Abstract
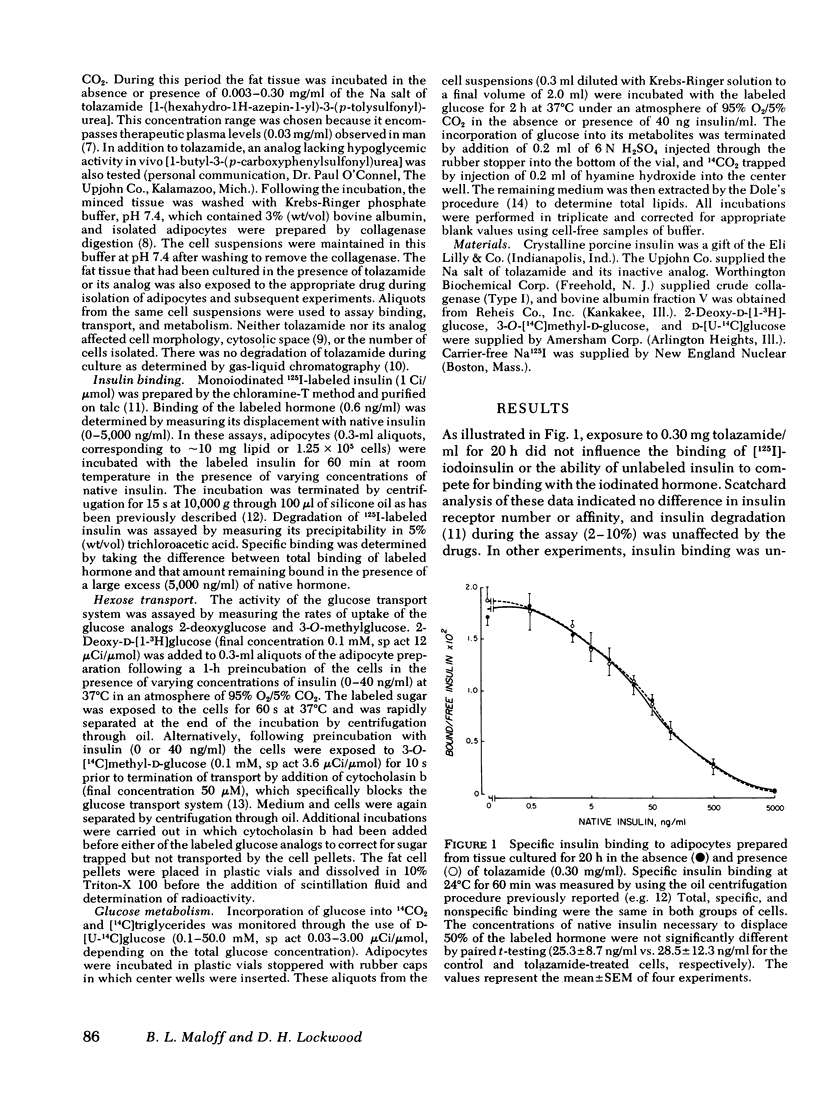
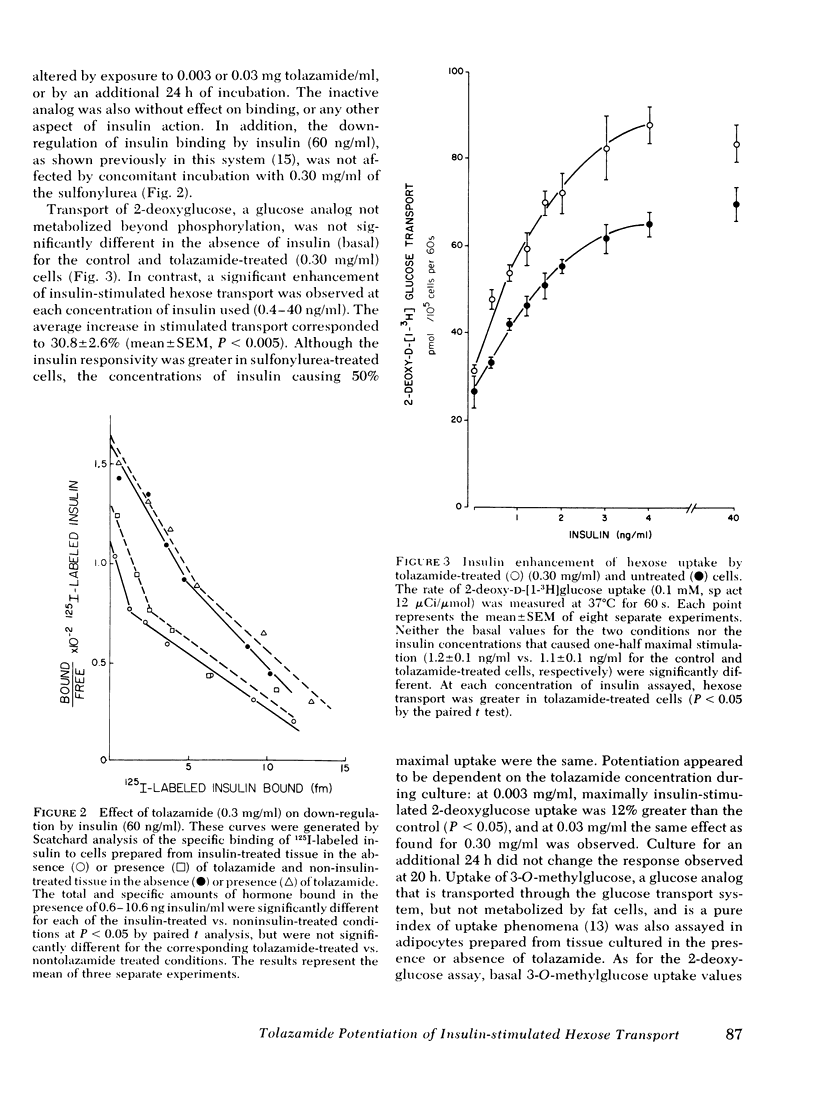
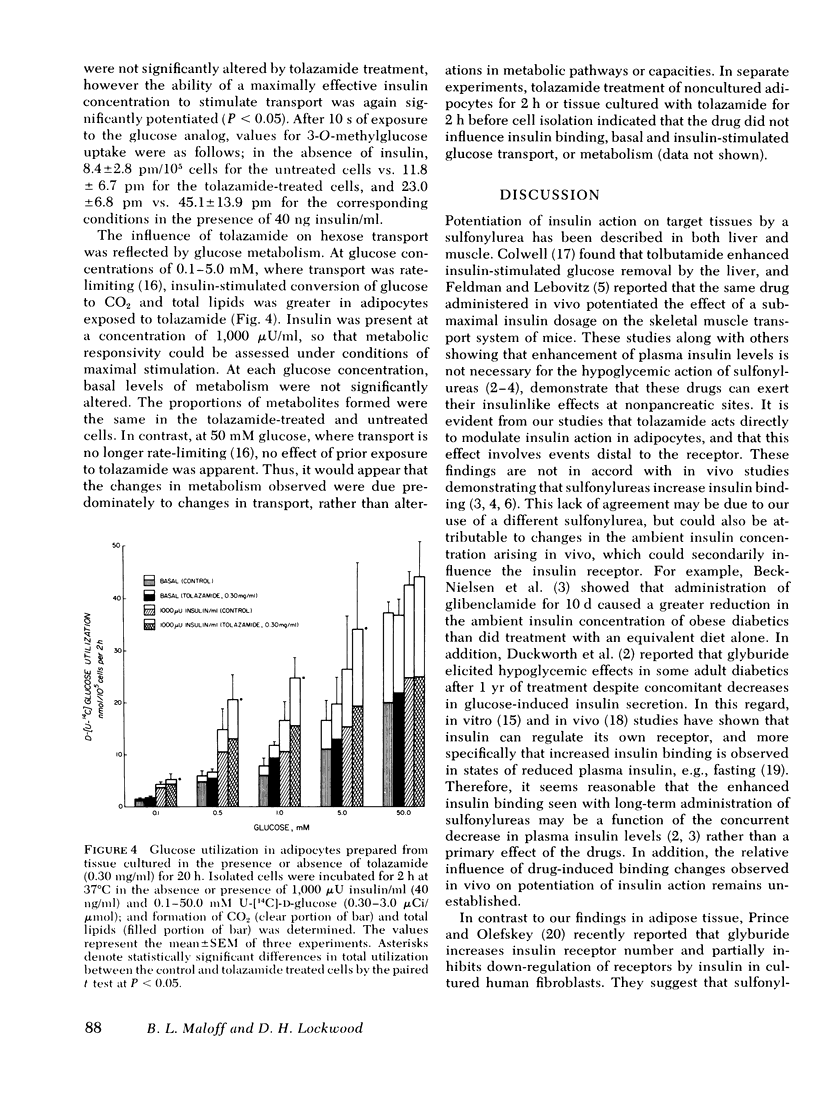
The mechanism(s) by which the oral sulfonylurea, tolazamide, exerts its extrapancreatic hypoglycemic effects was studied using rat epididymal adipose tissue maintained 20-44 h in the presence or absence of the drug. Insulin binding, hexose transport and glucose metabolism were compared in adipocytes isolated from the cultured tissue. In contrast to earlier reports that suggested that sulfonylureas alter the binding of insulin, neither receptor number nor affinity were changed by tolazamide treatment. The uptake of the glucose analogs 2-deoxyglucose and 3-0-methylglucose in the absence of insulin (i.e., basal) was also unchanged. However, exposure to tolazamide resulted in a potentiation of the stimulatory effects of insulin by approximately 30% at each hormone concentration assayed (0.4-40 ng/ml). This potentiation was dependent on the tolazamide concentration (0.003-0.30 mg/ml), with a maximal effect observed at therapeutic levels. A tolazamide analog hypoglycemic activity in vivo was found not to enhance either basal or insulin-stimulated uptake in vitro. Conversion of 0.1-5.0 mM glucose to CO2 and total lipids in the presence of insulin was also potentiated by tolazamide treatment. The inability of the drug to directly stimulate basal glucose uptake was paralleled by its lack of effect on glucose metabolism. At 50 mM glucose, where transport is no longer rate-limiting, tolazamide did not potentiate metabolism in the absence or the presence of insulin. These studies demonstrate that tolazamide in vitro alters postreceptor insulin action without influencing the receptor, and suggests insulin-stimulated hexose transport as the cellular process responsible for the hypoglycemic effect of sulfonyureas in adipose tissue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal V., Sunshine I. Determination of sulfonylureas and metabolites by pyrolysis gas chromatography. Clin Chem. 1974 Feb;20(2):200–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda J. M., Finch E. D. Modulation of hexose uptake and insulin action by cell membrane fluidity. The effects of temperature on membrane fluidity, insulin action, and insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2619–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D., Jr, Prince