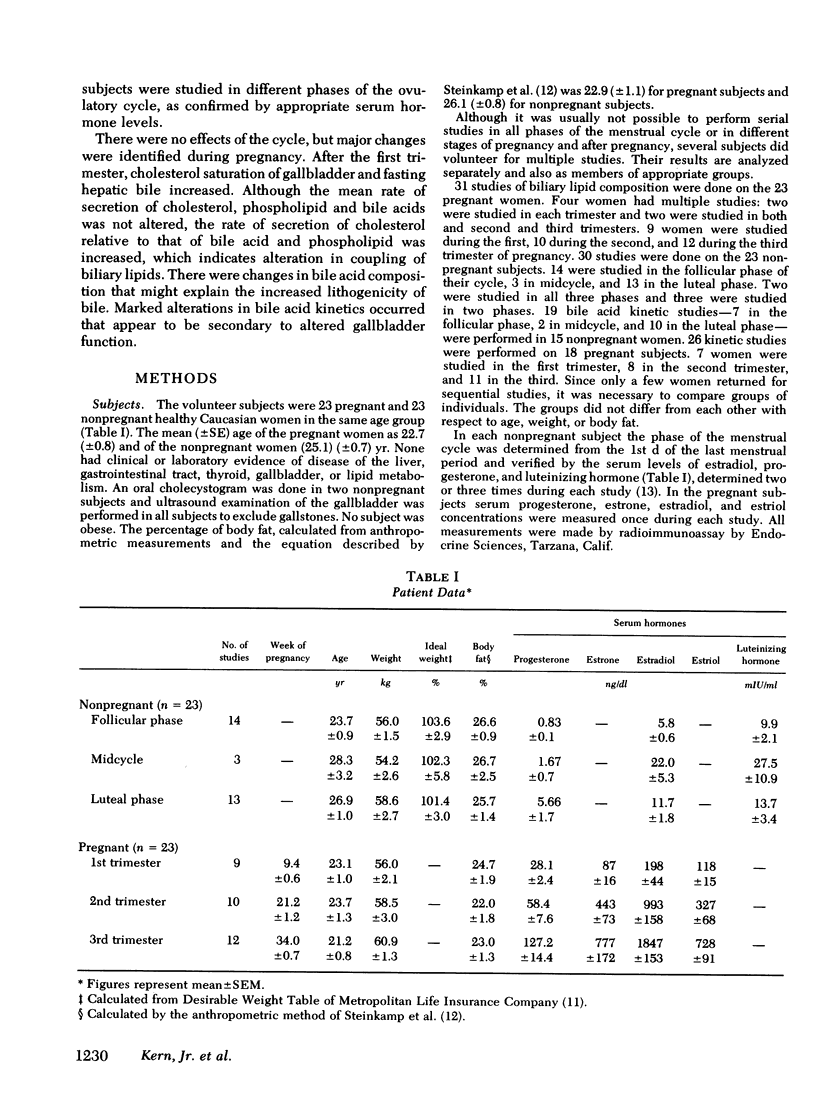
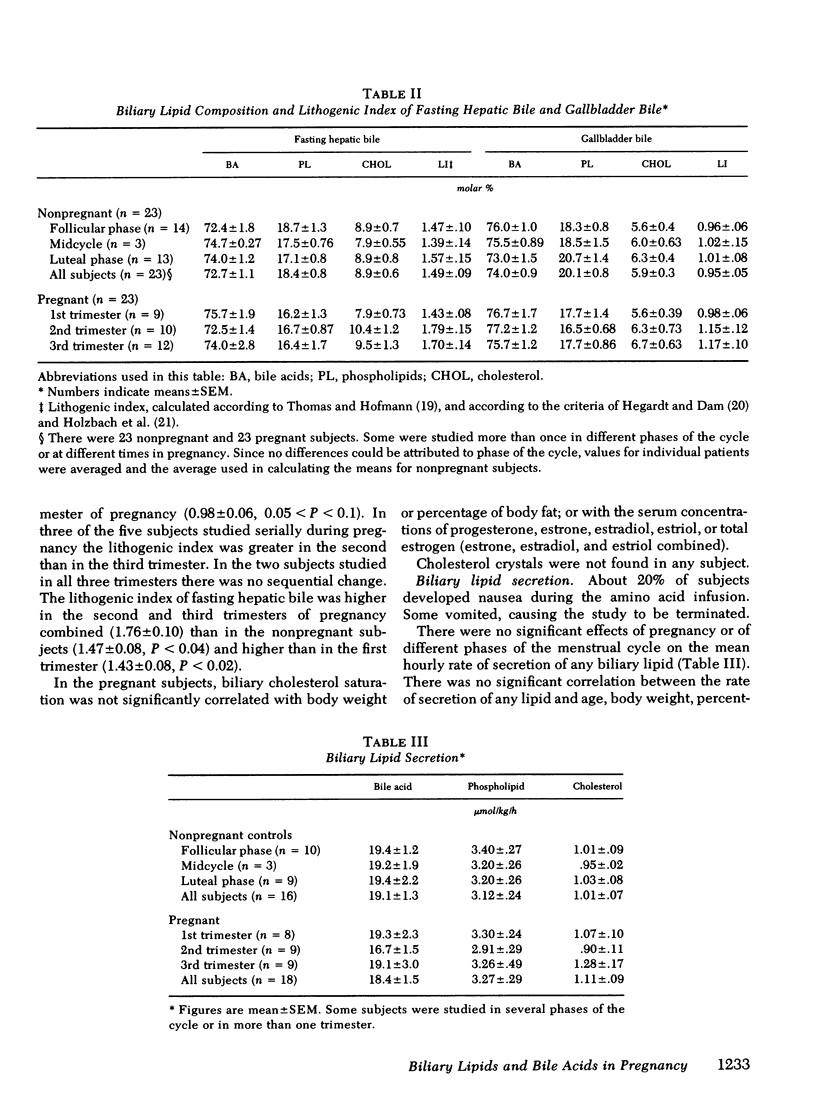
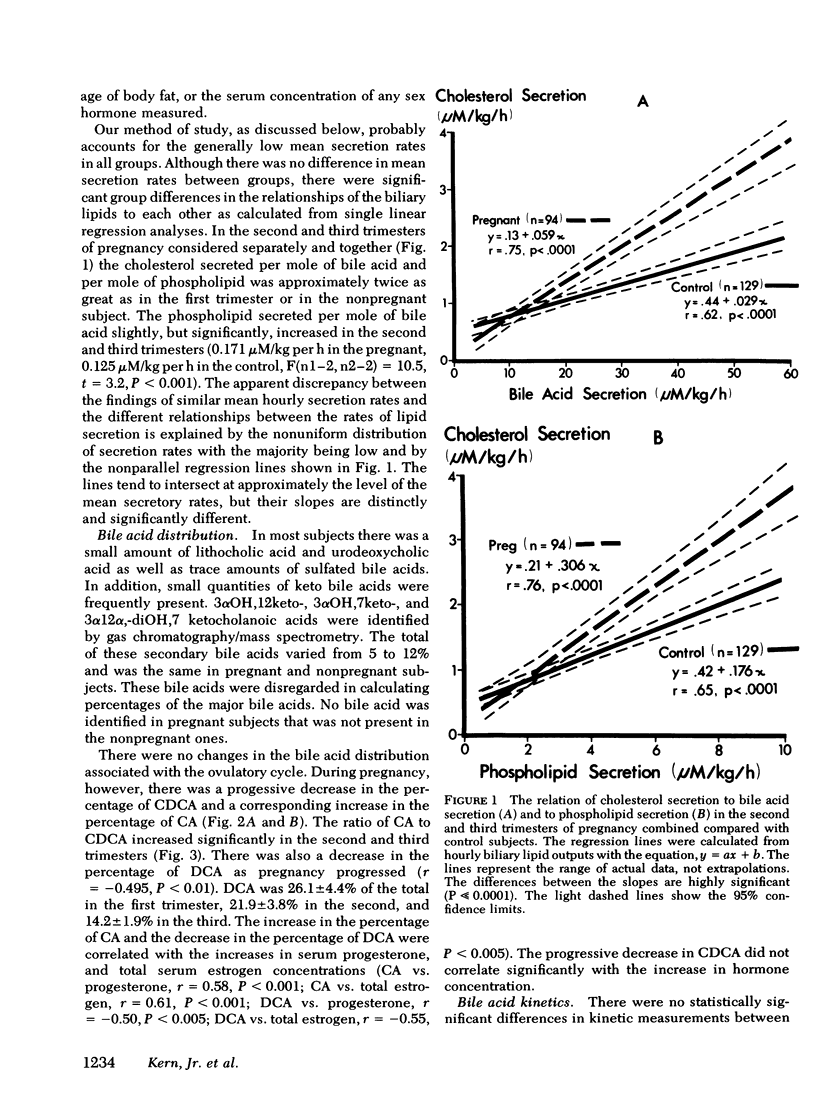
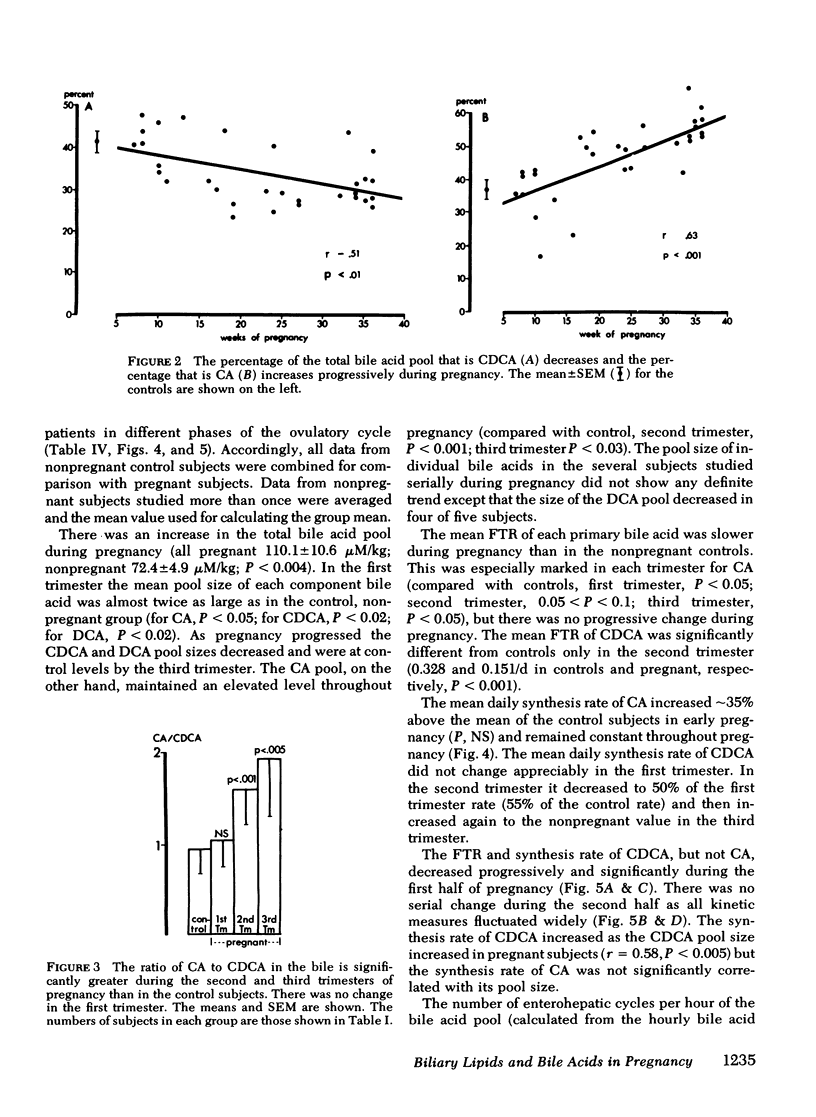
Abstract
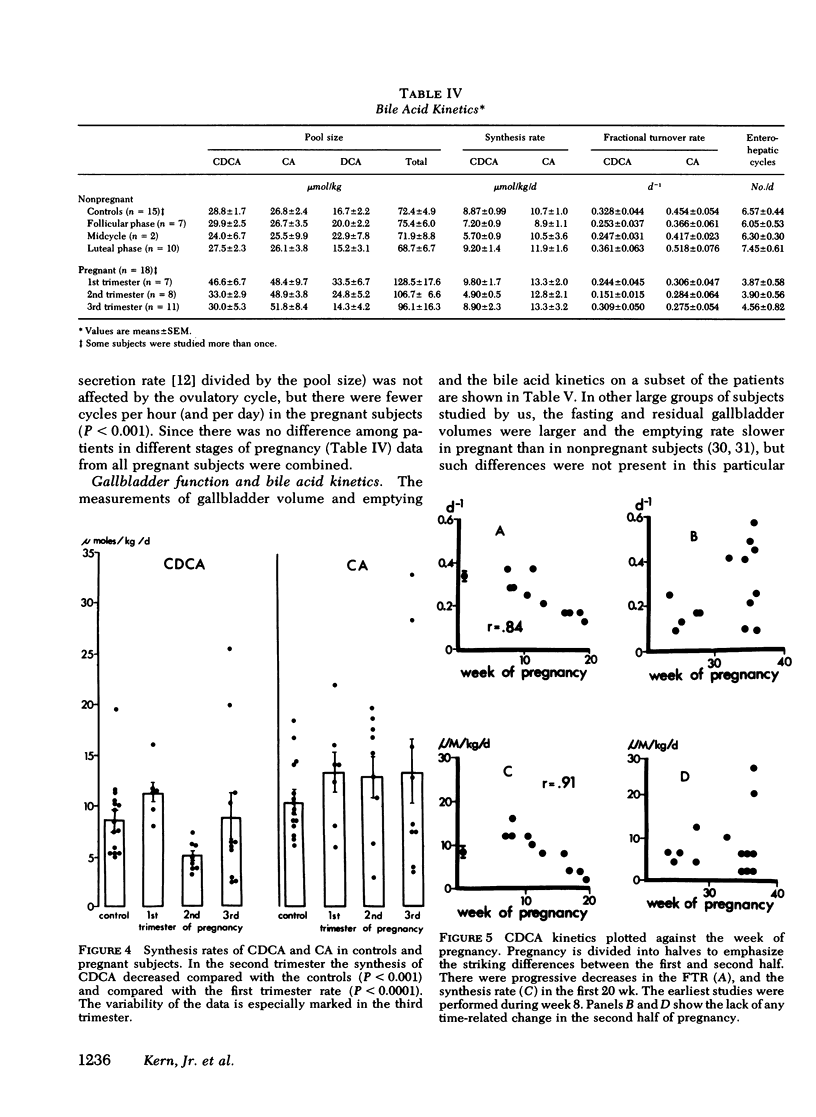
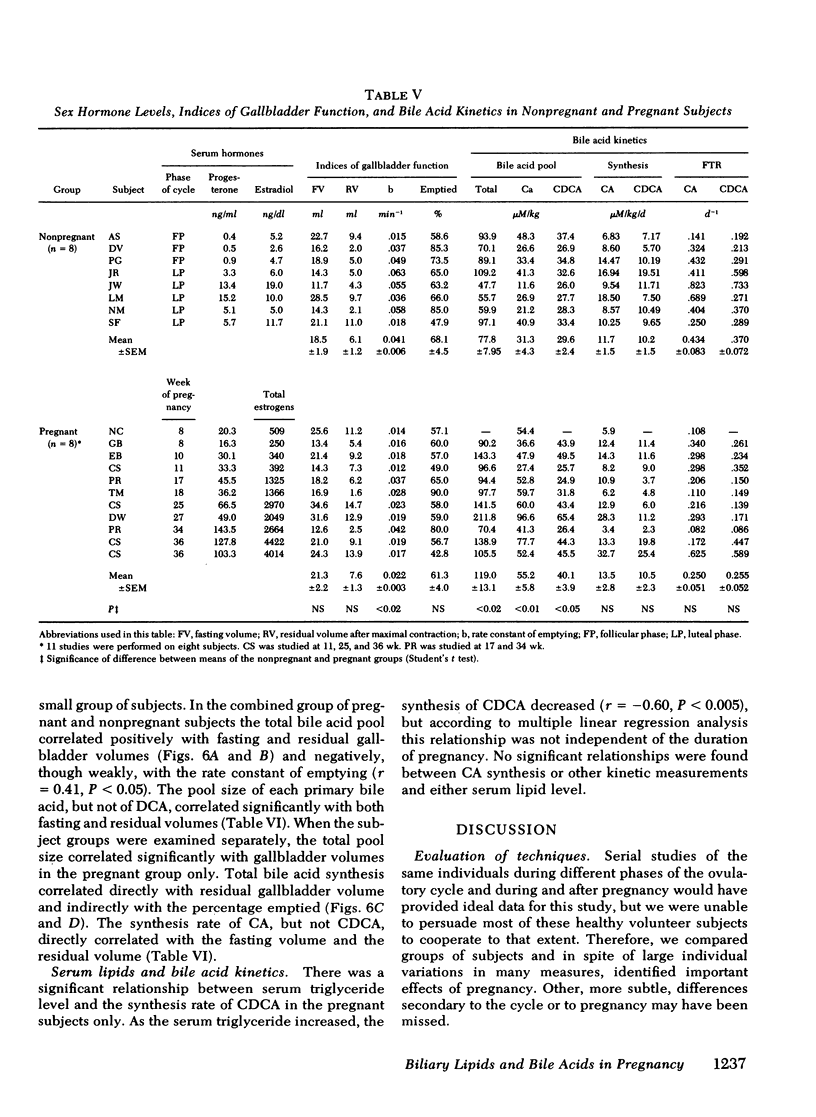
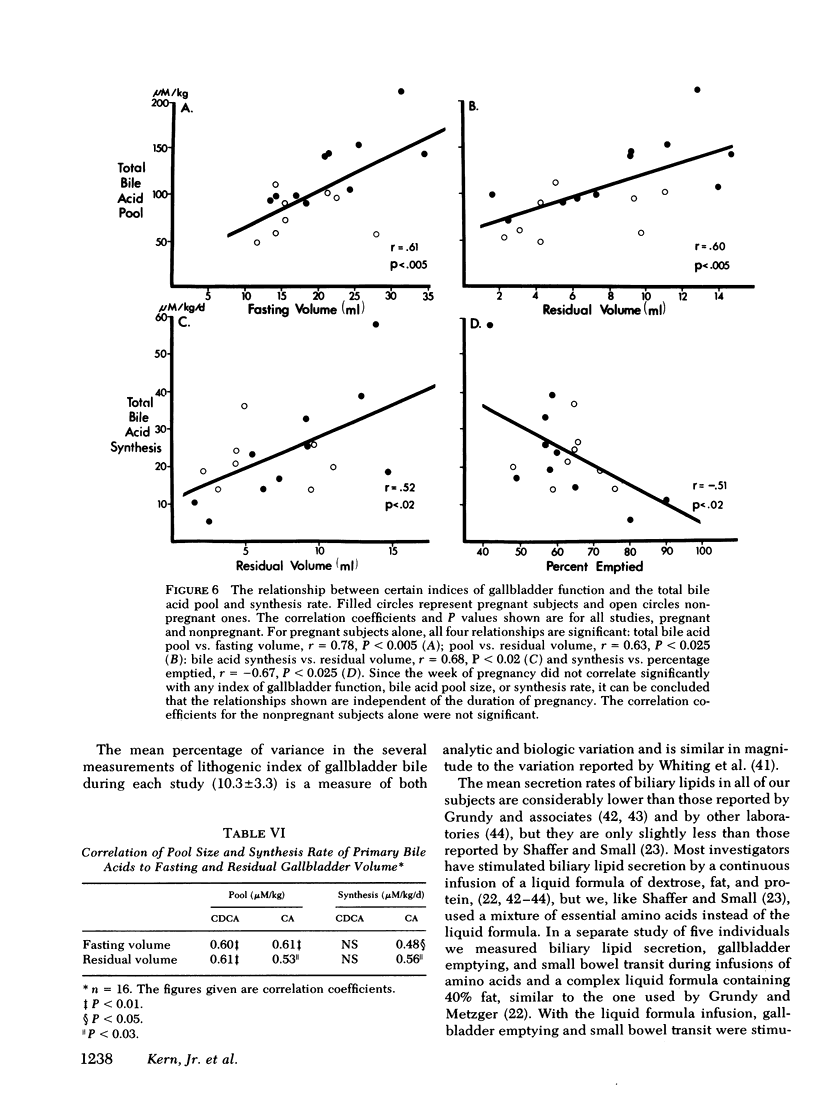
To study the events that might lead to an increased risk of cholesterol gallstones, we examined biliary lipid composition and secretion and bile acid composition and kinetics at different stages of pregnancy or ovulation in young, nonobese, healthy women. Lipid composition and bile acid distribution were determined in duodenal fluid obtained in the fasting state and after stimulation of the gallbladder. Biliary lipid secretion was measured by the marker-perfusion technique. Bile acid kinetics were determined with cholic and chenodeoxycholic acids labeled with carbon13, by measuring the relative abundance of 13C in duodenal bile acids for 4--5 d. In a subset of patients we measured gallbladder storage and emptying during the kinetic study. The phase of the ovulatory cycle had no effects, but there were significant changes during pregnancy. The lithogenic or cholesterol saturation index of fasting hepatic and gallbladder bile increased during the second and third trimesters. The mean secretion rate of biliary lipids was not altered, but in the last two-thirds of pregnancy, cholesterol secretion increased in relation to bile acid and phospholipid secretion. There was a progressive decrease in the percentage of chenodeoxycholic acid and a similar increase in the percentage of cholic acid. The pool size of each major bile acid increased in the first trimester. Chenodeoxycholic acid and deoxycholic acid pools, but not cholic acid pools, subsequently decreased. The fractional turnover rate of both primary bile acids was slower during pregnancy. The synthesis rate of chenodeoxycholic but not cholic acid decreased in a linear manner during the first 20 wk of pregnancy. The rate of enterohepatic cycling of the bile acid pool was