Abstract
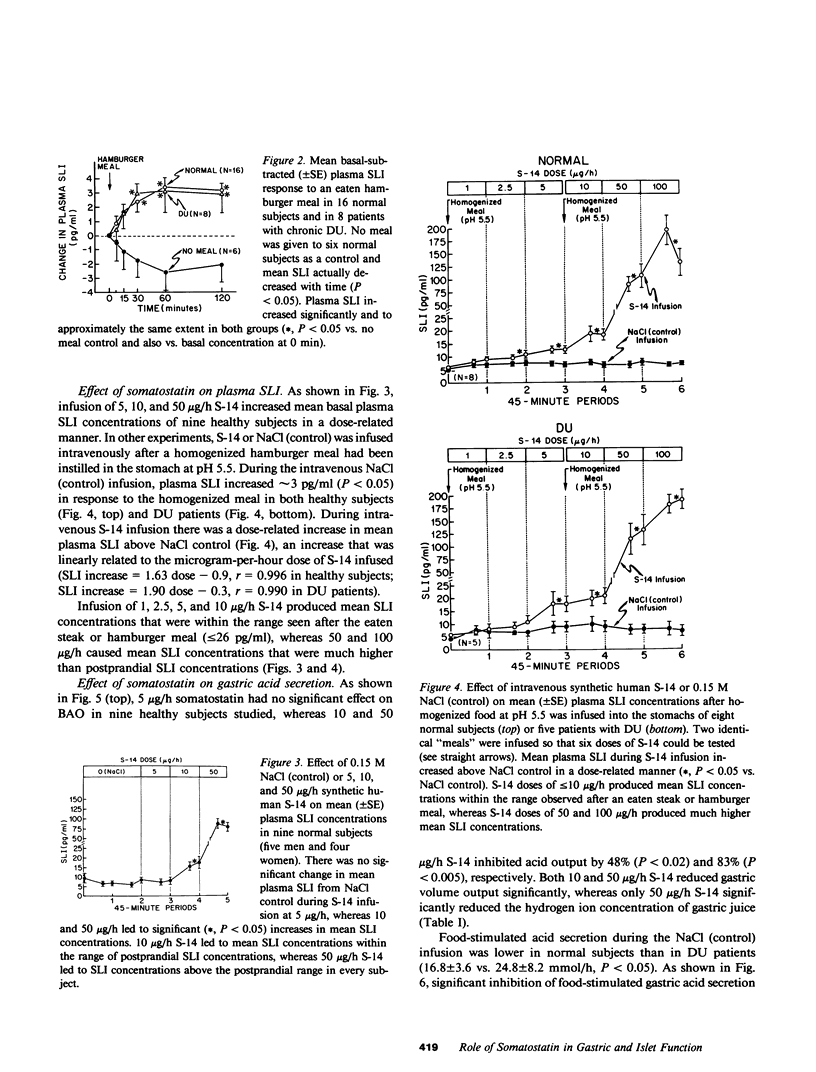
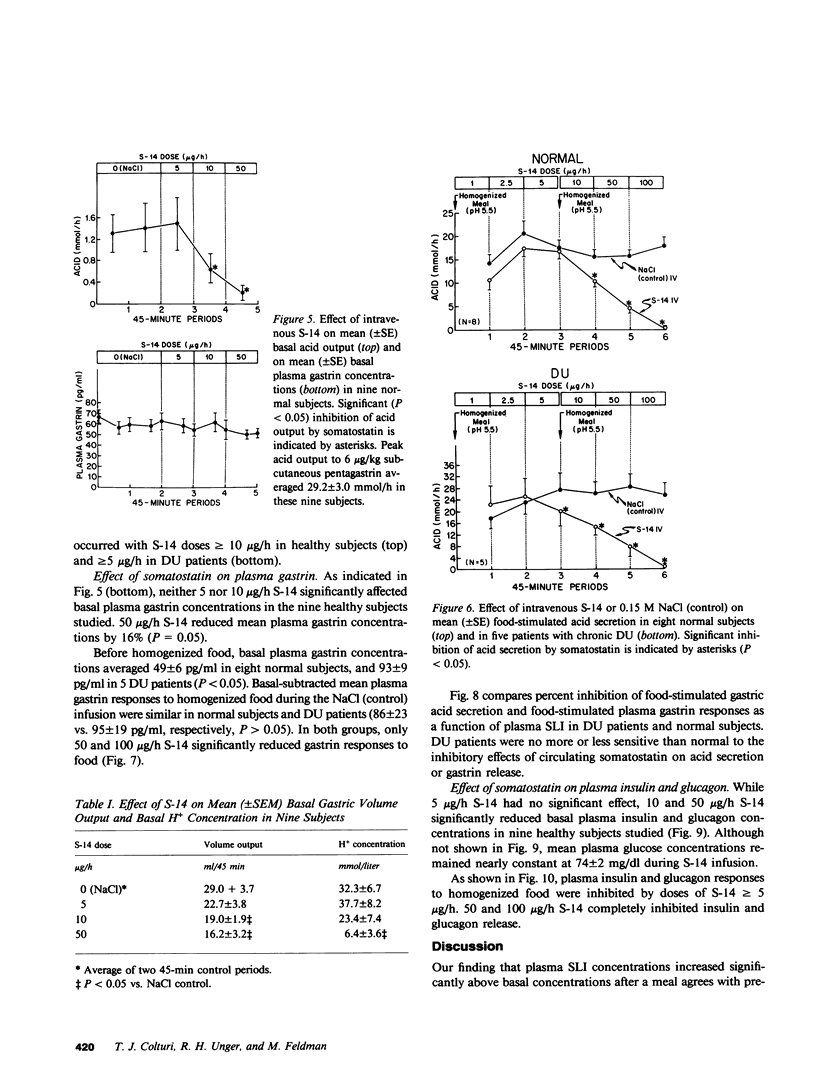
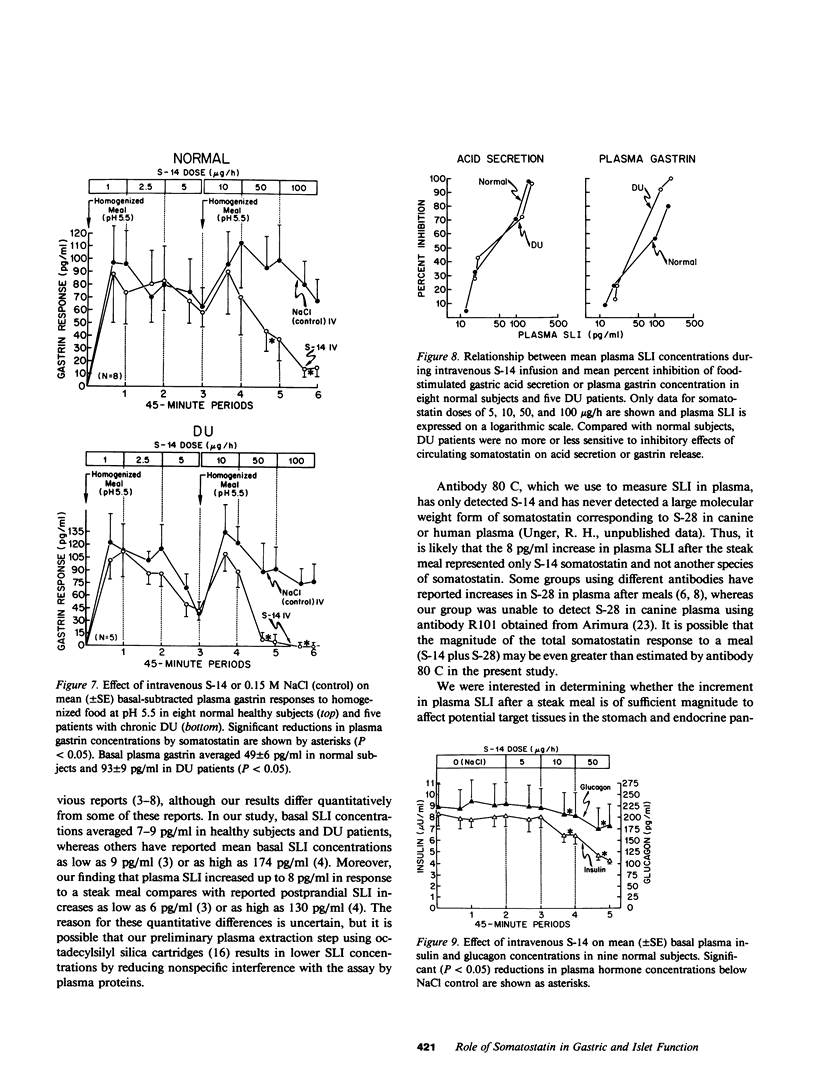
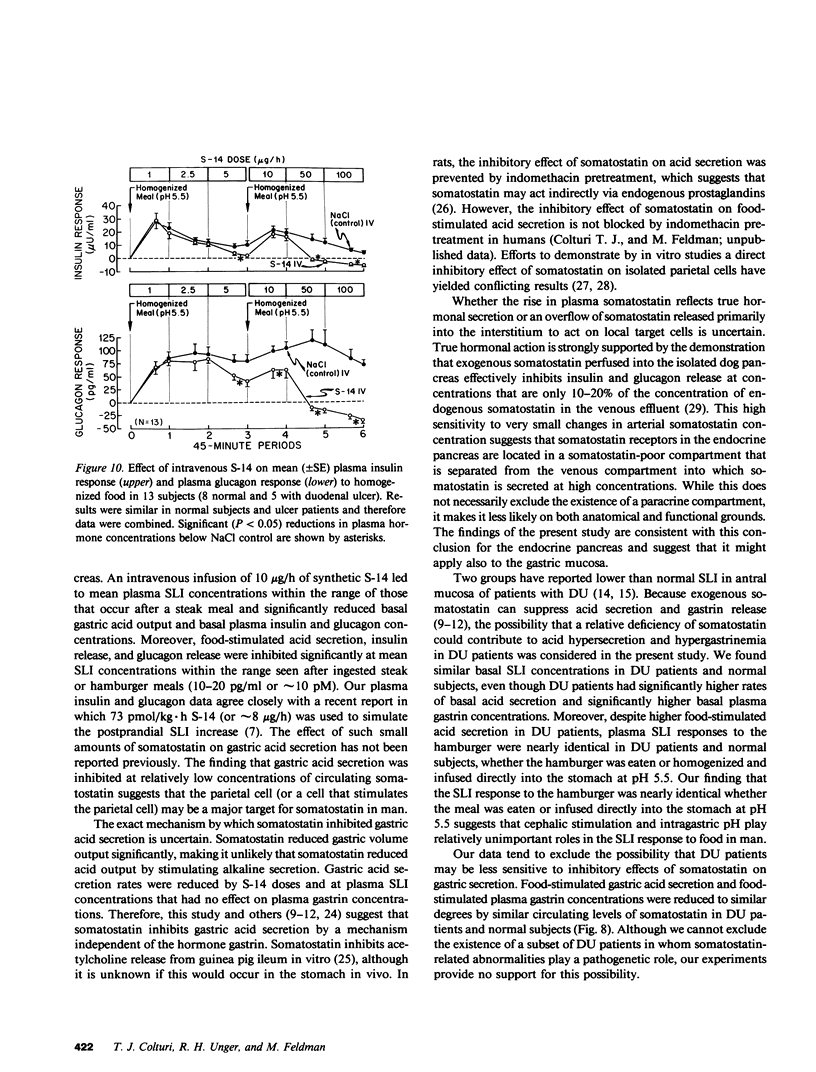
Studies were designed (a) to determine whether somatostatin is released into the circulation after meals in sufficient amounts to regulate gastric or pancreatic islet function in humans and (b) to investigate the possible role of somatostatin in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer disease. Mean plasma somatostatin-like immunoreactivity (SLI) increased from 6.2 +/- 1.5 pg/ml to a peak level of 13.8 +/- 1.3 pg/ml in eight healthy subjects after a 1,440-cal steak meal (P less than 0.005). When somatostatin-14 was infused intravenously, basal and food-stimulated gastric acid secretion and also basal and food-simulated plasma insulin and glucagon concentrations were reduced significantly at mean plasma SLI concentrations within the range seen after a meal. Thus, the amount of somatostatin reaching the systemic circulation after a steak meal was sufficient to inhibit gastric acid secretion and islet cell function. On the other hand, basal and food-stimulated plasma gastrin concentrations were reduced by intravenous somatostatin only at plasma SLI concentrations that were several-fold greater than post-prandial SLI concentrations. Although duodenal ulcer patients had significantly higher basal, food-stimulated, and peak pentagastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretion rates than healthy controls, duodenal ulcer patients and controls had nearly identical basal and food-stimulated SLI concentrations. Moreover, food-stimulated gastric acid secretion and gastrin release were inhibited by intravenous somatostatin to the same extent in ulcer patients and controls. These studies suggest that duodenal ulcer patients release normal amounts of somatostatin into the circulation and that target cells controlling acid secretion and gastrin release are normally sensitive to somatostatin in these patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom S. R., Mortimer C. H., Thorner M. O., Besser G. M., Hall R., Gomez-Pan A., Roy V. M., Russell R. C., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J. Inhibition of gastrin and gastric-acid secretion by growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone. Lancet. 