Abstract
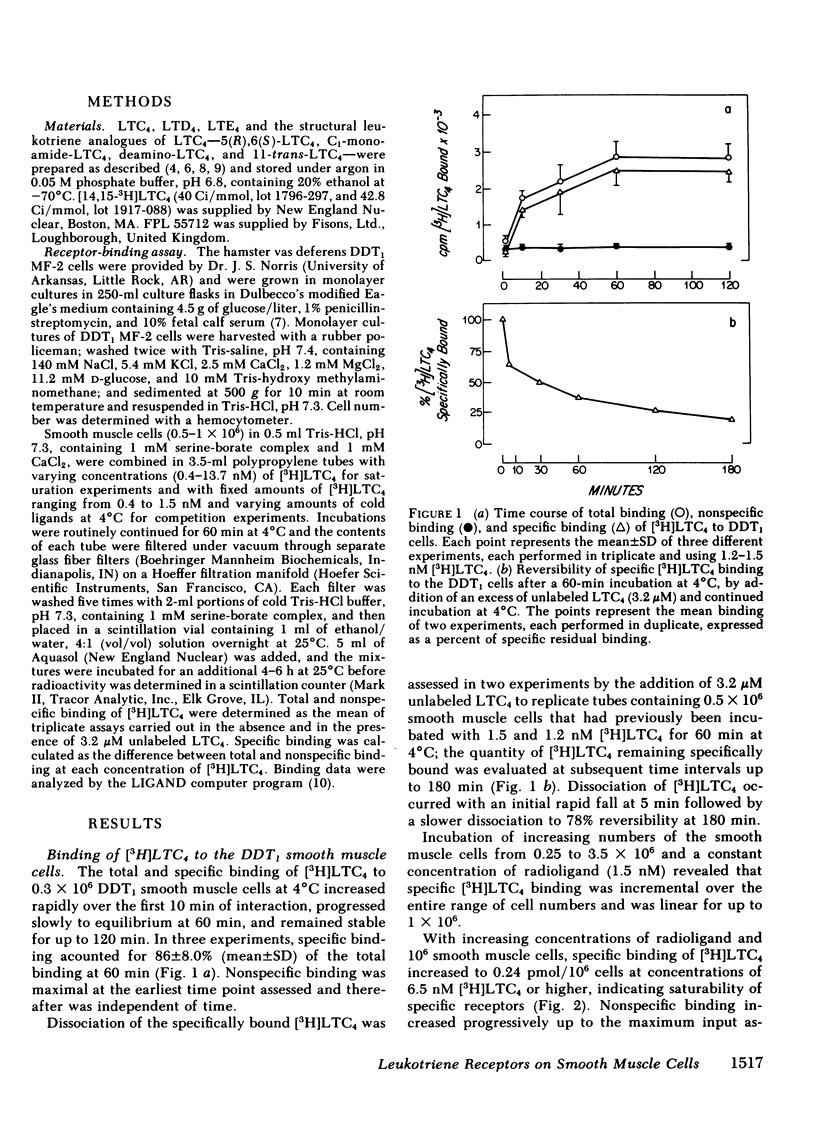
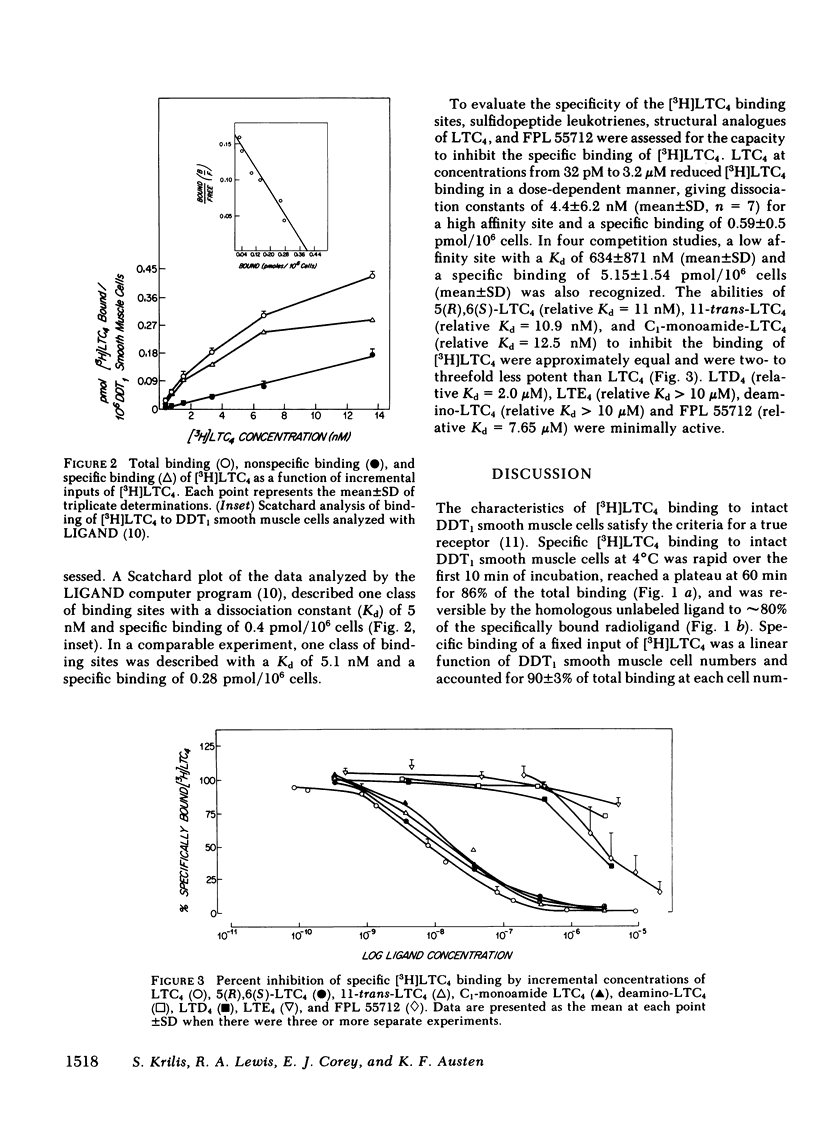
Specific receptors for leukotriene C4 (LTC4) have been identified on an intact smooth muscle cell line, DDT1 MF-2 cells derived from the Syrian hamster vas deferens. Specific [3H]LTC4 binding at a fixed input at 4 degrees C was rapid, reached a plateau at 86% of total binding at 60 min, and was reversible upon addition of excess homoligand. With incremental inputs of radioligand and a constant cell number, specific [3H]LTC4 binding reached a plateau indicative of saturable binding sites. LIGAND analysis of the Scatchard plot demonstrated a single high affinity binding site with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 5 nM. With incremental inputs of unlabeled LTC4, LIGAND analysis of the Scatchard plot demonstrated a single high affinity site with a Kd of 4.4 nM and in some experiments an additional low affinity site with a Kd of 634 nM. The myotonically active structural analogues of LTC4, 5(R),6(S)-LTC4, 11-trans-LTC4, and C1-monoamide-LTC4, competed effectively with radiolabeled LTC4 such that the relative Kd values of these heteroligands were within one log of that of the homoligand. In contrast, the other native sulfidopeptide leukotrienes, leukotriene D4 and leukotriene E4, exhibited relative Kd values that were 2-3 logs less than that of LTC4. Thus, the high affinity receptor on the DDT1 smooth muscle cell line is specific for a single constituent, LTC4, of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Identification of a component of rat mononuclear cell SRS as leukotriene D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1121–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett L. E., Norris J. S. Characterization of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype in a smooth muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):694–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Toda M., Brion F., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Contractile activities of structural analogs of leukotrienes C and D: necessity of a hydrophobic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3195–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Clark D. A., Corey E. J. Identification of the C(6)-S-conjugate of leukotriene A with cysteine as a naturally occurring slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). Importance of the 11-cis-geometry for biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Toda M., Brion F., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Contractile activities of structural analogs of leukotrienes C and D: role of the polar substituents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Lee C. W., Levine L., Morgan R. A., Weiss J. W., Drazen J. M., Oh H., Hoover D., Corey E. J., Austen K. F. Biology of the C-6-sulfidopeptide leukotrienes. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:15–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin W. M., Huang C. K., Becker E. L. The formylpeptide chemotactic receptor on rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. I. Evidence for two binding sites with different affinities. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Piper P. J., Tippins J. R. Structure of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):104–106. doi: 10.1038/285104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orning L., Hammarström S. Kinetics of the conversion of leukotriene C by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1304–1309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Serine-borate complex as a transition-state inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4806–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


