Abstract
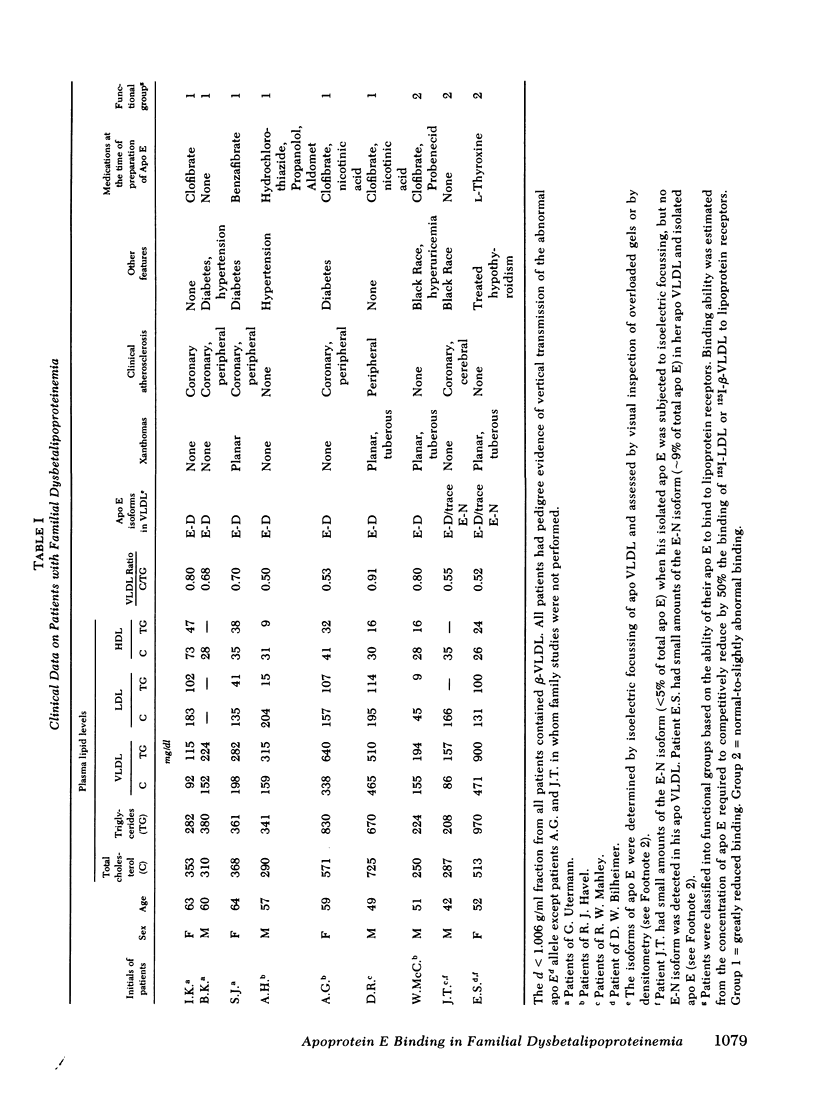
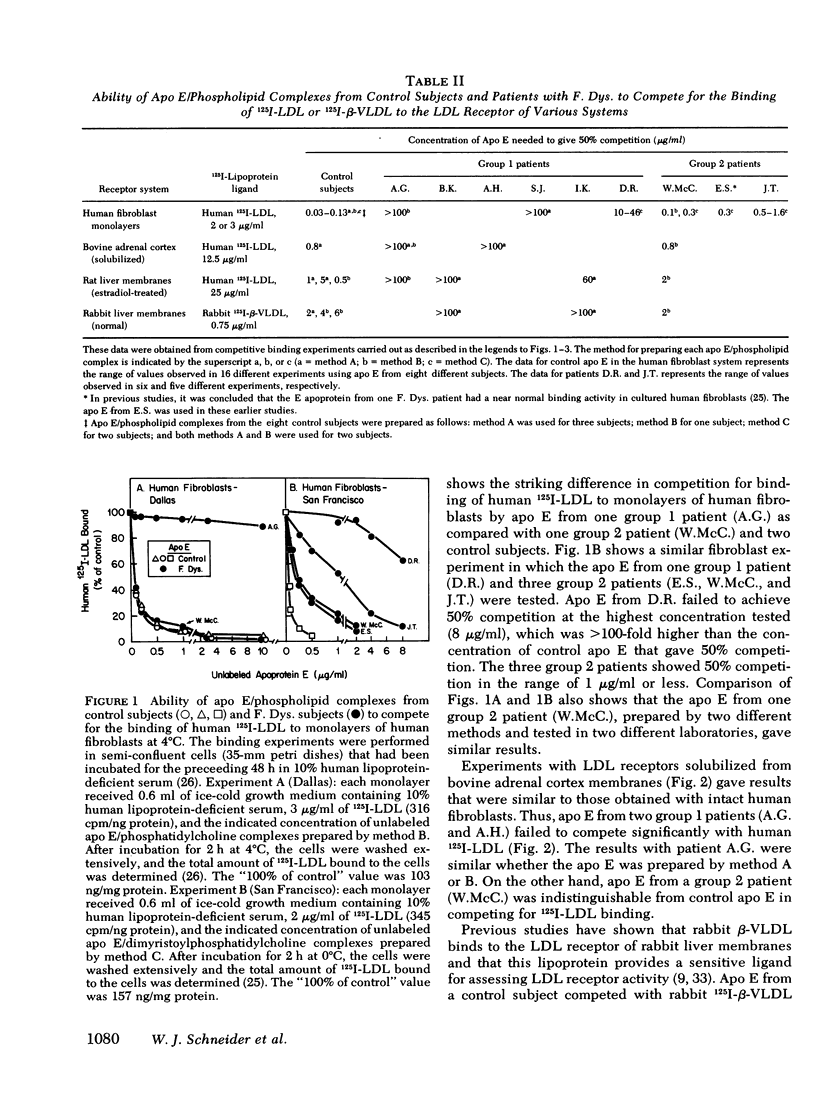
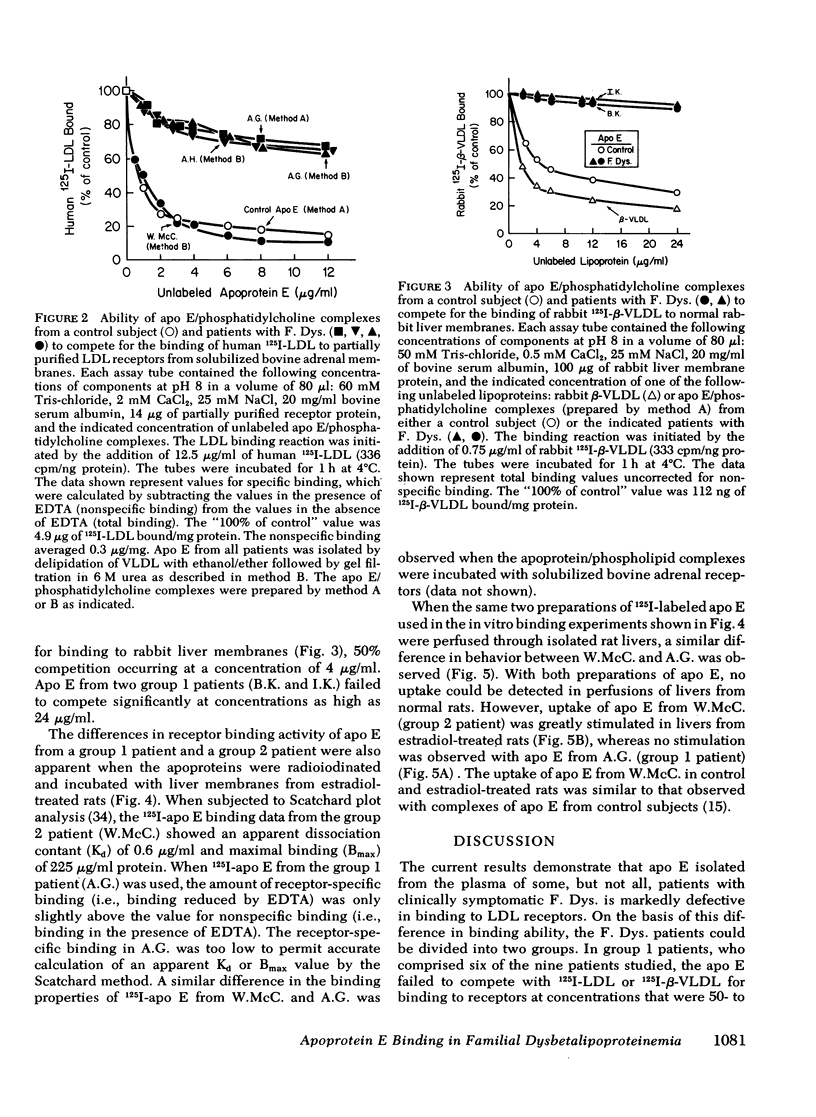
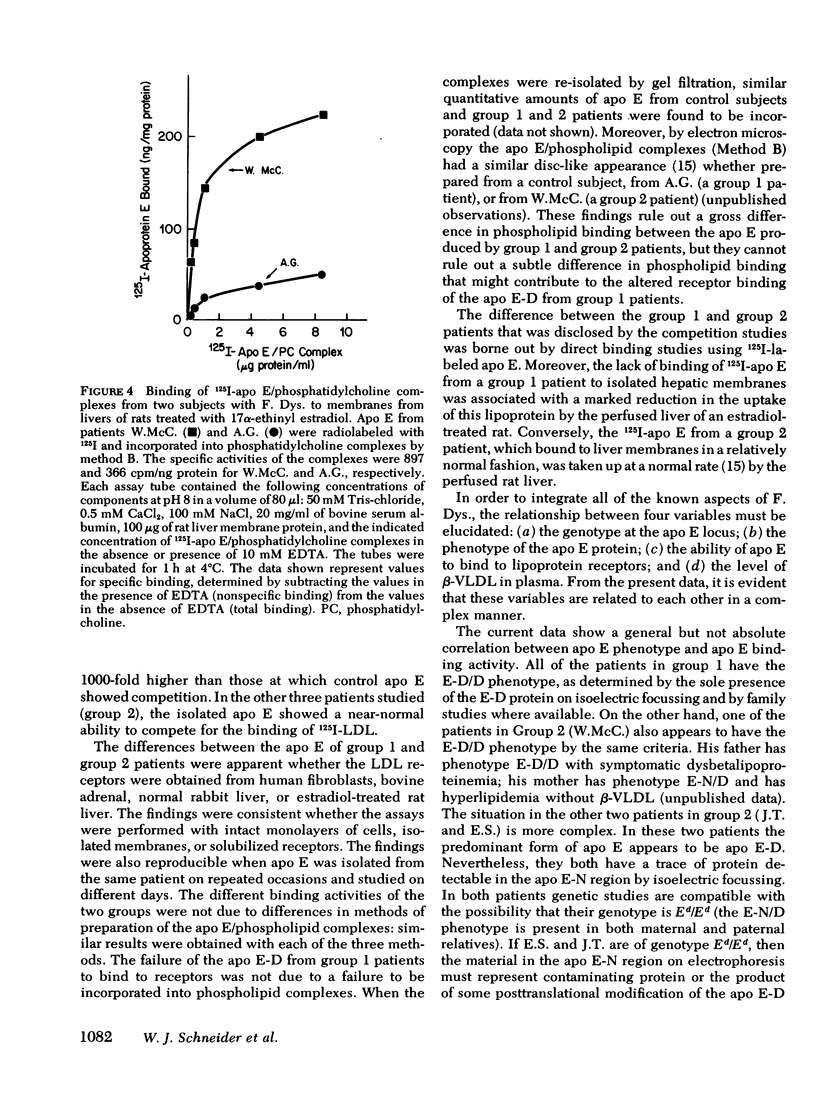
Patients with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (F. Dys.), also called familial type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia, are homozygous for a mutant allele, Ed, that specifies an abnormal form of apoprotein (apo) E, a prominent constituent of remnant lipoproteins derived from very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and chylomicrons. Apo E is thought to mediate the removal of remnant lipoproteins from the plasma by virtue of its ability to bind to hepatic lipoprotein receptors. In F. Dys. patients, remnant-like lipoproteins accumulate, apparently because of delayed clearance by the liver. In the current studies, we show that the abnormal protein specified by the Ed allele (apo E-D) from some, but not all, patients with F. Dys. has a markedly deficient ability to bind to low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors. Apo E was isolated from eight control subjects and nine patients with F. Dys. and incorporated into phospholipid complexes. The complexes were tested for their ability to compete with human 125I-LDL or rabbit 125I-beta-VLDL fo binding to LDL receptors in four assay systems: cultured human fibroblasts, solubilized receptors from bovine adrenal cortex, liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol, and liver membranes from normal rabbits. The apo E-D from six of the nine patients with F. Dys. showed binding affinities for LDL receptors that were reduced by greater than 98% in all receptor assays (group 1 patients). All of these group 1 patients were unequivocally of phenotype apo E-D/D by the criterion of isoelectric focussing. The apo E from the three other F. Dys. patients showed a near normal binding ability in all