1974 Nov 9;2(7889):1106–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90869-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chayvialle J. A., Descos F., Bernard C., Martin A., Barbe C., Partensky C. Somatostatin in mucosa of stomach and duodenum in gastroduodenal disease. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew C. S. Inhibitory action of somatostatin on isolated gastric glands and parietal cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):G221–G229. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.2.G221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Walsh J. H. Gastric acid secretion rate and buffer content of the stomach after eating. Results in normal subjects and in patients with duodenal ulcer. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):645–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI107226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R. Somatostatin inhibits the release of acetylcholine induced electrically in the myenteric plexus. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1653–1654. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai K., Ipp E., Orci L., Perrelet A., Unger R. H. Circulating somatostatin acts on the islets of Langerhans by way of a somatostatin-poor compartment. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):477–478. doi: 10.1126/science.6126931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Swierczek J., Kwiecień N., Mikoś E., Oleksy J., Wierzbicki Z. Effect of somatostatin on meal-induced gastric secretion in duodenal ulcer patients. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Nov;22(11):981–988. doi: 10.1007/BF01076197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Goltermann N., de Magistris L., Rehfeld J. F., Schwartz T. W. Somatostatin cell processes as pathways for paracrine secretion. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1393–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.382360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Goto Y., Debas H., Yamada T. Prostaglandins mediate inhibition of gastric acid secretion by somatostatin in the rat. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6129701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE E. W., SCARLATA R. W. THE DETERMINATION OF GASTRIC ACIDITY BY THE GLASS ELECTRODE. Gastroenterology. 1965 Aug;49:178–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman E., Wass J. A., Medbak S., Morgan L., Lewis J. M., Besser G. M., Rees L. H. Response of circulating immunoreactive somatostatin to nutritional stimuli in normal subjects. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):692–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Payne N. A., Gerber J. G. Effect of somatostatin, secretin, and glucagon on secretagogue stimulated aminopyrine uptake in isolated canine parietal cells. Agents Actions. 1983 Jun;13(4):265–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01971476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillip J., Domschke S., Domschke W., Urbach H. J., Reiss M., Demling L. Inhibition by somatostatin of gastrin release and gastric acid responses to meals and to pentagastrin in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(3):261–265. doi: 10.3109/00365527709180926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Shoelson S. E., Docherty H. M. Plasma somatostatin 28 increases in response to feeding in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1172/JCI110907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schusdziarra V., Zyznar E., Rouiller D., Harris V., Unger R. H. Free somatostatin in the circulation: amounts and molecular sizes of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in portal, aortic, and vena caval plasma of fasting and meal-stimulated dogs. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1572–1576. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souquet J. C., Rambliere R., Riou J. P., Beylot M., Cohen R., Mornex R., Chayvialle J. A. Hormonal and metabolic effects of near physiological increase of plasma immunoreactive somatostatin 14. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 May;56(5):1076–1079. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-5-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumii K., Fukushima T., Hirata K., Matsumoto Y., Sanuki E., Tsumaru S., Sumioka M., Miyoshi A., Miyachi Y. Antral gastrin and somatostatin concentrations in peptic ulcer patients. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 2):281–283. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda K., Sakurai H., Seino Y., Seino S., Tanigawa K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. Somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in human peripheral plasma measured by radioimmunoassay following affinity chromatography. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):471–474. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez B., Harris V., Unger R. H. Extraction of somatostatin from human plasma on octadecylsilyl silica. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Oct;55(4):807–809. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-4-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatn M. H., Schrumpf E., Hanssen K. F., Myren J. The effect of somatostatin on pentagastrin-stimulated gastric secretion and on plasma gastrin in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(7):833–839. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A. I., Levitt N. S., Pimstone B. L., Wagner L. Peripheral plasma somatostatin-like immunoreactive responses to insulin hypoglycemia and a mixed meal in healthy subjects and in noninsulin-dependent maturity-onset diabetics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Feb;52(2):330–337. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wass J. A., Penman E., Dryburgh J. R., Tsiolakis D., Goldberg P. L., Dawson A. M., Besser G. M., Rees L. H. Circulating somatostatin after food and glucose in man. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1980 Jun;12(6):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1980.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


