Abstract
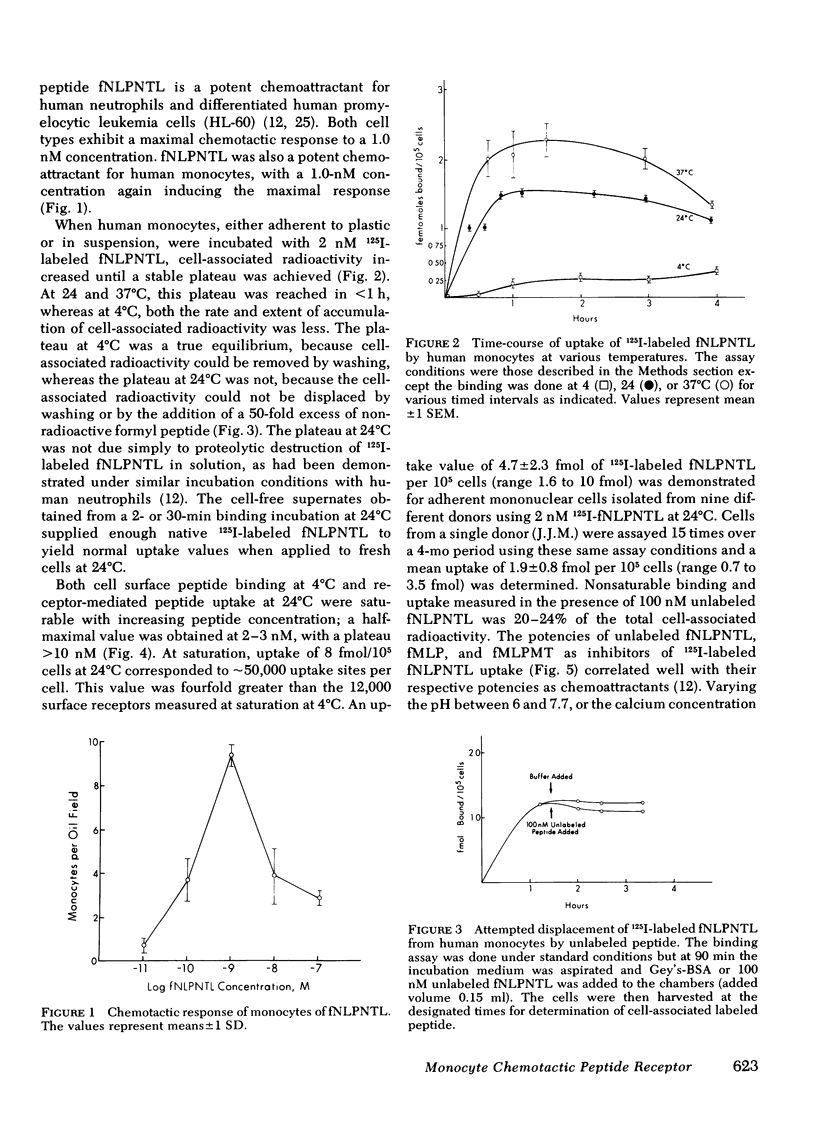
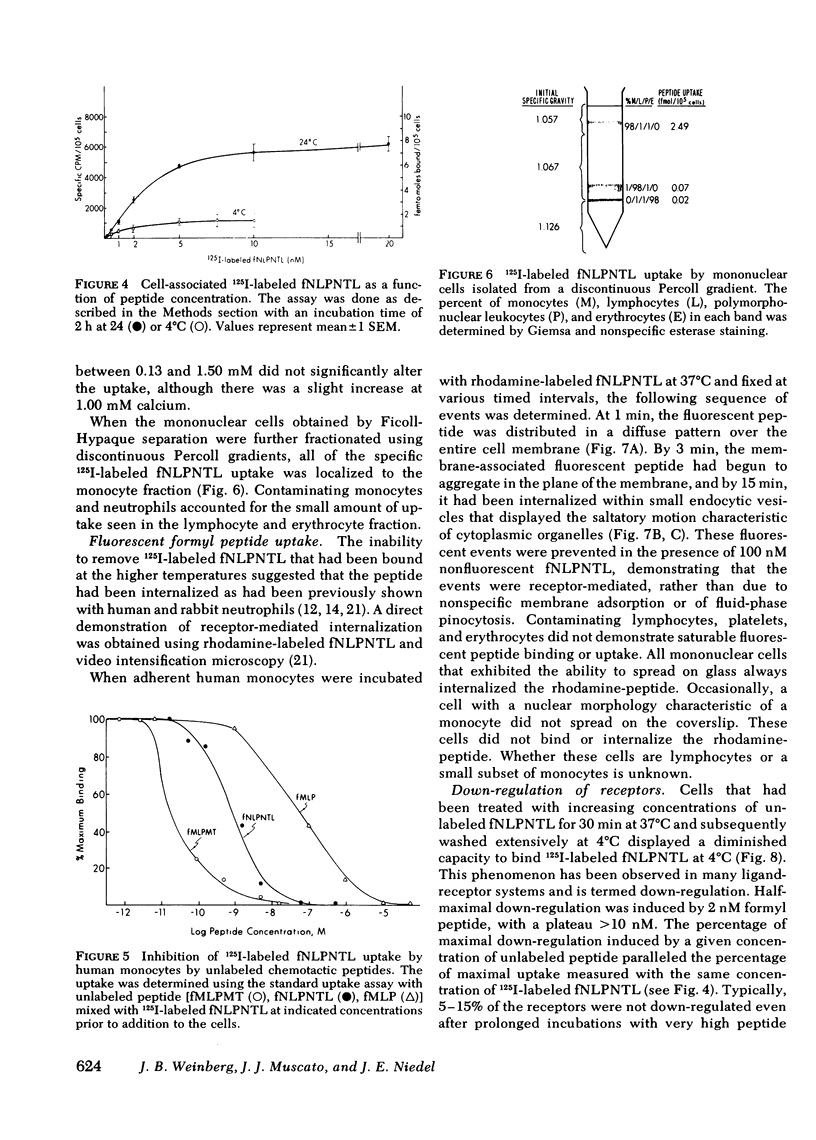
Monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils will demonstrate several important cellular functions in response to synthetic formylated oligopeptides. N-formyl-norleucyl-leucyl-phenylalanyl-norleucyl-tyrosyl-lysine (fNLPNTL) was a potent chemoattractant for human blood monocytes; a 1.0-nM concentration induced a maximal chemotactic response. Binding of 125I-labeled fNLPNTL to the monocyte formyl peptide receptor was rapid, specific, and saturable at 4, 24, or 37 degrees C. At 4 degrees C, monocytes from several different donors demonstrated between 10,000 and 18,000 receptors/cell with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 1.7-2.7 nM. The association of the 125I peptide with the cells was irreversible at the elevated temperatures and exceeded the amount of surface receptor by approximately four-fold, suggesting receptor-mediated peptide endocytosis. Processing of rhodamine-labeled fNLPNTL by monocytes was observed directly by video intensification microscopy. At 37 degrees C, diffuse membrane fluorescence was seen initially, followed by rapid aggregation and internalization of the peptide. Monocytes incubated with fNLPNTL displayed a temperature dependent loss of surface binding capacity (receptor down-regulation). This decrease was due to a decrease in surface receptor number rather than to a decrease in receptor affinity. A dose-response curve for peptide-induced receptor down-regulation correlated with a dose-response curve for 125I-labeled fNLPNTL uptake, suggesting that each uptake event led to the loss of one surface receptor. Surface receptor replenishment following down-regulation was rapid and not dependent on new protein synthesis, but was inversely related to both the time and peptide concentration used to induce down-regulation. An exact correlation between receptor down-regulation and functional deactivation of the chemotactic response could not be demonstrated.
