Abstract
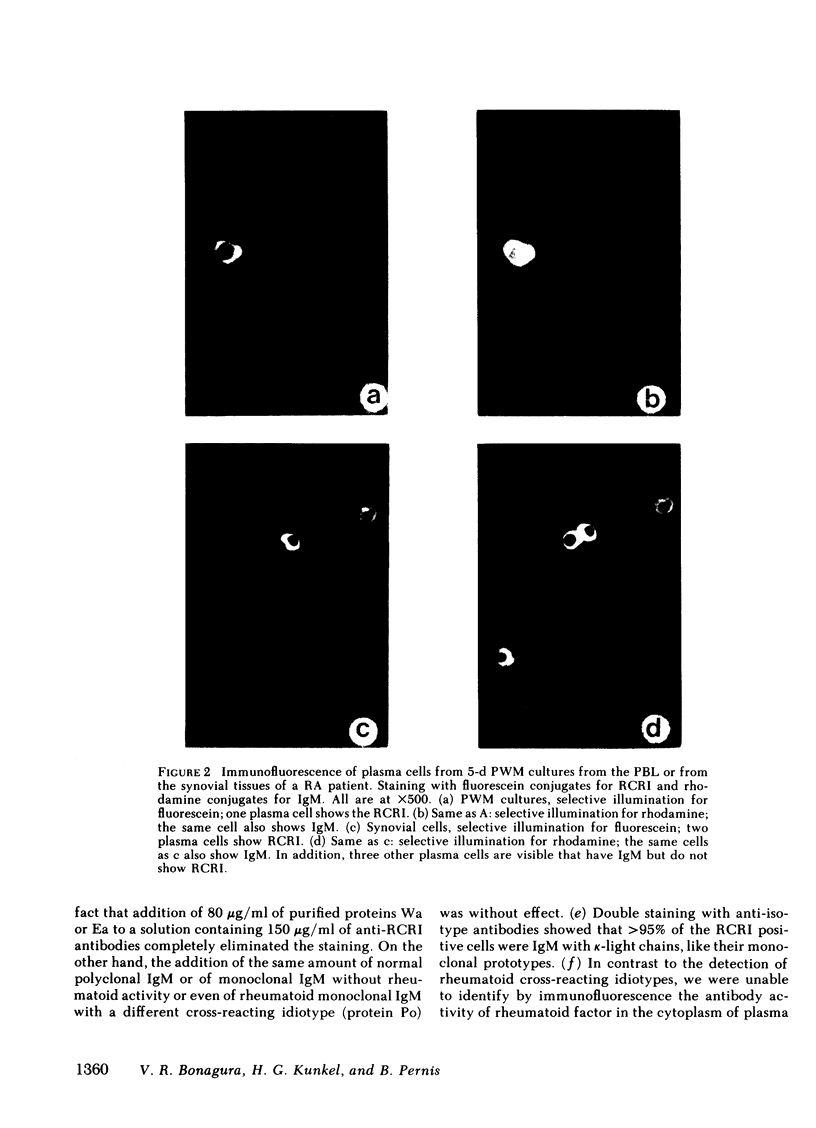
the stimulation of lymphocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients with pokeweed mitogen produces a large number of plasma cells that express the dominant cross-reactive idiotype previously found on monoclonal IgM anti-gamma-globulins from patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia. Similar experiments with the cells of normal individuals show a much lower percentage of these cells with a lower intensity of staining with the fluorescent reagents utilized. Efforts to demonstrate rheumatoid factor in the same cells by fluorescent staining with aggregated gammaglobulin were entirely unsuccessful. This also proved to be the case for pokeweed mitogen-stimulated cells from the mixed cryoglobulinemic patients with large amounts of rheumatoid factor in the serum, despite high percentages of cells expressing the cross-reactive idiotype and also the individual idiotype. On the other hand, native plasma cells from synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis patients showed some cells with both the cross-reactive idiotype and aggregate staining. The exact reason for the failure to demonstrate rheumatoid factor by aggregate staining in pokeweed mitogen-stimulated cultures remains to be determined despite considerable effort to resolve the problem. The most likely possibility is that these plasma cells are relatively immature and have not accumulated polymeric IgM in their cytoplasm to the degree seen in synovial tissue plasma cells. The monomeric forms are readily recognized by the antiidiotypic antibodies and these reagents appear to be of particular value for cellular studies of this type.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Arbetter A., Ibanez de Kasep G., Powell R., Tan E. M., Joslin F. Evidence for a subset of rheumatoid factors that cross-react with DNA-histone and have a distinct cross-idiotype. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1514–1527. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askonas B. A., Parkhouse R. M. Assembly of immunoglobulin M. Blocked thiol groups of intracellular 7S subunits. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):629–634. doi: 10.1042/bj1230629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C. A., Fauci A. S. In vitro idiotypic suppression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes secreting monoclonal immunoglobulin M anti-sheep erythrocyte antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):761–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI109724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Mongini P. K., Stein K. E., Paul W. E. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. I. Expression of cross-reactive idiotypes and Ir gene control of the response to IgG2a of the b allotype. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1334–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J., Scharff M. D. The synthesis, assembly, and secretion of gamma globulin by mouse myeloma cells. VI. Assembly of IgM proteins. J Exp Med. 1973 Jul 1;138(1):278–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J., Zolla S., Scharff M. D., Franklin E. C. Synthesis and assembly of immunoglobulins by malignant human plasmacytes and lymphocytes. II. Heterogeneity of assembly in cells producing IgM proteins. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1118–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Pasquali J. L., Tsoukas C. D., Fong S., Slovin S. F., Lawrance S. K., Slaughter L., Vaughan J. H. Physiology and pathology of rheumatoid factors. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1981;4(2):161–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01857093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Lamoyi E., Nisonoff A., Capra J. D. Structural studies on induced antibodies with defined idiotypic specificities. IX. Framework differences in the heavy- and light-chain-variable regions of monoclonal anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies from A/J mice differing with respect to a cross-reactive idiotype. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):863–875. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J., Steel M., Arthur E. A hemagglutination inhibition technique for detection of immunoglobulins in supernatants of human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Kunkel H. G., Roelcke D. Cross idiotypic specificity among cold agglutinins in relation to combining activity for blood group-related antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Oct;18(2):283–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Common structural and antigenic properties of human gamma M anti-gamma globulins. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1527–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O., Dobloug J. H., Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Evidence of similar idiotypic determinants on different rheumatoid factor populations. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halper J., Fu S. M., Wang C. Y., Winchester R., Kunkel H. G. Patterns of expression of human "Ia-like" antigens during the terminal stages of B cell development. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1480–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Schrohenloher R. E. Enhanced in vitro synthesis of IgM rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Sep;23(9):985–992. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubagawa H., Vogler L. B., Capra J. D., Conrad M. E., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Studies on the clonal origin of multiple myeloma. Use of individually specific (idiotype) antibodies to trace the oncogenic event to its earliest point of expression in B-cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):792–807. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Joslin F., Hurley J. Blocking of certain antigenic sites in the F(ab) region by combination of univalent fragments of Rh antibodies with red cell antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1532–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J., Joslin F. G., Capra J. D. Similarities in the light chains of anti-gamma-globulins showing cross-idiotypic specificities. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):128–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N. R., Bishop S., Jefferis Use of antibody-coated red cells for the sensitive detection of antigen and in rosette tests for cells bearing surface immunoglobulins. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Heimer R., Corcos J., Korngold L. CELLULAR ORIGIN OF RHEUMATOID FACTOR. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 30;110(6):875–886. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudawwar F., Awdeh Z., Ault K., Geha R. S. Regulation of monoclonal immunoglobulin G synthesis by antiidiotypic antibody in a patient with hypogammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1202–1209. doi: 10.1172/JCI109775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Immunglobulin classes, subclasses and complexes of IgG rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid plasma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROHENLOHER R. E., KUNKEL H. G., TOMASI T. B. ACTIVITY OF DISSOCIATED AND REASSOCIATED 19S ANTI-GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1215–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling J., Clevinger B., Davie J. M., Hood L. Amino acid sequence of homogeneous antibodies to dextran and DNA rearrangements in heavy chain V-region gene segments. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):35–40. doi: 10.1038/283035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott D. I., Feinstein A. Biosynthesis and assembly of IgM. Free thiol groups present on the intracellular subunits. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Apr;3(4):229–235. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]