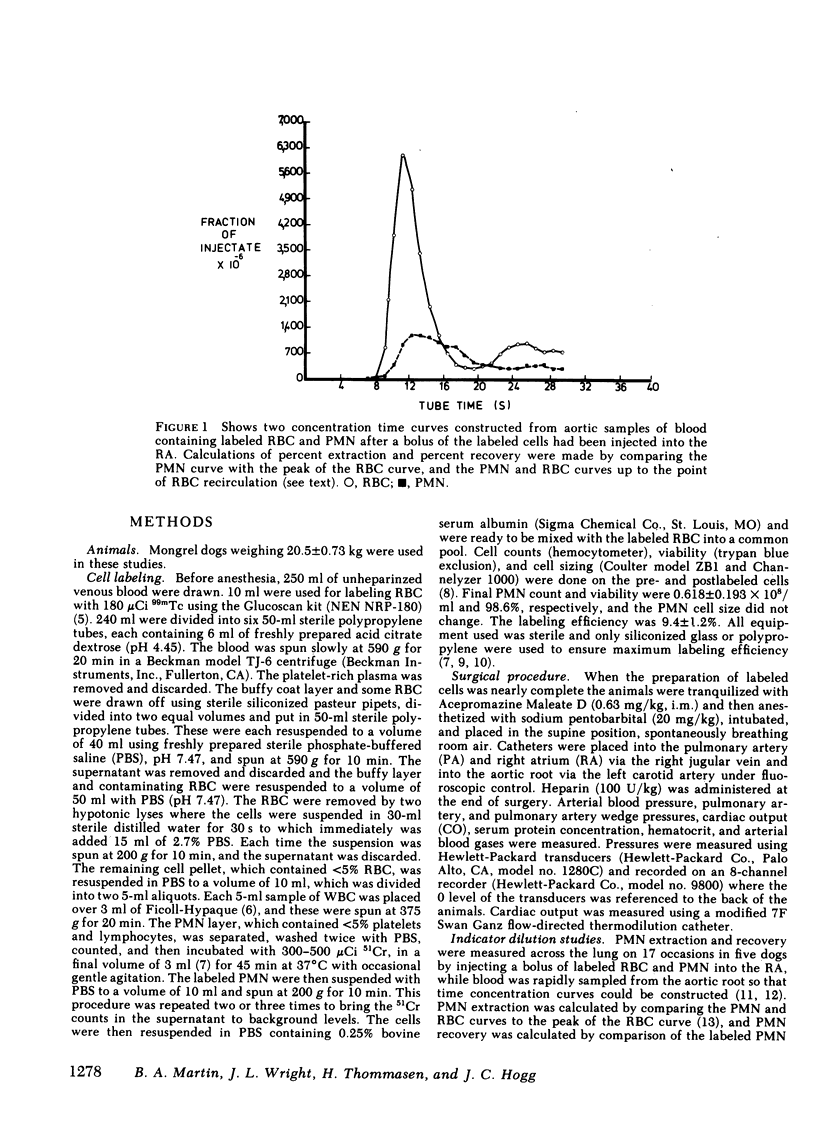
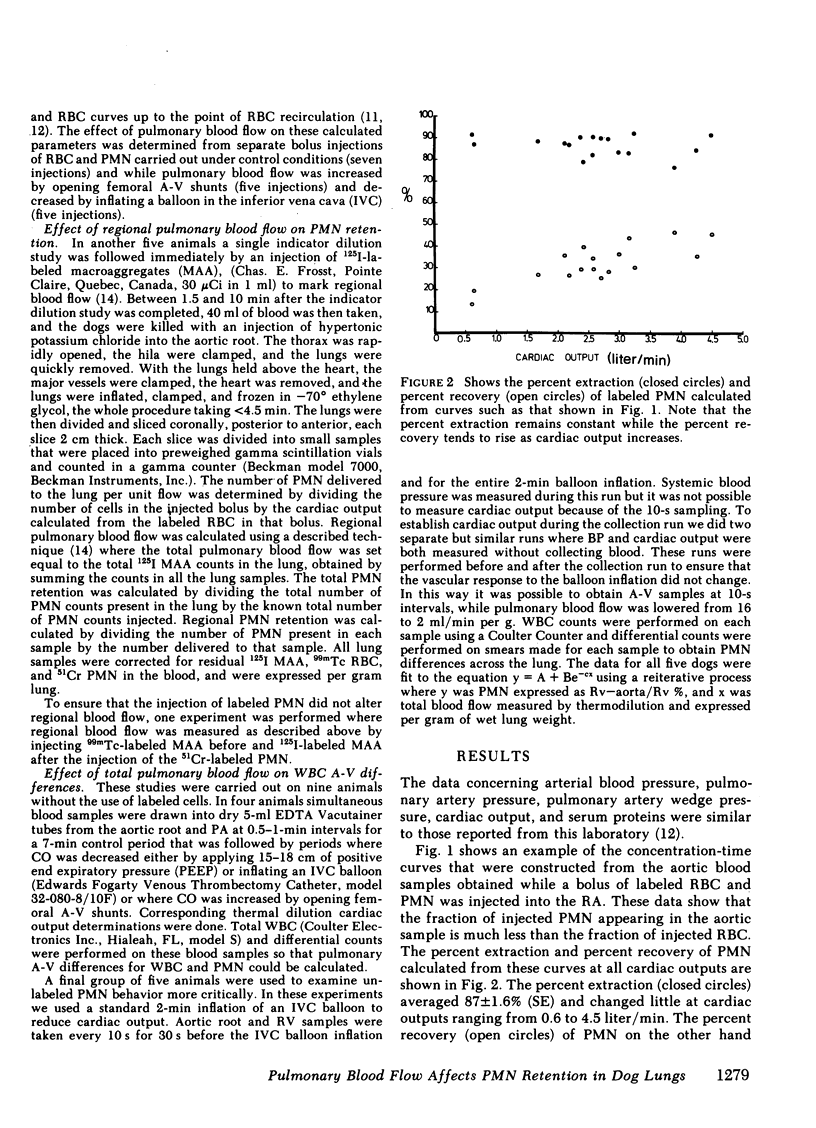
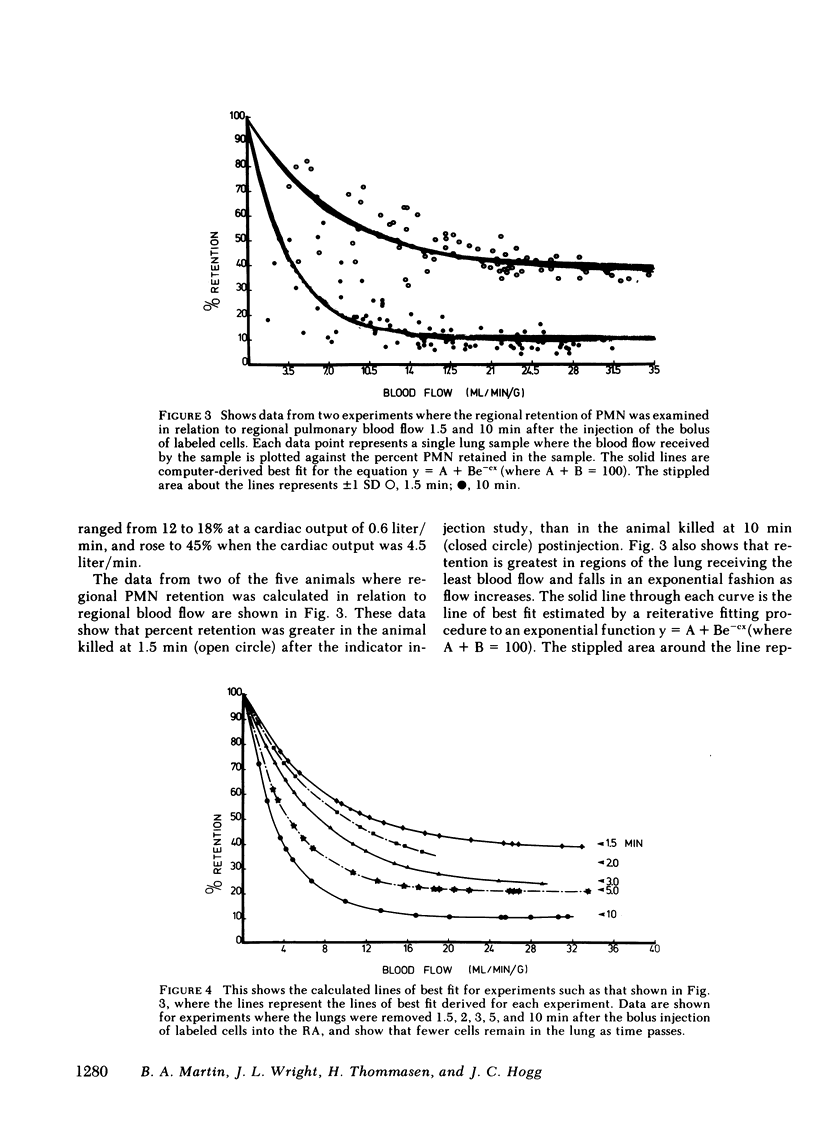
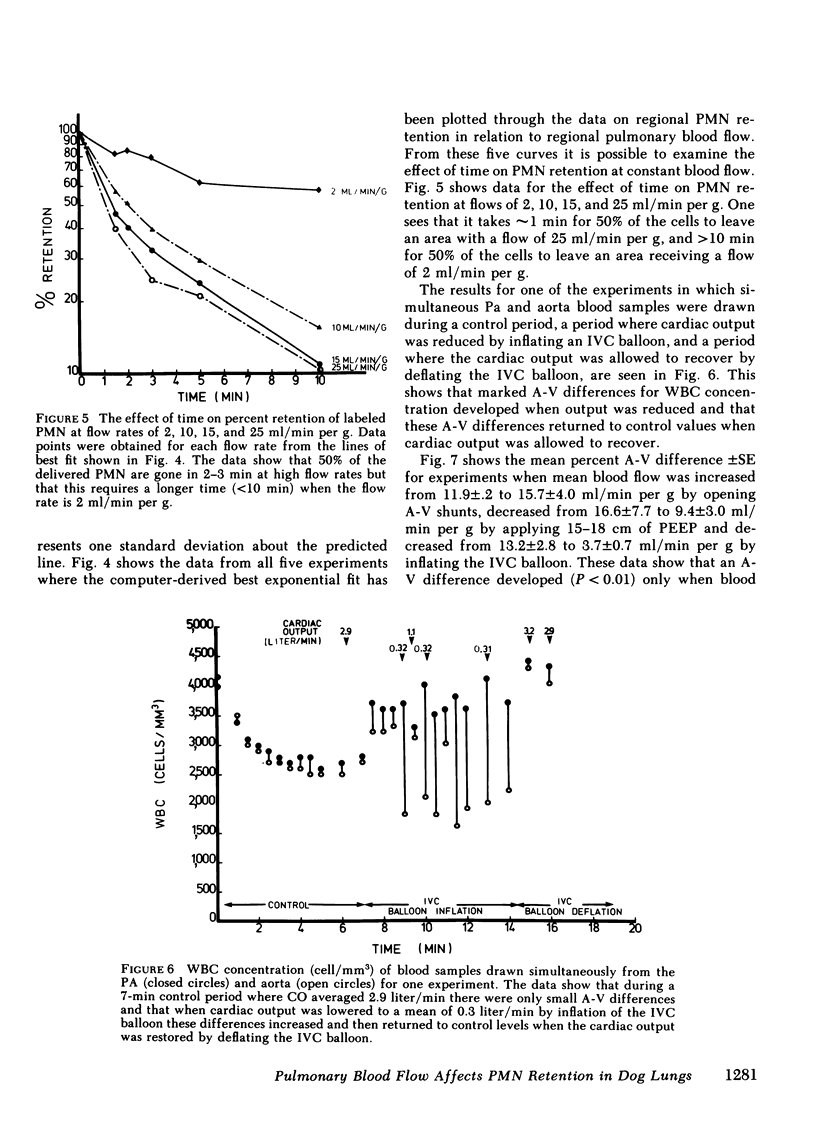
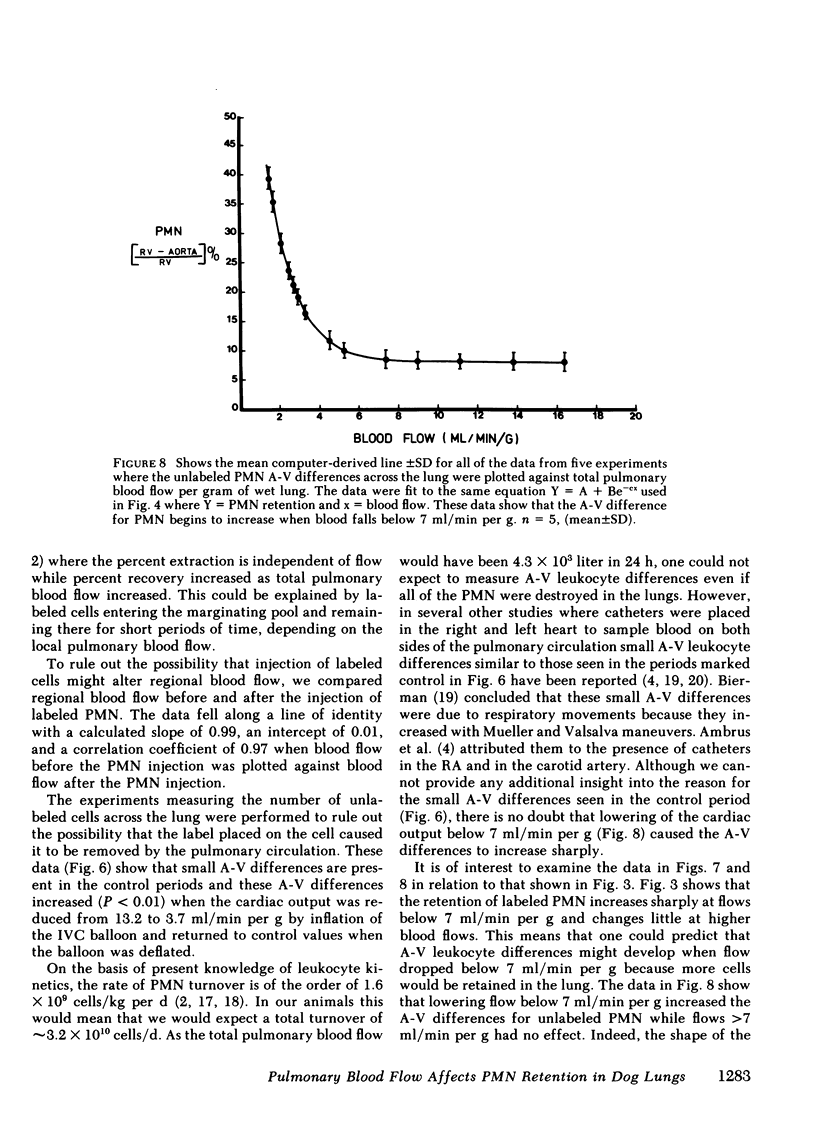
The effect of pulmonary blood flow on the exchange between the circulating was marginating pool of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) was examined in three sets of experiments. In the first we used the double indicator dilution technique with labeled PMN and erythrocytes (RBC) to calculate the percent extraction and percent recovery of PMN at different levels of cardiac output (CO). In the second group of experiments we took advantage of the wide range of blood flow in the lung to determine the effect of regional blood flow on regional PMN retention, and in the third set we measured total leukocyte (WBC) and PMN counts in simultaneous samples from the pulmonary artery and aorta over a wide range of cardiac output. The studies showed that 80-90% of the labeled PMN were removed in a single pass through the lung and that regional retention of labeled