Abstract
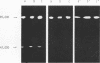
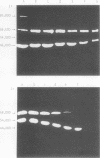
Two different plasmatic plasminogen activators (PA) can be demonstrated after sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of plasma freshly collected from resting volunteers, followed by transfer of the gels onto plasminogen-rich fibrin-agarose plates. These two PA are also present in plasmas deficient in coagulation Factor XI, Factor XII, prekallikrein, or high molecular weight-kininogen. The slower-moving PA has an apparent 85,000 Mr and is immunologically unrelated to urokinase (UK). The faster moving PA was isolated by immunoadsorption of plasma on anti-UK IgG coupled to Sepharose 4B and appears to be identical to urinary high molecular weight-UK.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B. Purification and characterization of human vascular plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 27;621(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B., Holmberg L. Immunological identity of urokinase and ovarian carcinoma plasminogen activator released in tissue culture. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):595–597. doi: 10.1038/261595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B. No crossreaction between circulating plasminogen activator and urokinase. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):535–539. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARR P. O., BJURSTEDT H., COLERIDGE J. C. Reflex control of respiration in the anesthetized dog during prolonged exposure to positive radial acceleration. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Sep 30;47:1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder B. R., Spragg J., Austen K. F. Purification and characterization of human vascular plasminogen activator derived from blood vessel perfusates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucinski C. S., Fletcher A. P., Sherry S. Effect of urokinase antiserum on plasminogen activators: demonstration of immunologic dissimilarity between plasma plasminogen activator and urokinase. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1238–1253. doi: 10.1172/JCI105816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H. The participation of plasma thromboplastin antecedent (Factor XI) in contact-activated fibrinolysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jun;164(2):153–157. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijngaards G., Kluft C., Groeneveld E. Demonstration of urokinase-related fibrinolytic activity in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):165–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Schleuning W. D., Reich E. Isolation and characterization of urokinase from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3276–3283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]