Abstract
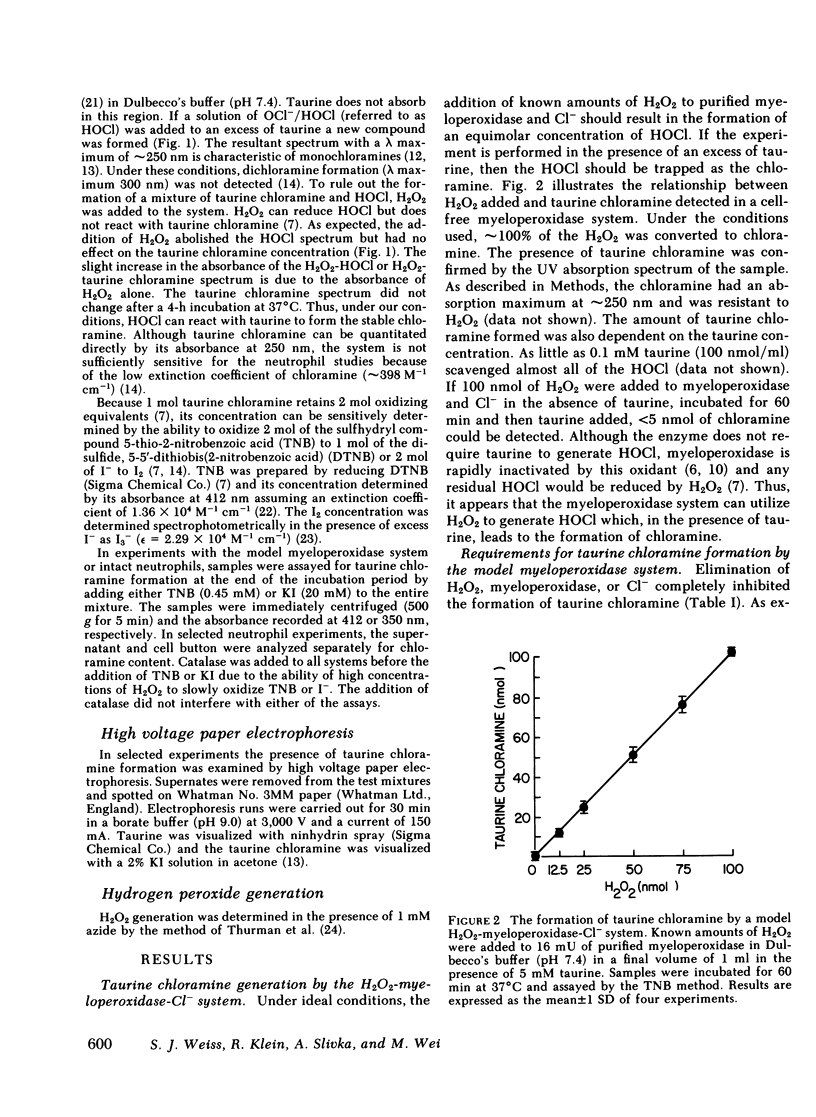
The model hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase-chloride system is capable of generating the powerful oxidant hypochlorous acid, which can be quantitated by trapping the generated species with the β-amino acid, taurine. The resultant stable product, taurine chloramine, can be quantitated by its ability to oxidize the sulfhydryl compound, 5-thio-2-nitro-benzoic acid to the disulfide, 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitroben-zoic acid) or to oxidize iodide to iodine. Using this system, purified myeloperoxidase in the presence of chloride and taurine converted stoichiometric quantities of hydrogen peroxide to taurine chloramine. Chloramine generation was absolutely dependent on hydrogen peroxide, myeloperoxidase, and chloride and could be inhibited by catalase, myeloperoxidase inhibitors, or chloride-free conditions. In the presence of taurine, intact human neutrophils stimulated with either phorbol myristate acetate or opsonized zymosan particles generated a stable species capable of oxidizing 5-thio-2-nitrobenzoic acid or iodide. Resting cells did not form this species. The oxidant formed by the stimulated neutrophils was identified as taurine chloramine by both ultraviolet spectrophotometry and electrophoresis. Taurine chloramine formation by the neutrophil was dependent on the taurine concentration, time, and cell number. Neutrophil-dependent chloramine generation was inhibited by catalase, the myeloperoxidase inhibitors, azide, cyanide, or aminotriazole and by chloride-free conditions, but not by superoxide dismutase or hydroxyl radical scavengers. Thus, it appears that stimulated human neutrophils can utilize the hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase-chloride system to generate taurine chloramine. Based on the demonstrated ability of the myeloperoxidase system to generate free hypochlorous acid we conclude that neutrophils chlorinate taurine by producing this powerful oxidant. The biologic reactivity and cytotoxic potential of hypochlorous acid and its chloramine derivatives suggest that these oxidants play an important role in the inflammatory response and host defense.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrich J. M., McCarthy C. A., Hurst J. K. Biological reactivity of hypochlorous acid: implications for microbicidal mechanisms of leukocyte myeloperoxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L. Active oxygen species and the functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Szot S. Chemotactic factor inactivation by stimulated human neutrophils mediated by myeloperoxidase-catalyzed methionine oxidation. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1507–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Szot S. The myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system as effector of neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1295–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Soodak M., Strout H. V., Neary J. T., Nakamura C., Maloof F. Thiourea and cyanamide as inhibitors of thyroid peroxidase: the role of iodide. Endocrinology. 1979 Apr;104(4):919–924. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-4-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Pabalan S., Schultz J. The subunit structure of crystalline canine myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan-Müller J. W., Weening R. S., Roos D. Production of hydrogen peroxide by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):198–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandl R. C., André-Schwartz J., Borges-DuBois L., Kipnes R. S., McMurrich B. J., Babior B. M. Termination of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1176–1185. doi: 10.1172/JCI109033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Hager L. P. Mechanism of the inhibition of enzymatic halogenation by antithyroid agents. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3582–3589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M., Schonbaum G. R. Peroxidase-catalyzed halogenation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:861–888. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naskalski J. W. Myeloperoxidase inactivation in the course of catalysis of chlorination of taurine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 8;485(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paredes J. M., Weiss S. J. Human neutrophils transform prostaglandins by a myeloperoxidase-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2738–2740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Zgliczynski J. M., Paul B. B., Sbarra A. J. Chlorination or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides by myeloperoxidase: a novel bactericidal mechanism. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Jan;27(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., LoBuglio A. F., Weiss S. J. A potential role for hypochlorous acid in granulocyte-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelmaszyńska T., Zgliczynski J. M. N-(2-Oxoacyl)amino acids and nitriles as final products of dipeptide chlorination mediated by the myeloperoxidase/H2O2/Cl- system. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelmaszyńska T., Zgliczyński J. M. Myeloperoxidase of human neutrophilic granulocytes as chlorinating enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: effect of exogenous amines on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.110-116.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman R. G., Ley H. G., Scholz R. Hepatic microsomal ethanol oxidation. Hydrogen peroxide formation and the role of catalase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Slivka A. Monocyte and granulocyte-mediated tumor cell destruction. A role for the hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase-chloride system. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):255–262. doi: 10.1172/JCI110447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T. Chlorinating ability of human phagocytosing leucocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):157–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T., Domański J., Ostrowski W. Chloramines as intermediates of oxidation reaction of amino acids by myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 16;235(3):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


