Abstract
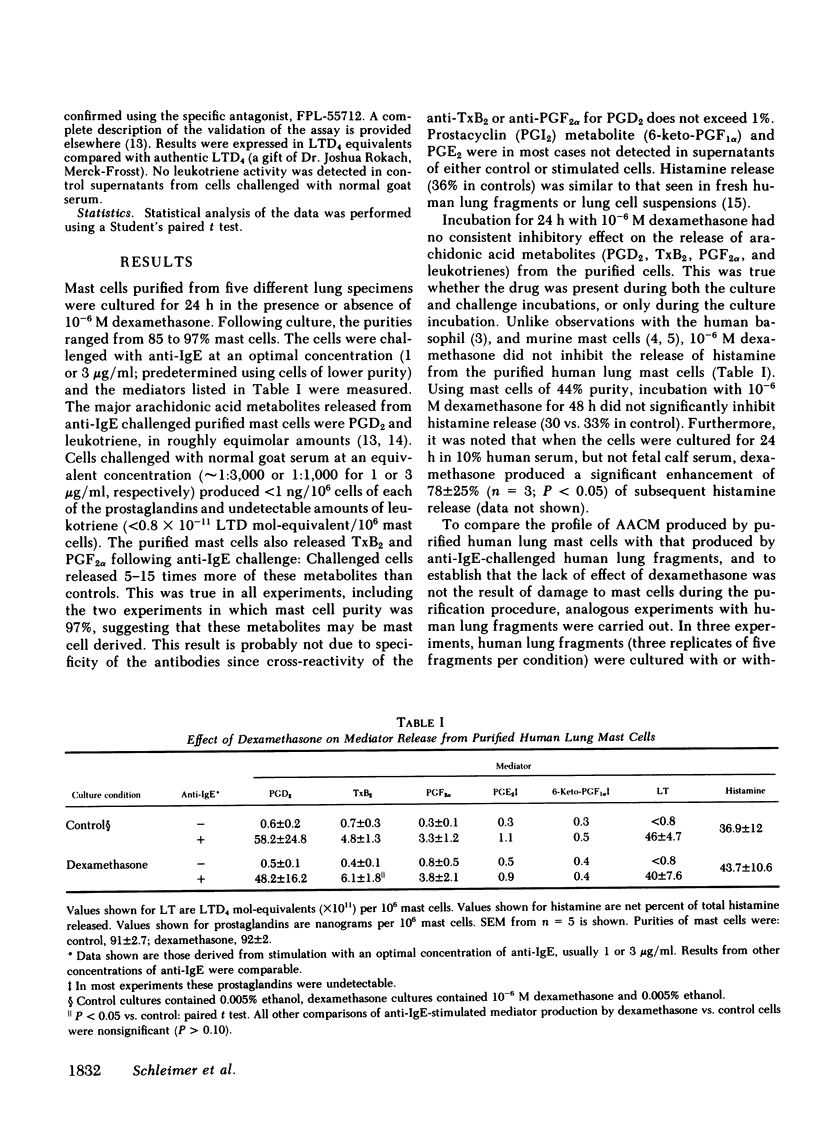
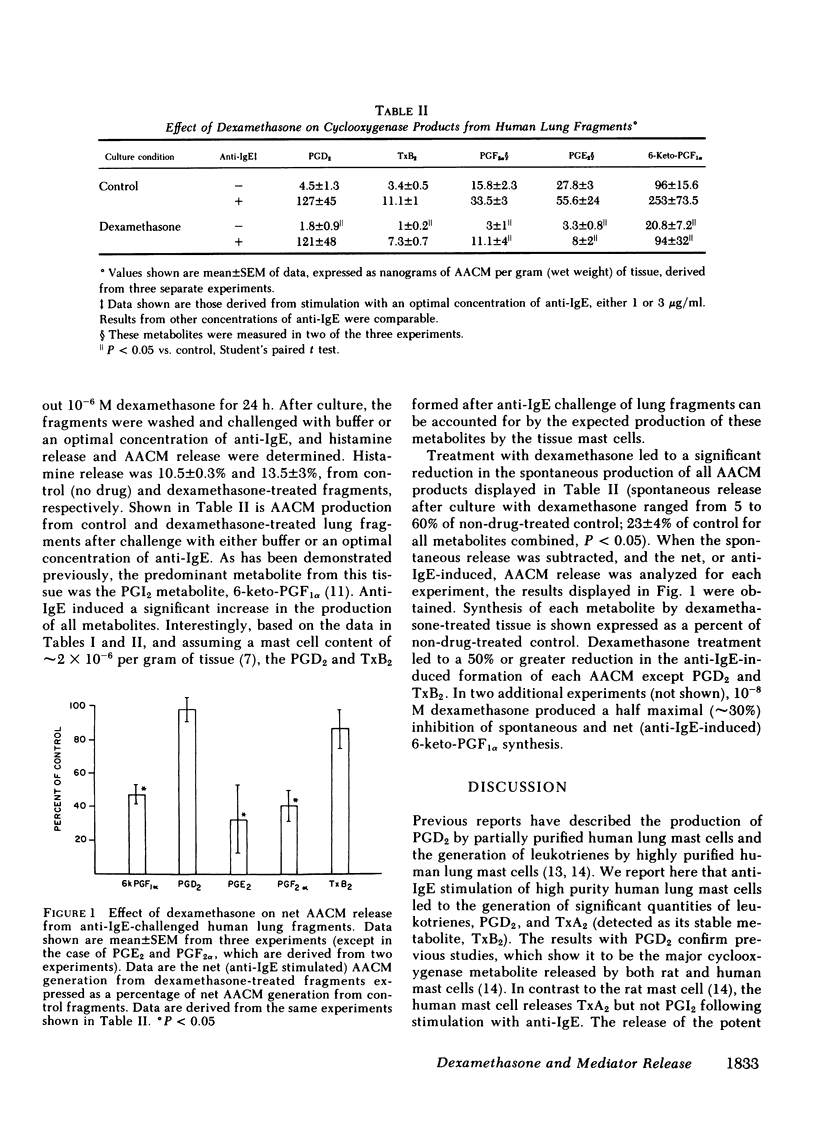
Purified human lung mast cells released histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandin (PG) D2, thromboxane B2 (TxB2), and PGF2 alpha in response to anti-IgE stimulation. Incubation of the cells for 24 h with 10(-6) M dexamethasone, a treatment that inhibits mediator release from human basophils, had no effect on the release of these mediators from mast cells. Dexamethasone treatment of human lung fragments led to little or no inhibition of anti-IgE-induced release of the mast cell-derived mediator, histamine, but produced a significant inhibition of the release of PGE2, PGF2 alpha, and 6-keto-PGF1 alpha. As was the case with purified mast cells, the steroid did not inhibit the release of PGD2 or TxB2 from human lung fragments. Comparison of the quantities of PGD2 and TxB2 produced by purified cells and human lung fragments reveals that the mast cells produce quantities of these metabolites sufficient to account for the entire amount produced by challenged lung fragments. Dexamethasone inhibited spontaneous release from lung fragments of all cyclooxygenase products measured. These results suggest that the human lung parenchymal mast cell phospholipase is not inhibited by dexamethasone, whereas other phospholipase(s) in the lung are inhibited by the steroid. These results may be useful in explaining the resistance of acute allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, to steroids, despite the potent antiinflammatory activity of steroids on subacute and chronic inflammation, such as in bronchial asthma, which may be initiated by IgE-dependent mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., Nijkamp F. P., Vane J. R. Phospholipase A2 activity of guinea-pig isolated perfused lungs: stimulation, and inhibition by anti-inflammatory steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Sterk A. R., Hirata F., Ishizaka T. Biochemical analysis of glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of IgE-mediated histamine release from mouse mast cells. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1212–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. S., Ornstein L. Basophil counting with a new staining method using alcian blue. Blood. 1975 Aug;46(2):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J. The late phase of the immunoglobulin E-mediated reaction: a link between anaphylaxis and common allergic disease? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Sep;70(3):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. W., Plummer V. M. Glucocorticoid inhibition of antigen-evoked histamine release from human skin. Immunology. 1974 Sep;27(3):359–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Panczenko B., Korbut R., Grodzinska L., Ocetkiewicz A. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin release from perfused mesenteric blood vessels of rabbit and from perfused lungs of sensitized guinea pig. Prostaglandins. 