Abstract
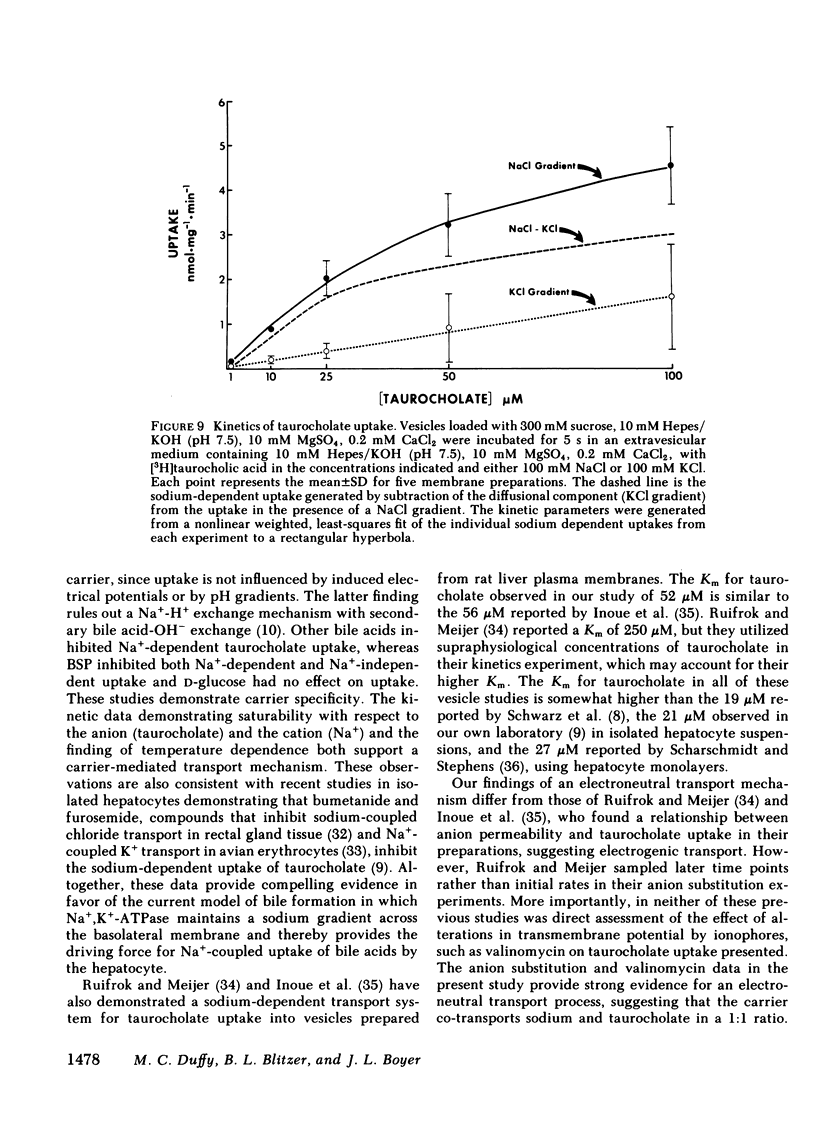
To determine directly the driving forces for bile acid entry into the hepatocyte, the uptake of [3H]taurocholic acid into rat liver plasma membrane vesicles was studied. The membrane preparation contained predominantly right-side-out vesicles, and was highly enriched in plasma membrane marker enzymes. The uptake of taurocholate at equilibrium was inversely related to medium osmolarity, indicating transport into an osmotically sensitive space. In the presence of an inwardly directed sodium gradient (NaCl or sodium gluconate), the initial rate of uptake was rapid and taurocholate was transiently accumulated at a concentration twice that at equilibrium (overshoot). Other inwardly directed cation gradients (K+, Li+, choline+) or the presence of sodium in the absence of a gradient (Na+ equilibrated) resulted in a slower initial uptake rate and did not sustain an overshoot. Bile acids inhibited sodium-dependent taurocholate uptake, whereas bromsulphthalein inhibited both sodium-dependent and sodium-independent uptake and D-glucose had no effect on uptake. Uptake was temperature dependent, with maximal overshoots occurring at 25 degrees C. Imposition of a proton gradient across the vesicle (pHo less than pHi) in the absence of a sodium gradient failed to enhance taurocholate uptake, indicating that double ion exchange (Na+-H+, OH- -anion) is unlikely. Creation of a negative intravesicular potential by altering accompanying anions or by valinomycin-induced K+-diffusion potentials did not enhance taurocholate uptake, suggesting an electroneutral transport mechanism. The kinetics of taurocholate uptake demonstrated saturability with a Michaelis constant at 52 microM and maximum velocity of 4.5 nmol X mg-1 X protein X min-1. These studies provide definitive evidence for a sodium gradient-dependent, carrier-mediated, electrically neutral transport mechanism for hepatic taurocholate uptake. These findings are consistent with a model for bile secretion in which the basolateral enzyme Na+,K+-ATPase provides the driving force for "uphill" bile acid transport by establishing a trans-membrane sodium gradient.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K. H., Staehelin L. A. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli as detected by freeze-cleave electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.888-899.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Identifying secondary active solute transport in epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F1–11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cellular mechanisms of bile formation. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):346–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Ratoosh S. L., Donovan C. B., Boyer J. L. Effects of inhibitors of Na+-coupled ion transport on bile acid uptake by isolated rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):G48–G53. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.1.G48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. New concepts of mechanisms of hepatocyte bile formation. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):303–326. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Reno D. Properties of (Na+ plus K+)-activated ATPase in rat liver plasma membranes enriched with bile canaliculi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:103–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delage Y., Erlinger S., Duval M., Bpenhamou J. P. Influence of dehydrocholate and taurocholate on bromsulphthalein uptake, storage, and excretion in the dog. Gut. 1975 Feb;16(2):105–108. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Hepatocellular uptake of taurocholate in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):419–426. doi: 10.1172/JCI107946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSHIRT H., KOSS F. W., MORIANZ K. [Studies on the quantitative evaluation of thin-layer chromatography. 2. Separation and determination of bile acids]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1960 Nov;10:943–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goresky C. A., Nadeau B. E. Uptake of materials by the intact liver. The exchange of glucose across the cell membranes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):634–646. doi: 10.1172/JCI107598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Petersen O. H. Cell membrane potential and resistance in liver. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase W., Schäfer A., Murer H., Kinne R. Studies on the orientation of brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):57–62. doi: 10.1042/bj1720057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Evans W. H. Transverse organization of phospholipids across the bilayer of plasma-membrane subfractions of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1740563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man. Clin Gastroenterol. 1977 Jan;6(1):3–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver sinusoidal membrane vesicles: evidence of sodium cotransport. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):572–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefee E. B., Scharschmidt B. F., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Studies of relationship among bile flow, liver plasma membrane NaK-ATPase, and membrane microviscosity in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1590–1598. doi: 10.1172/JCI109620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laperche Y., Preaux A. M., Berthelot P. Two systems are involved in the sulfobromophthalein uptake by rat liver cells: one is shared with bile salts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 1;30(11):1333–1336. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90317-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lücke H., Stange G., Kinne R., Murer H. Taurocholate--sodium co-transport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat ileum. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):951–958. doi: 10.1042/bj1740951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U. Demonstration of electrogenic Na+-dependent D-glucose transport in intestinal brush border membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):484–488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O S. Y., Dupont J. Identification and quantitation of cholanoic acids in hepatic and extra-hepatic tissues of rat. Lipids. 1975 Jun;10(6):340–347. doi: 10.1007/BF02532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okishio T., Nair P. P. Studies on bile acids. Some observations on the intracellular localization of major bile acids in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3662–3668. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Takesue S. A new method for simultaneous purification of cytochrome b5 and NADPH-cytochrome c reductase from rat liver microsomes. J Biochem. 1970 Feb;67(2):249–257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Feit P. W., Greengard P. cAMP-stimulated cation cotransport in avian erythrocytes: inhibition by "loop" diuretics. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):C139–C148. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.3.C139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pries J. M., Sherman C. A., Williams G. C., Hanson R. F. Hepatic extraction of bile salts in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E191–E197. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Uptake of bile acids by perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):734–742. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse D. J., Lack L. Ion requirements for taurocholate transport by ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 2;25(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruifrok P. G., Meijer D. K. Sodium ion-coupled uptake of taurocholate by rat-liver plasma membrane vesicles. Liver. 1982 Mar;2(1):28–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1982.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Keeffe E. B., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Validation of a recording spectrophotometric method for measurement of membrane-associated Mg- and NaK-ATPase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):790–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Stephens J. E. Transport of sodium, chloride, and taurocholate by cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Waggoner J. G., Berk P. D. Hepatic organic anion uptake in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1280–1292. doi: 10.1172/JCI108204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz L. R., Burr R., Schwenk M., Pfaff E., Greim H. Uptake of taurocholic acid into isolated rat-liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):617–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Brown D., Oonk R., Orci L. Orientation of rat-liver plasma membrane vesicles. A biochemical and ultrastructural study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Van Amelsvoort J. M., Van Dam K. Amino acid transport in plasma-membrane vesicles from rat liver. Characterization of L-alanine transport. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Rubin W., Rifkind A. B., Kappas A. Plasma membranes of the rat liver. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of a fraction rich in bile canaliculi. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):124–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uptake of bromosulfophthalein by isolated liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware A. J., Carey M. C., Combes B. Solution properties of sulfobromophthalein sodium (BSP) compounds alone and in association with sodium taurocholate (TC). J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Mar;87(3):443–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Burckhardt G., Murer H., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J. Sodium-coupled taurocholate transport in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney in vivo and in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1141–1150. doi: 10.1172/JCI110128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amelsvoort J. M., Sips H. J., Apitule M. E., van Dam K. Heterogeneous distribution of the sodium-dependent alanine transport activity in the rat hepatocyte plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):950–960. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90497-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amelsvoort J. M., Sips H. J., van Dam K. Sodium-dependent alanine transport in plasma-membrane vesicles from rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):1083–1086. doi: 10.1042/bj1741083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]