Abstract
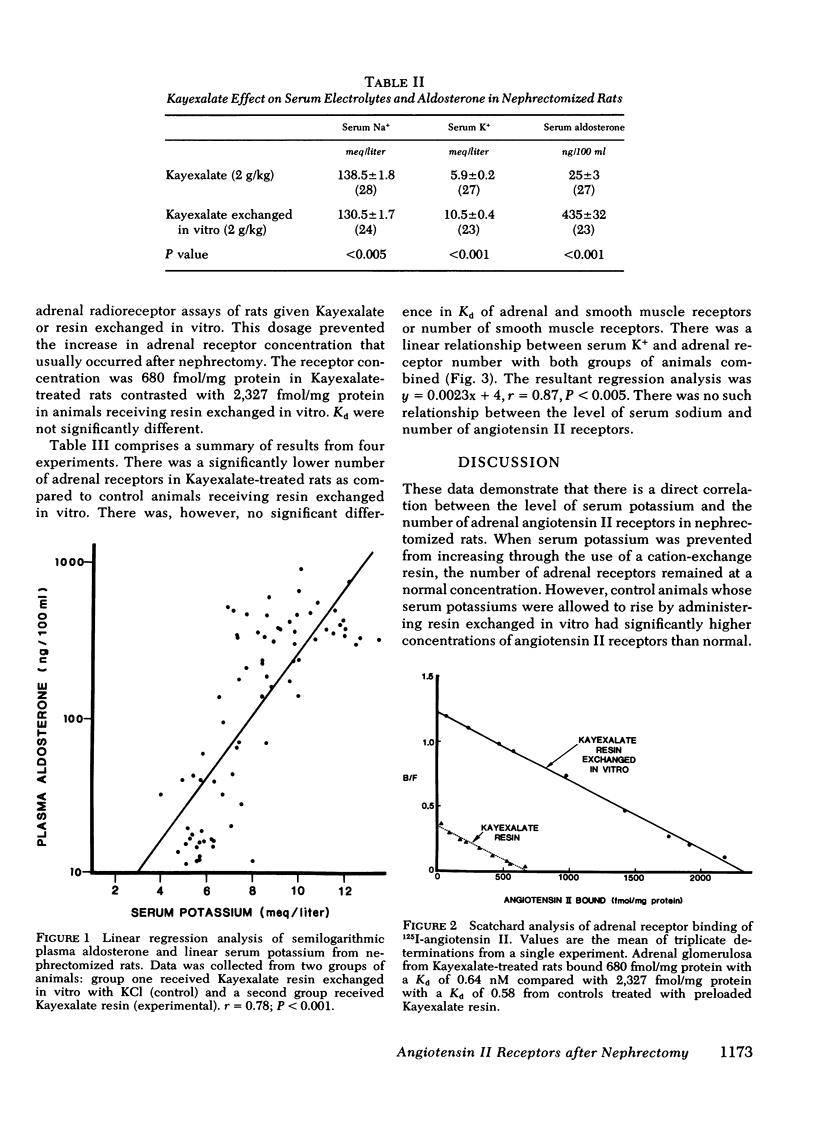
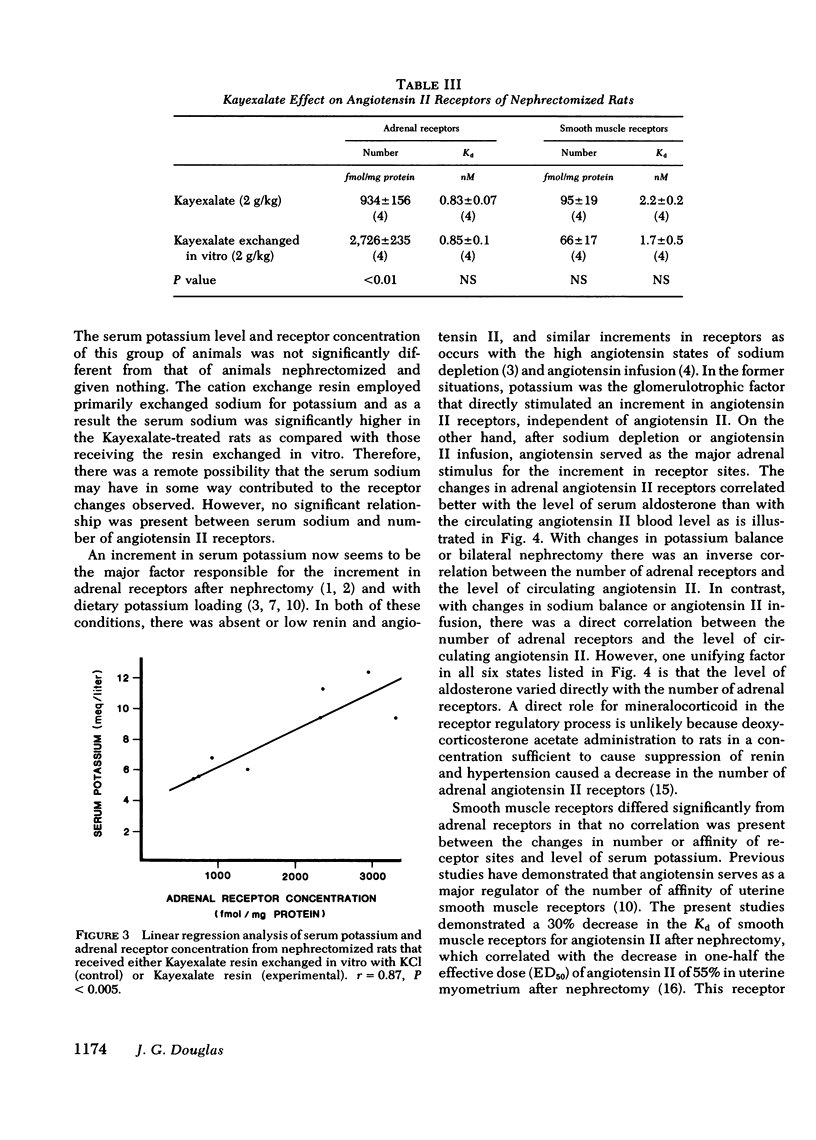
At 48 h after bilateral nephrectomy in rats there is a two- to threefold increase in the number of adrenal angiotensin II receptors and a decrease in Kd of smooth muscle angiotensin II receptors. These changes have been attributed to the absence of circulating angiotensin II. Serum K+, which increases after nephrectomy may be an important and overlooked modulator. Therefore, the present experiments were designed to assess the role of K+ as a regulator of angiotensin II receptors after nephrectomy. Serum K+ was controlled with Na polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate), a resin designed to exchange Na+ for K+ in the gastrointestinal tract. Acutely nephrectomized rats were divided into two groups: experimental animals received Kayexalate resin every 12 h for four doses, and controls received Kayexalate exchanged with KCl in vitro before gavage. There was a significant positive correlation serum K+ and aldosterone (r = 0.78, P less than 0.001). Kayexalate maintained a normal serum K+ of 5.9 +/- 0.2 meq/liter (n = 27), aldosterone 25 +/- 3 ng/dl (n = 27) and adrenal receptor concentration of 934 +/- 156 fmol/mg protein (n = 4). Control animals had significantly higher serum K+ of 10.5 +/- 0.4 meq/liter (n = 23), aldosterone 435 +/- 32 (n = 23), and adrenal receptors of 2726 +/- 235 fmol/mg protein (n = 4). There was a linear relationship between serum K+ and number of adrenal receptors (r = 0.87). No such relationship was present in uterine smooth muscle. Therefore, these studies demonstrate that K+ modulates the number of adrenal but not smooth muscle angiotensin II receptors after nephrectomy. This is the first evidence that potassium modulates angiotensin II receptors independently of changes in angiotensin II blood levels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAQUIER P., HOOBLER S. W., SCHROEDER J., GOMEZ A., KREULEN T. Effect of bilateral nephrectomy on pressor response to renin. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:339–343. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayard F., Cooke C. R., Tiller D. J., Beitins I. Z., Kowarski A., Walker W. G., Migeon C. J. The regulation of aldosterone secretion in anephric man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1585–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI106646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., URQUHART J., HIGGINS J. T., Jr The effects of alteration of plasma sodium and potassium concentration on aldosterone secretion. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI104750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Burwell L. R., Bartter F. C. Inhibition of the effects of angiotensin II on adrenal steroid production by dietary sodium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):718–723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Pernollet M. G., Matthews P. G., Macdonald G. J., Raisman R. S., Meyer P. Sodium intake and plasma angiotensin level as modulators of adrenal and uterine angiotensin II receptors in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):163–179. doi: 10.1097/00005344-197903000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Pernollet M. G., Matthews P. G., Macdonald G. J., Raisman R. S., Meyer P. Sodium intake and plasma angiotensin level as modulators of adrenal and uterine angiotensin II receptors in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):163–179. doi: 10.1097/00005344-197903000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Rouzaire-Dubois B., Chevillotte E., Meyer P. Variations in the number of uterine angiotensin receptors following changes in plasma angiotensin levels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;40(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G., Michailov M., Khosla M. C., Bumpus F. M. Comparative receptor-binding properties of heptapeptide and octapeptide antagonists of angiotensin II in rat adrenal glomerulosa and uterine smooth muscle. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):120–124. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G. Potassium ion as a regulator of adrenal angiotensin II receptors. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):E317–E321. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.5.E317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J., Catt K. J. Regulation of angiotensin II receptors in the rat adrenal cortex by dietary electrolytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):834–843. doi: 10.1172/JCI108536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauger R. L., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Angiotensin II regulates its receptor sites in the adrenal glomerulosa zone. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):176–178. doi: 10.1038/271176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaa R. E., McCaa C. S., Read D. G., Bower J. D., Guyton A. C. Increased plasma aldosterone concentration in response to hemodialysis in nephrectomized man. Circ Res. 1972 Oct;31(4):473–480. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. K., Clements J. A. Simplified radioimmunoassay for serum aldosterone utilizing increased antibody specificity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):622–627. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer P., Papadimitriou A., Worcel M. Specific supersensitivity of smooth muscle to angiotensin II after nephrectomy. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;51(3):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb10679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Genuth S. M., Berman L. B., Vertes V. Aldosterone secretion in anephric patients. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 13;286(2):61–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201132860204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmore W. P., Marieb N. J., Mulrow P. J. Stimulation of aldosterone secretion by sodium depletion in nephrectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1969 Jun;84(6):1342–1351. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-6-1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernollet M. G., Devynck M. A., Matthews P. G., Meyer P. Post-nephrectomy changes in adrenal angiotensin II receptors in the rat; influence of exogenous angiotensin and a competitive inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 15;43(4):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read V. H., McCaa C. S., Bower J. D., McCaa R. E. Effect of hemodialysis on the metabolic clearance rate, plasma concentration and blood production rate of aldosterone in anephric man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):773–778. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzaire-Dubois B., Devynck M. A., Chevillotte E., Meyer P. Angiotensin receptors in rat uterine membranes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouder D. A., Wathen R. L. Augmented vascular response of the nephrectomized rat to angiotensin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):548–551. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