Full text
PDF

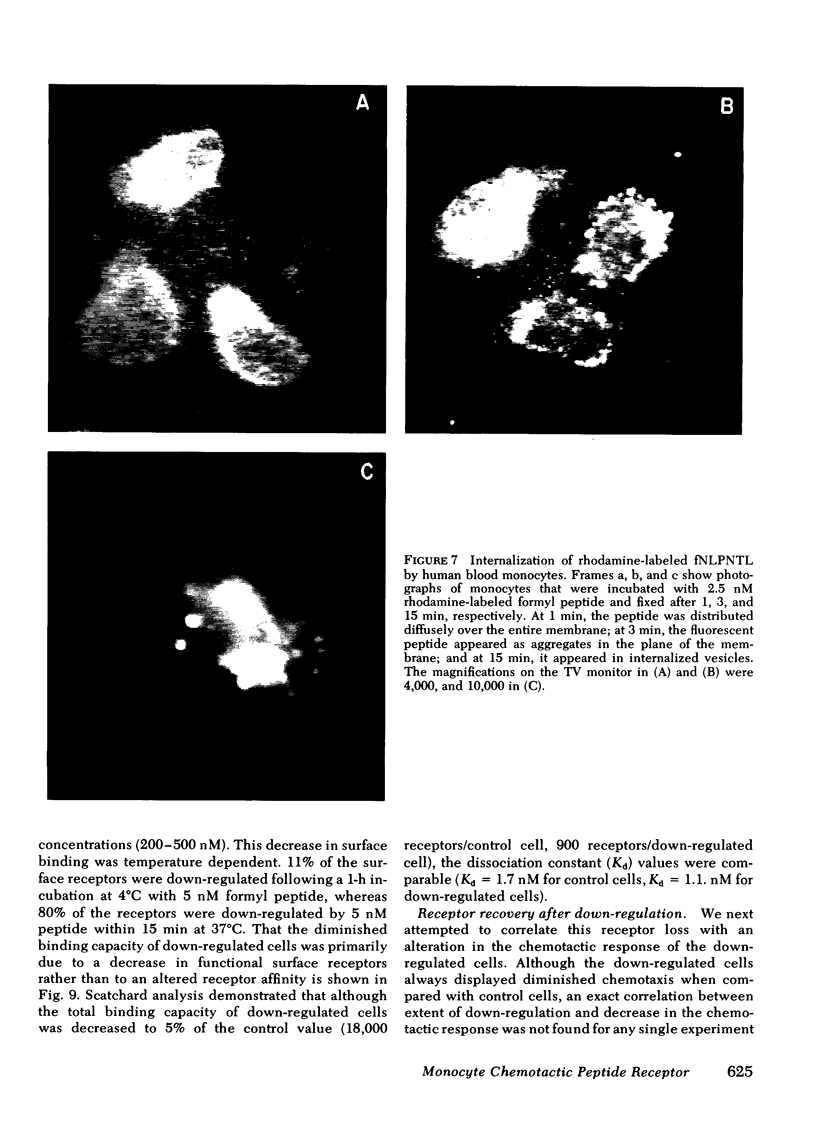
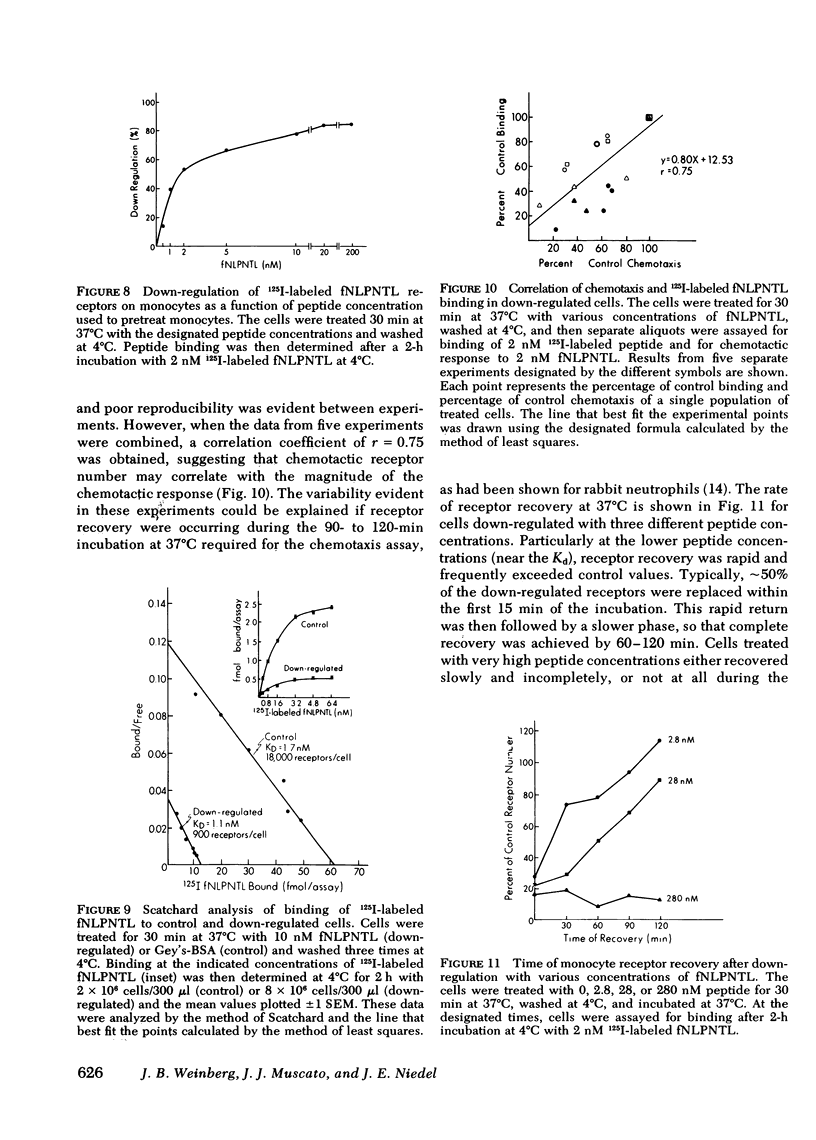
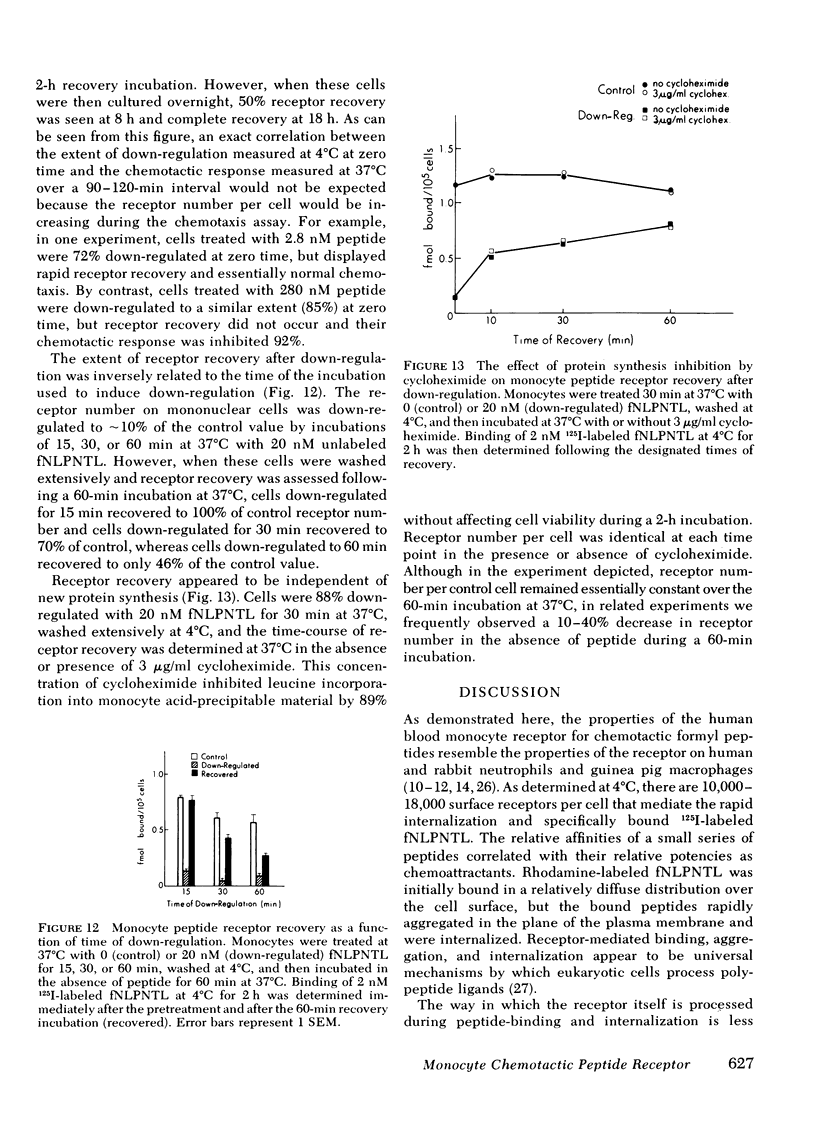



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Studies of the macrophage complement receptor. Alteration of receptor function upon macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1278–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli increase the availability of receptors on human neutrophils for the chemoattractant f-met-leu-phe. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1585–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Schiffmann E. Role of secretory events in modulating human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1364–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI109257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. The macrophage as an antineoplastic surveillance cell: biological perspectives. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):549–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Evidence for reutilization of surface receptors for alpha-macroglobulin.protease complexes in rabbit alveolar macrophages. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Tomasulo P. A., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in human blood and demonstration of an inhibitor. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):903–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. S., Freer R. J. Cryptic receptors for chemotactic peptides in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 28;93(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Fiegel V. D., Herron M. J., Simmons R. L. Chemotactic deactivation of human neutrophils: relationship to loss of cytotaxin receptor function and temporal nature of the phenomenon. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Sep;28(3):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., McCormack R. T., Fiegel V. D., Simmons R. L. Chemotactic deactivation of human neutrophils: evidence for nonspecific and specific components. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):441–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.441-444.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Cuatrecasas P. Formyl peptide chemotactic receptors of leukocytes and macrophages. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;17:137–170. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152817-1.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kahane I., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated internalization of fluorescent chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.472759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Kahane I., Lachman L., Cuatrecasas P. A subpopulation of cultured human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) displays the formyl peptide chemotactic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1000–1004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Vitkauskas G., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Selective neutrophil desensitization to chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):564–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Williams D., Becker E. L., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. Desensitization and deactivation of the secretory responsiveness of rabbit neutrophils induced by the chemotactic peptide, formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Feb;25(2):139–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Patrick R. A., Hassett C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Effects of chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):221–229. doi: 10.1172/JCI109293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Altman L. C., Hausman M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Human mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis: a quantitative assay for humoral and cellular chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Fudman E. J. Demonstration of a chemotactic factor receptor on macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2754–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. J., Zigmond S. H. Chemotactic peptide receptor modulation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):703–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D. Discontinuous density gradient separation of human mononuclear leucocytes using Percoll as gradient medium. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. The regulatory role of macrophages in antigenic stimulation. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:95–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitkauskas G., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Specific binding of synthetic chemotactic peptides to rabbit peritoneal neutrophils: effects on dissociability of bound peptide, receptor activity and subsequent biologic responsiveness (deactivation). Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Characterization of the effects of endotoxin on macrophage tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Sullivan S. J. Sensory adaptation of leukocytes to chemotactic peptides. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]