M., Marshall S., Davies P., Olefsky J. M. Regulation of insulin receptors: evidence for involvement of an endocytotic internalization pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5975–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Harrison L. C., Muggeo M., Gorden P., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors in normal and abnormal physiology in humans. Adv Intern Med. 1979;24:23–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Nielsen H., Pedersen O., Lindskov H. O. Increased insulin sensitivity and cellular insulin binding in obese diabetics following treatment with glibenclamide. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Mar;90(3):451–462. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL A. R., Jr POTENTIATION OF INSULIN ACTION ON THE LIVER BY TOLBUTAMIDE. Metabolism. 1964 Nov;13:1310–1317. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(64)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofford O. B. The uptake and inactivation of native insulin by isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Regulation of the D-glucose transport system in isolated fat cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Mar 26;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01792833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Davies D. R., Levitzki A., Maxfield F. R., Milhaud P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Transglutaminase is essential in receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and polypeptide hormones. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):162–167. doi: 10.1038/283162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Solomon S. S., Kitabchi A. E. Effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on plasma insulin and proinsulin levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Oct;35(4):585–591. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-4-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinglos M. N., Lebovitz H. E. Sulphonylureas increase the number of insulin receptors. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):184–185. doi: 10.1038/276184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Lebovitz H. E. An insulin dependent effect of chronic tolbutamide administration on the skeletal muscle carbohydrate transport system. Diabetes. 