reduced throughout pregnancy. The volume of the fasting gallbladder and the residual volume after a physiologically stimulated contraction were directly correlated with bile acid pool size. The residual volume was also directly related to total bile acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. S., Javitt N. B. Quantitative estimation os bile salts in serum. Can J Biochem. 1970 Sep;48(9):1054–1057. doi: 10.1139/o70-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Sjövall J., Sjövall K. Monohydroxy bile acids in plasma in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Identification by computerized gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Med Biol. 1974 Feb;52(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balistreri W. F., Cowen A. E., Hofmann A. F., Szczepanik P. A., Klein P. D. Validation of use of 11,12-2H-labeled chenodeoxycholic acid in isotope dilution measurements of bile acid kinetics in man. Pediatr Res. 1975 Oct;9(10):752–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beher W. T., Lin G. J., Stradnieks S., Konde W. N., Rajan K. S. The effects of cholecystectomy on the bile salt pool of the syrian hamster. Digestion. 1977;15(4):338–347. doi: 10.1159/000198020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J. Changes in bile lipids accompanying oophorectomy in a premenopausal woman. N Engl J Med. 1977 Sep 29;297(13):709–711. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197709292971308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Drobny E., Knowler W. C., Ginsberg R. L., Garnick M. B., Adler R. D., Duane W. C. Sex differences in the size of bile acid pools. Metabolism. 1978 Aug;27(8):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Ginsberg R. L., Gernick M. B., Bennett P. H. Effects of oral contraceptives on the gallbladder bile of normal women. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 22;294(4):189–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601222940403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Grundy S. M. Effects of obesity and caloric intake on biliary lipid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):996–1011. doi: 10.1172/JCI108180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Grundy S. M. Risk factors for the development of cholelithiasis in man (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 23;299(21):1161–1167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Knowler W. C., Mott D. M., Spagnola A. M., Bennett P. H. Development of lithogenic bile during puberty in Pima indians. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 19;300(16):873–876. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904193001601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam H., Hegardt F. G. The relation between formation of gallstones rich in cholesterol and the solubility of cholesterol in aqueos solutions of bile salts and lecithin. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1971 Apr;10(3):239–252. doi: 10.1007/BF02020935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C., Bond J. H., Jr Prolongation of intestinal transit and expansion of bile acid pools by propantheline bromide. Gastroenterology. 1980 Feb;78(2):226–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C., Hanson K. C. Role of gallbladder emptying and small bowel transit in regulation of bile acid pool size in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Dec;92(6):858–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C. Simulation of the defect of bile acid metabolism associated with cholesterol cholelithiasis by sorbitol ingestion in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jun;91(6):969–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., Braverman D. Z., Johnson M. L., Kern F., Jr A critical evaluation of real-time ultrasonography for the study of gallbladder volume and contraction. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G. D., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. The epidemiology of gallbladder disease: observations in the Framingham Study. J Chronic Dis. 1966 Mar;19(3):273–292. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go V. L., Hofmann A. F., Summerskill W. H. Pancreozymin bioassay in man based on pancreatic enzyme secretion: potency of specific amino acids and other digestive products. J Clin Invest. 1970 Aug;49(8):1558–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI106373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Metzger A. L. A physiological method for estimation of hepatic secretion of biliary lipids in man. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jun;62(6):1200–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Metzger A. L., Adler R. D. Mechanisms of lithogenic bile formation in American Indian women with cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3026–3043. doi: 10.1172/JCI107130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLOCK B., TALALAY P. Principles of the enzymatic measurement of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):37–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holan K. R., Holzbach R. T., Hermann R. E., Cooperman A. M., Claffey W. J. Nucleation time: a key factor in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstone disease. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):611–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbach R. T., Marsh M., Olszewski M., Holan K. Cholesterol solubility in bile. Evidence that supersaturated bile is frequent in healthy man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1467–1479. doi: 10.1172/JCI107321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Davis R. A., Kern F., Jr Increased sulfation and decreased 7alpha-hydroxylation of deoxycholic acid in ethinyl estradiol-induced cholestasis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):314–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F., Jr, Eriksson H., Curstedt T., Sjövall J. Effect of ethynylestradiol on biliary excretion of bile acids, phosphatidylcolines, and cholesterol in the bile fistula rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):623–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F., Jr, Eriksson H., Curstedt T., Sjövall J. Effect of ethynylestradiol on biliary excretion of bile acids, phosphatidylcolines, and cholesterol in the bile fistula rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):623–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key P. H., Bonorris G. G., Marks J. W., Chung A., Schoenfield L. J. Biliary lipid synthesis and secretion in gallstone patients before and during treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jun;95(6):816–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. D., Haumann J. R., Hachey D. L. Stable isotope ratiometer-multiple ion detector unit for quantitative and qualitative stable isotope studies by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1253–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSTEDT S. The turnover of cholic acid in man: bile acids and steroids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Sep 17;40(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Validity of using 2,4-3H-labeled bile acids to study bile acid kinetics in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Nov;84(5):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laatikainen T., Lehtonen P., Hesso A. Biliary bile acids in uncomplicated pregnancy and in cholestasis of pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: Effects of the normal menstrual cycle on human gallbladder bile. N Engl J Med. 1976 May 20;294(21):1187–1188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605202942126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad L., Lundholm K., Scherstén T. Influence of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid on biliary cholesterol secretion in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):383–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Heaton S. T., Read A. E. Gallbladder inertia and sluggish enterohepatic circulation of bile-salts in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1971 May 15;1(7707):991–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Pomare E. W., Read A. E. The effect of coeliac disease upon bile salts. Gut. 1973 Mar;14(3):204–208. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Wicks A. C., Heaton K. W., Durrington P., Yeates J. Fluctuations of serum and bile lipid concentrations during the menstrual cycle. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 18;1(6076):1568–1570. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6076.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKITA M., WELLS W. W. Quantitative analysis of fecal bile acids by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jun;5:523–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWMAN H. F., NORTHUP J. D. The autopsy incidence of gallstones. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1959 Jul;109(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. Gallbladder disease and sex hormones. A statistical study. Acta Chir Scand. 1966 Sep;132(3):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomare E. W., Heaton K. W. The effect of cholecystectomy on bile salt metabolism. Gut. 1973 Oct;14(10):753–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J., Nestel P. J. Cholesterol balance during pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jul 1;87(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Kern F., Jr Effect of pregnancy on bile flow and biliary lipids in the hamster. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):144–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda E., Aldini R., Mazzella G., Roda A., Sama C., Festi D., Barbara L. Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids after cholecystectomy. Gut. 1978 Jul;19(7):640–649. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.7.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roovers J., Evrard E., Vanderhaeghe H. An improved method for measuring human blood bile acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Mar;19(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGSON D., MARINO J., DODSON E. Determination of sulfobromophthalein in serum. Clin Chem. 1957 Oct;3(5):638–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E., Bennett P. H., Comess L. J., Rose F. A., Burch T. A. Gallbladder disease in pima indians. Demonstration of high prevalence and early onset by cholecystography. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 17;283(25):1358–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012172832502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller D. A. A review of the satatistical considerations involved in the treatment of isotope dilution calibration data. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1976 Dec;3(6):265–271. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200030603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedaghat A., Grundy S. M. Cholesterol crystals and the formation of cholesterol gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1274–1277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Small D. M. Biliary lipid secretion in cholesterol gallstone disease. The effect of cholecystectomy and obesity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):828–840. doi: 10.1172/JCI108705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp R. C., Cohen N. L., Siri W. E., Sargent T. W., Walsh H. E. Measures of body fat and related factors in normal adults. I. Introduction and methodology. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Dec;18(12):1279–1291. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stempel J. M., Duane W. C. Bilary lipids and bile acid pool size after vagotomy in man. Evidence against a predisposition to gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanik P. A., Hachey D. L., Klein P. D. Characterization of bile acid methyl ester acetate derivatives using gas-liquid chromatography, electron impact, and chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jul;17(4):314–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanik P. A., Hachey D. L., Klein P. D. Evaluation