four of the receptor assays (group 2 patients). One of these group 2 patients appeared to have the apo E-D/D phenotype by isoelectric focussing. In the other two patients in group 2, apo E-D was the predominant protein (phenotype, apo E-D/D), but traces of protein in the region corresponding to normal apo E (apo E-N) were also present. The difference between group 1 and group 2 patients was also apparent when the apo E was iodinated and tested directly for binding to liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. The 125I-labeled apo E from a group 2 patient, but not a group 1 patient, showed enhanced uptake when perfused through the liver of an estradiol-treated rate, indicating that the receptor binding ability of apo E correlated with uptake in the intact liver. The current studies allow the subdivision of patients with F. Dys. into two groups. In group 1, the elevated plasma level of remnants appears to be due to a diminished receptor binding activity of the abnormal protein specified by the Ed allele; in group 2 patients, the cause of the elevated plasma level of remnants remains to be explained.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Characterization of the low density lipoprotein receptor in membranes prepared from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3852–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Kovanen P. T., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of plasma cholesterol by lipoprotein receptors. Science. 1981 May 8;212(4495):628–635. doi: 10.1126/science.6261329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Imaizumi K. Radioimmunoassay of arginine-rich apolipoprotein of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):144–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: defective metabolism of an abnormal apolipoprotein E. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.7455696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Jr, Goerke J., Guo L. S., Williams M. C., Havel R. J. Unilamellar liposomes made with the French pressure cell: a simple preparative and semiquantitative technique. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):981–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Chao Y., Windler E. E., Kotite L., Guo L. S. Isoprotein specificity in the hepatic uptake of apolipoprotein E and the pathogenesis of familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kotite L., Vigne J. L., Kane J. P., Tun P., Phillips N., Chen G. C. Radioimmunoassay of human arginine-rich apolipoprotein, apoprotein E. Concentration in blood plasma and lipoproteins as affected by apoprotein E-3 deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI109988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein binding to canine hepatic membranes. Metabolically distinct apo-E and apo-B,E receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5646–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Binding of arginine-rich (E) apoprotein after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the low density lipoprotein receptors of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4186–4190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Goldstein J. L. Deficiency of low density lipoprotein receptors in liver and adrenal gland of the WHHL rabbit, an animal model of familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Increased binding of low density lipoprotein to liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11367–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. H., Phillips N. R., Havel R. J. Mathematical evaluation of methods for estimation of the concentration of the major lipid components of human serum lipoproteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Sep;88(3):491–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Basu S. K., McPhaul M. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Solubilization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Partial purification and characterization of the low density lipoprotein receptor from bovine adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11442–11447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson G., Noel S. P., Havel R. J. Catabolism of the apoprotein of low density lipoproteins by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):628–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Isolation and partial characterization of an arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: apolipoprotein E. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jul;356(7):1113–1121. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Pruin N., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. III. Effect of a single polymorphic gene locus on plasma lipid levels in man. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Assmann G. The rat arginine-rich apoprotein and its redistribution following injection of iodinated lipoproteins into normal and hypercholesterolemic rats. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Oct;28(2):121–140. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Kovanen P. T., Chao Y. S., Brown M. S., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. The estradiol-stimulated lipoprotein receptor of rat liver. A binding site that membrane mediates the uptake of rat lipoproteins containing apoproteins B and E. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10464–10471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Just P. W., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein E isoprotein subclasses are genetically determined. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jan;33(1):11–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