PMN and A-V differences for unlabeled PMN increased with decreasing blood flow. The data for regional retention of labeled PMN and the A-V differences observed for unlabeled cells both fit the equation Y = A + Be-cx (where A + B = 100), which showed that PMN accumulate in the lung as blood flow is reduced. We conclude that a dynamic equilibrium exists between the circulating and marginating pools of leukocytes in the lung and that blood flow primarily effects the reentry of cells into the circulating pool so that the marginating pool of PMN within the lung accumulates cells when blood flow is reduced below 7 ml/min per g.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBRUS C. M., AMBRUS J. L., JOHNSON G. C., PACKMAN E. W., CHERNICK W. S., BACK N., HARRISSON J. W. Role of the lungs in regulation of the white blood cell level. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jul;178(1):33–44. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATHENS J. W., HAAB O. P., RAAB S. O., MAUER A. M., ASHENBRUCKER H., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Leukokinetic studies. IV. The total blood, circulating and marginal granulocyte pools and the granulocyte turnover rate in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:989–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI104338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATHENS J. W., RAAB S. O., HAAB O. P., MAUER A. M., ASHENBRUCKER H., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Leukokinetic studies. III. The distribution of granulocytes in the blood of normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:159–164. doi: 10.1172/JCI104230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN H. R., KELLY K. H., CORDES F. L., BYRON R. L., Jr, POLHEMUS J. A., RAPPOPORT S. The release of leukocytes and platelets from the pulmonary circulation by epinephrine. Blood. 1952 Jul;7(7):683–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN H. R., KELLY K. H., CORDES F. L., PETRAKIS N. L., KASS H., SHPIL E. L. The influence of respiratory movements upon the circulating leukocytes. Blood. 