of Poly S-179 as a stationary phase for the gas-liquid chromatography-mass-spectrometry of bile acid methyl ester acetates. J Lipid Res. 1978 Feb;19(2):280–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Eckhart K. L., Jr, Nensel R. E., Nobrega F. T., Poehling G. G., Reimer M., Schoenfield L. J. Prevalence of gallbladder disease among Chippewa Indians. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Sep;46(9):603–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F., Yu P. Y., Ott B. Effect of varying doses of chenodeoxycholic acid on bile lipid and biliary bile acid composition in gallstone patients: a dose-response study. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jan;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF01077389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Letter: A simple calculation of the lithogenic index of bile: expressing biliary lipid composition on rectangular coordinates. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tserng K. Y., Klein P. D. An improved synthesis of 24-13C-labeled bile acids using formyl esters and a modified lead tetraacetate procedure. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):400–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. T., Tournut R. A., Scharplatz D., Kavlie H., Olson A. D., Hopton D. S. The effect of vagotomy on biliary secretions and bile salt pools in dogs. Ann Surg. 1974 Apr;179(4):406–411. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197404000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Down R. H., Watts J. M. Precision and accuracy in the measurement of the cholesterol saturation index of duodenal bile. Lack of variation due to the menstrual cycle. Gastroenterology. 1981 Mar;80(3):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahor A., Sternby N. H., Kagan A., Uemura K., Vanecek R., Vichert A. M. Frequency of cholelithiasis in Prague and Malmö. An autopsy study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(1):3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


