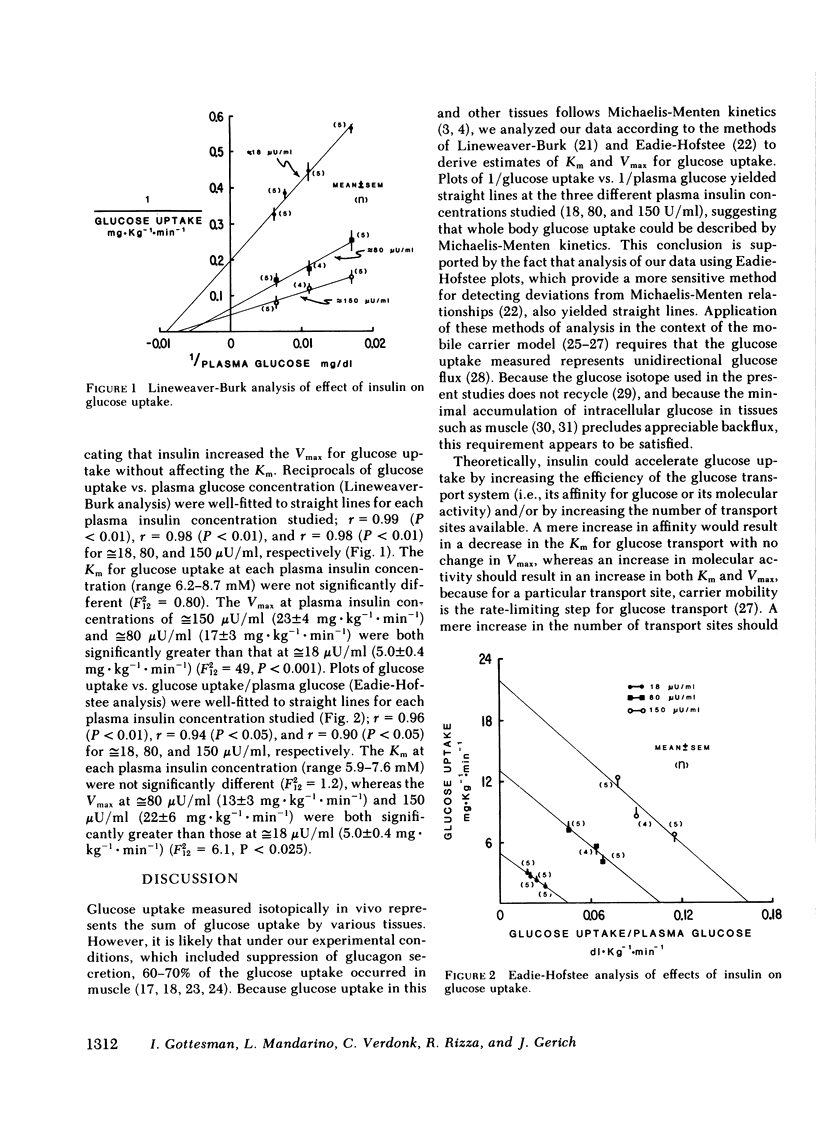
Abstract
The present studies were undertaken to assess the mechanism by which insulin increases glucose uptake in man. Because glucose uptake in most mammalian tissues occurs predominantly by a facilitated transport system that follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics, glucose uptake was measured isotopically in normal volunteers over the physiologic range of plasma glucose and insulin concentrations and was subjected to Lineweaver-Burk and Eadie-Hofstee analysis. With both methods, increases in plasma insulin from 18 microunits/ml to 80 and 150 microunits/ml were found to increase the maximum velocity (Vmax) for glucose uptake nearly three- and fivefold, respectively, (P less than 0.025 and P less than 0.001) without significantly altering the Michaelis constant (Km). Because an increase in the affinity or molecular activity of transport sites or provision of additional transport sites that differed from those present basally should have altered the Km, whereas a mere increase in the number of transport sites would have only increased the Vmax, our results indicate that in man, insulin may increase glucose uptake merely by providing additional transport sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTON H. G. PERMEABILITY OF THE HUMAN RED CELL TO LABELLED GLUCOSE. J Physiol. 1964 Jan;170:1–20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhanu P., Olefsky J. M. Effects of insulin and insulin-like agents on the glucose transport system of cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):523–529. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Sjöström L. Carbohydrate storage in man: speculations and some quantitative considerations. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1853–1865. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Gould M. K. Kinetics of glucose uptake in isolated soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Shikama H., Chu D. T., Exton J. H. Inhibitory effect of epinephrine on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):706–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI110306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G., Siegel J. A., Olefsky J. M. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport in human adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E621–E625. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Olefsky J. M. Coupling of insulin receptors to glucose transport: a temperature-dependent time lag in activation of glucose transport. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Mar;193(1):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Insulin action and the regulation of hexose transport. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):399–409. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Hexose transport in isolated brown fat cells. A model system for investigating insulin action on membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5421–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Wahren J., Felig P. Influence of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on splanchnic glucose exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Yorke R. E., Randle P. J. Measurement of concentrations of metabolites in adipose tissue and effects of insulin, alloxan-diabetes and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):407–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1000407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A., Katz J., Golden S., Chenoweth M. Estimation of glucose turnover and recycling in rabbits using various [3H, 14C]glucose labels. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1159–1162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germinario R. J., Oliveira M. Stimulation of hexose transport in cultured human skin fibroblasts by insulin. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):313–318. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Mott D. M., Fields R. M., Bennett P. H. Insulin stimulation of glucose entry in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Oct;101(1):129–138. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsen C., Jarett L. A comparison of basal and insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipocyte plasma membranes. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):373–378. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., REGEN D. M., PARK C. R. IDENTIFICATION OF A MOBILE CARRIER-MEDIATED SUGAR TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN MUSCLE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:369–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of the ability of insulin to activate the glucose-transport system in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):137–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1720137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccà L., Cicala M., Trimarco B., Ungaro B., Vigorito C. Differential effects of insulin on splanchnic and peripheral glucose disposal after an intravenous glucose load in man. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):117–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI110583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Liljenquist J. E., Williams P. E., Lacy W. W., Cherrington A. D. Glucose disposal during insulinopenia in somatostatin-treated dogs. The roles of glucose and glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):487–491. doi: 10.1172/JCI109150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonk C. A., Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E. Effects of plasma glucose concentration on glucose utilization and glucose clearance in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):535–537. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Gliemann J. Kinetic parameters of transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5276–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


