Abstract
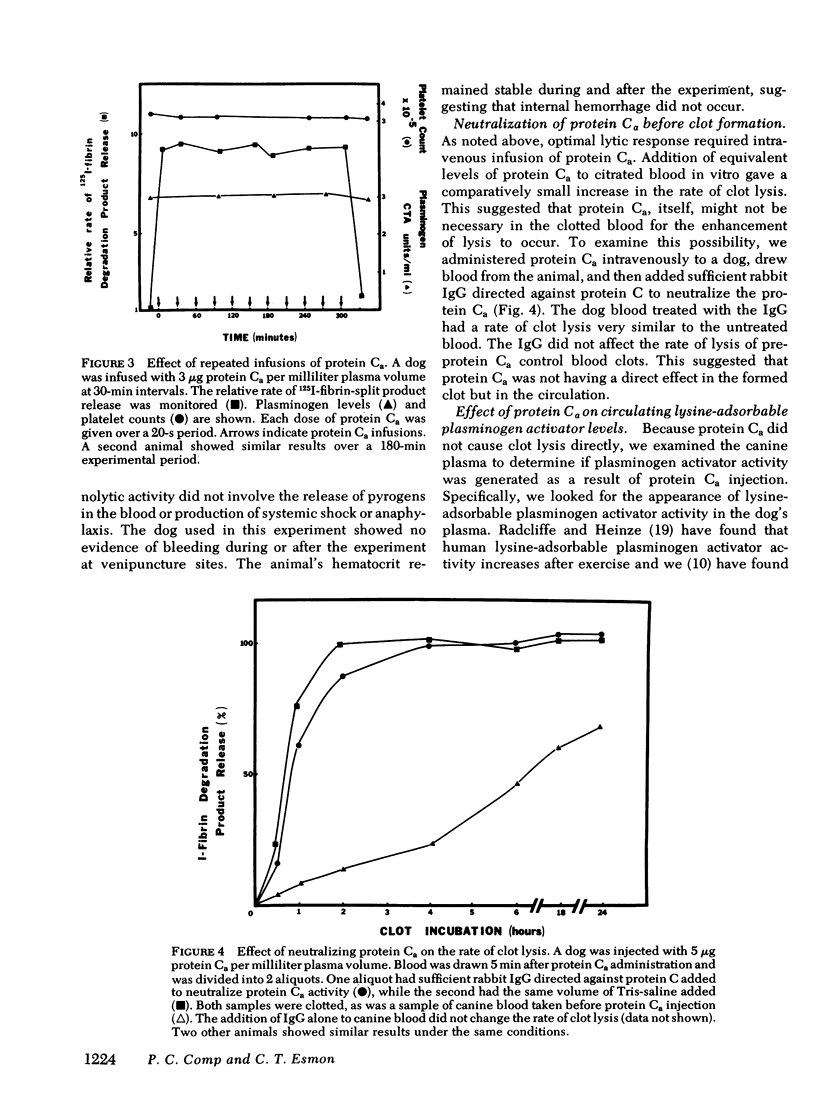
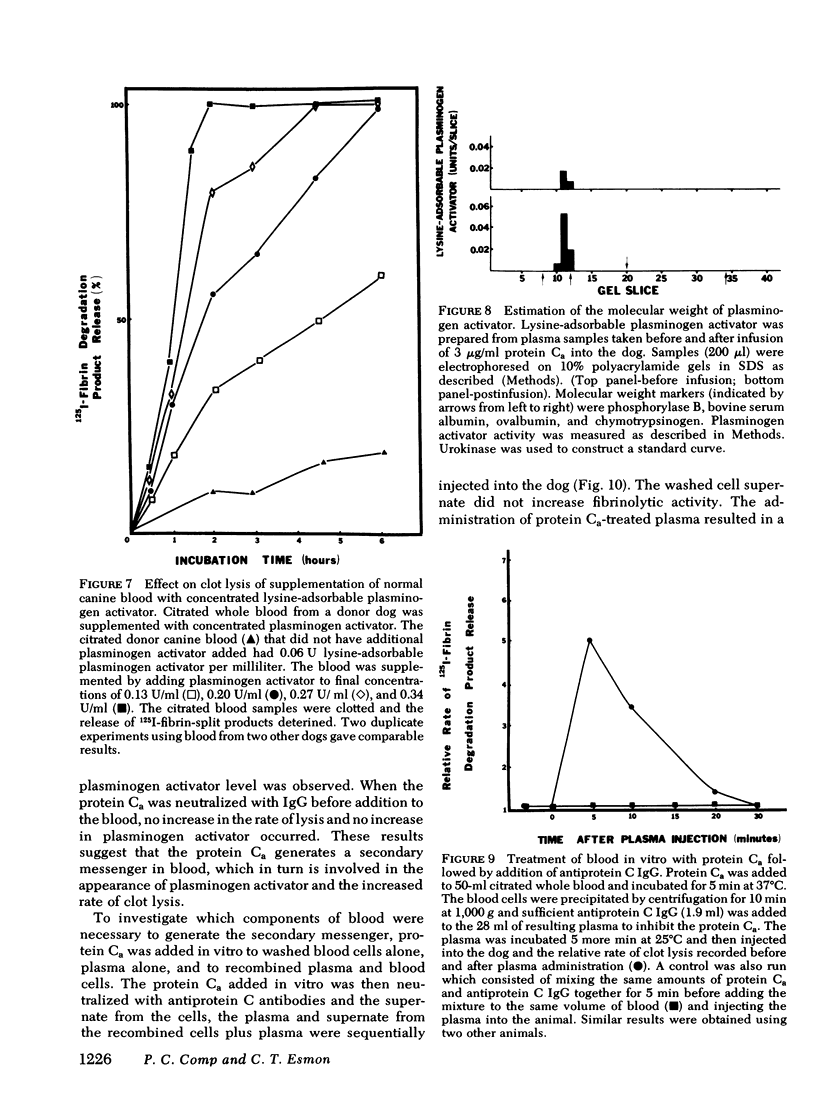
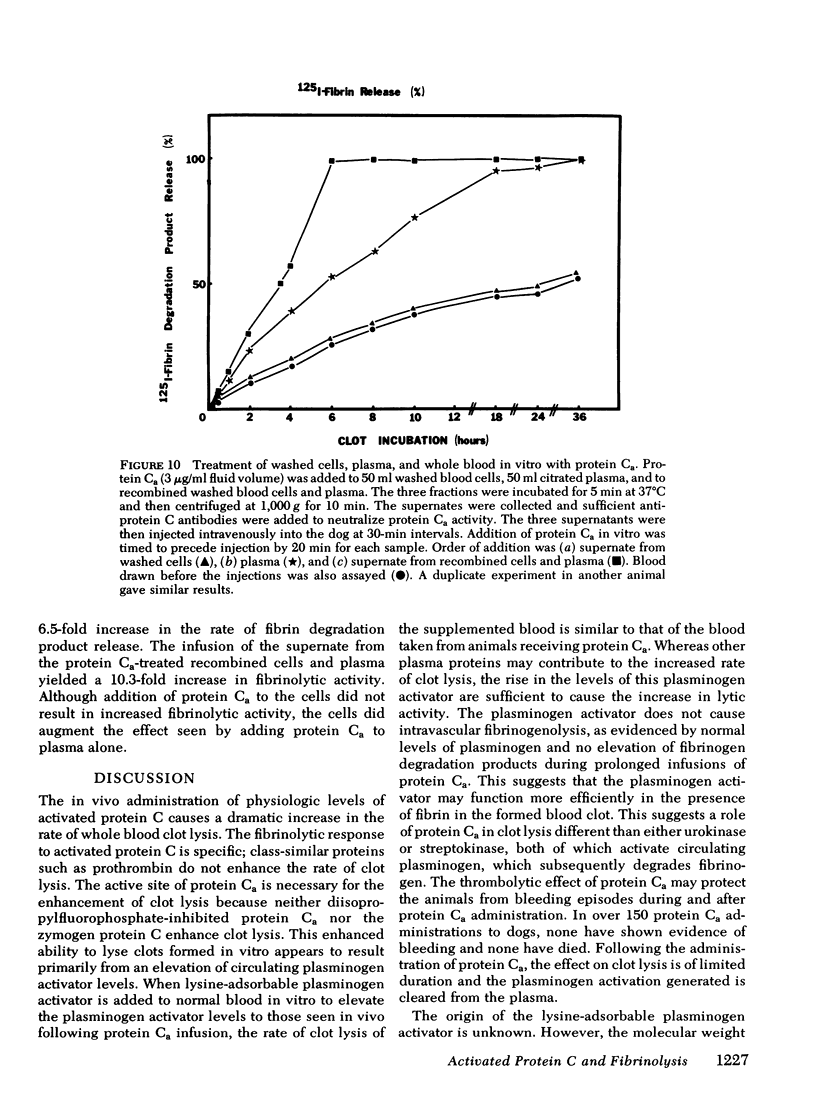
Bovine-activated protein C, administered intravenously to dogs, increases the rate of lysis of whole blood clots. Protein C, bovine prothrombin, and diisopropylfluorophosphate-inactivated protein Ca do not increase the rate of lysis. Repeated infusions of protein Ca sustain rapid blood clot lysis, but neither elevate circulating fibrin-split products nor decrease circulating plasminogen levels. The administration of protein Ca results in the elevation of the levels of lysine-adsorbable plasminogen activator activity in the plasma. When partially purified concentrates of this activator are added to normal dog blood at the levels seen following protein Ca injection, the rate of clot lysis is similar to that seen after protein Ca injection. The addition of protein Ca to citrated whole blood in vitro, with the subsequent neutralization of protein Ca with antibodies, results in increased rates of lysis when plasma made from the treated blood is reinjected into the animal. The generation of fibrinolytic activity is dependent on both cellular and plasma components of blood. A model of protein Ca fibrinolytic activity has a minimum of two components: a secondary messenger formed by protein Ca action on blood cells and plasma, and the subsequent appearance of plasminogen activator in the animal in response to that messenger.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder B. R., Spragg J., Austen K. F. Purification and characterization of human vascular plasminogen activator derived from blood vessel perfusates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash J. D. Effect of moderate exercise on the fibrinolytic system in normal young men and women. Br Med J. 1966 Aug 27;2(5512):502–506. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5512.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Activated protein C inhibits platelet prothrombin-converting activity. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1272–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Jacocks R. M., Rubenstein C., Radcliffe R. A lysine-absorbable plasminogen activator is elevated in conditions associated with increased fibrinolytic activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 May;97(5):637–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Proteolytic activation of protein C from bovine plasma. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4893–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Griffin J. H. Deficiency of protein C inhibitor in combined factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1186–1189. doi: 10.1172/JCI109952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. I. Characterization of the reaction products formed during the activation of bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):594–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Heinze T. Isolation of plasminogen activator from human plasma by chromatography on lysine-sepharose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jul;189(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Zaal-de Jong M., Welbergen J. Purification and partial characterization of plasminogen activator from human uterine tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 29;580(1):140–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER W. D., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIN N., SHERRY S. Studies on the thrombolytic activity of human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:426–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI104054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