1975 Aug;10(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer K. A., Lichtenstein L. M., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Fish J. E. Platelet activation during antigen-induced airway reactions in asthmatic subjects. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 4;304(23):1404–1407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106043042307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M. The purification of human basophils. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2519–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Schleimer R. P., Peters S. P., Schulman E. S., Adams G. K., 3rd, Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Generation of leukotrienes by purified human lung mast cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI110670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp F. P., Flower R. J., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Partial purification of rabbit aorta contracting substance-releasing factor and inhibition of its activity by anti-inflammatory steroids. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):479–482. doi: 10.1038/263479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Schulman E. S., Schleimer R. P., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Dispersed human lung mast cells. Pharmacologic aspects and comparison with human lung tissue fragments. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1034–1039. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poothullil J., Umemoto L., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E., Day R. P. Inhibition by prednisone of late cutaneous allergic responses induced by antiserum to human IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Feb;57(2):164–167. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P., Lichtenstein L. M., Gillespie E. Inhibition of basophil histamine release by anti-inflammatory steroids. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):454–455. doi: 10.1038/292454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Gillespie E., Lichtenstein L. M. Inhibition of basophil histamine release by anti-inflammatory steroids. II. Studies on the mechanism of action. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1632–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Peters S. P., Schleimer R. P., Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Human lung mast cells: purification and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., Newball H. H., Demers L. M., Fitzpatrick F. A., Adkinson N. F., Jr Anaphylactic release of thromboxane A2, prostaglandin D2, and prostacyclin from human lung parenchyma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Oct;124(4):402–406. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.4.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel L., Kaliner M. Prostaglandin-generating factor of anaphylaxis. Identification and isolation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12692–12698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