1952 May;7(5):533–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs D. R. The kinetics of neutrophilic leukocytes in health and in disease. Semin Hematol. 1967 Oct;4(4):359–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A. Separation of blood leucocytes, granulocytes and lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Cline M. J. Regulation of granulopoiesis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Dec 26;291(26):1388–1395. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197412262912606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenter C. A., Coalson J. J., Jacques J. Emphysema associated with intravascular leukocyte sequestration. Comparison with papain-induced emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):79–84. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowski R. F., Dworkin H. J. Kit-produced 99mTc-labeled red cells for spleen imaging. J Nucl Med. 1974 Dec;15(12):1187–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey W. C., Silva J. 51Cr labeling of concentrated phagocytes. J Nucl Med. 1973 Dec;14(12):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C., Holst P., Corry P., Ruff F., Housley E., Morris E. Effect of regional lung expansion and body position on pulmonary perfusion in dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):97–101. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. A., Dahlby R., Nicholls I., Hogg J. C. Platelet sequestration in lung with hemorrhagic shock and reinfusion in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1306–1312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R., Scott J. L. Leukocyte labeling with 51-Chromium. I. Technic and results in normal subjects. Blood. 1968 Nov;32(5):738–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlo S., Jalowayski A. A., Durand C. M., West J. B. Distribution of red and white blood cells in alveolar walls. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):117–124. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Usami S., Skalak R., Chien S. The interaction of leukocytes and erythrocytes in capillary and postcapillary vessels. Microvasc Res. 1980 Jan;19(1):45–70. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