1969 Feb;18(2):84–95. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.2.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Epstein G. H., Fanska R., Karam J. H. Pancreatic action of the sulfonylureas. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2714–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Inhibitors of 125I-epidermal growth factor internalization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):630–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. Effect of cytochalasin B and D on groups of insulin receptors and on insulin action in rat adipocytes. Possible evidence for a structural relationship of the insulin receptor to the glucose transport system. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):571–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. The natural occurrence of insulin receptors in groups on adipocyte plasma membranes as demonstrated with monomeric ferritin-insulin. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):45–59. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Direct measurements of sugar uptake in small and large adipocytes from young and adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Purvis B. J., Lockwood D. H. Insulin induced changes in insulin binding and insulin-sensitivity of adipocytes. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):2009–2014. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloff B. L., Levine J. H., Lockwood D. H. Direct effects of growth hormone on insulin action in rat adipose tissue maintained in vitro. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):538–544. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Effects of sulfonylurea therapy on insulin binding to mononuclear leukocytes of diabetic patients. Am J Med. 1976 Jan;60(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Insulin binding in diabetes. Relationships with plasma insulin levels and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):680–688. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince M. J., Olefsky J. M. Direct in vitro effect of a sulfonylurea to increase human fibroblast insulin receptors. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):608–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI109894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


