Abstract
Two sodium transport systems have been analyzed in this work: the voltage-sensitive sodium channel and the (Na+, K+) ATPase pump. The sodium channel has been studied using a tritiated derivative of tetrodotoxin; the sodium pump has been studied using tritiated ouabain. Properties of interaction of tritiated tetrodotoxin and of tritiated ouabain with their respective receptors were observed in normal human skeletal muscle and in muscles of patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy and with lower motor neuron impairment.
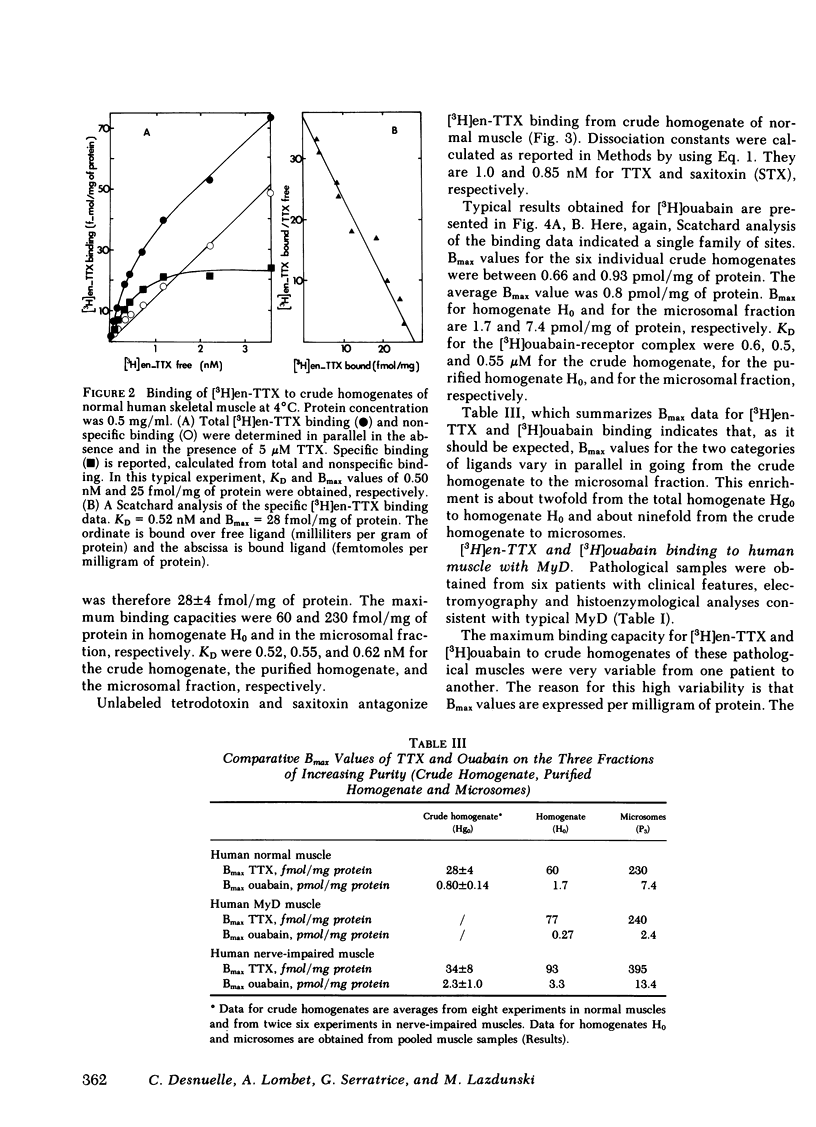
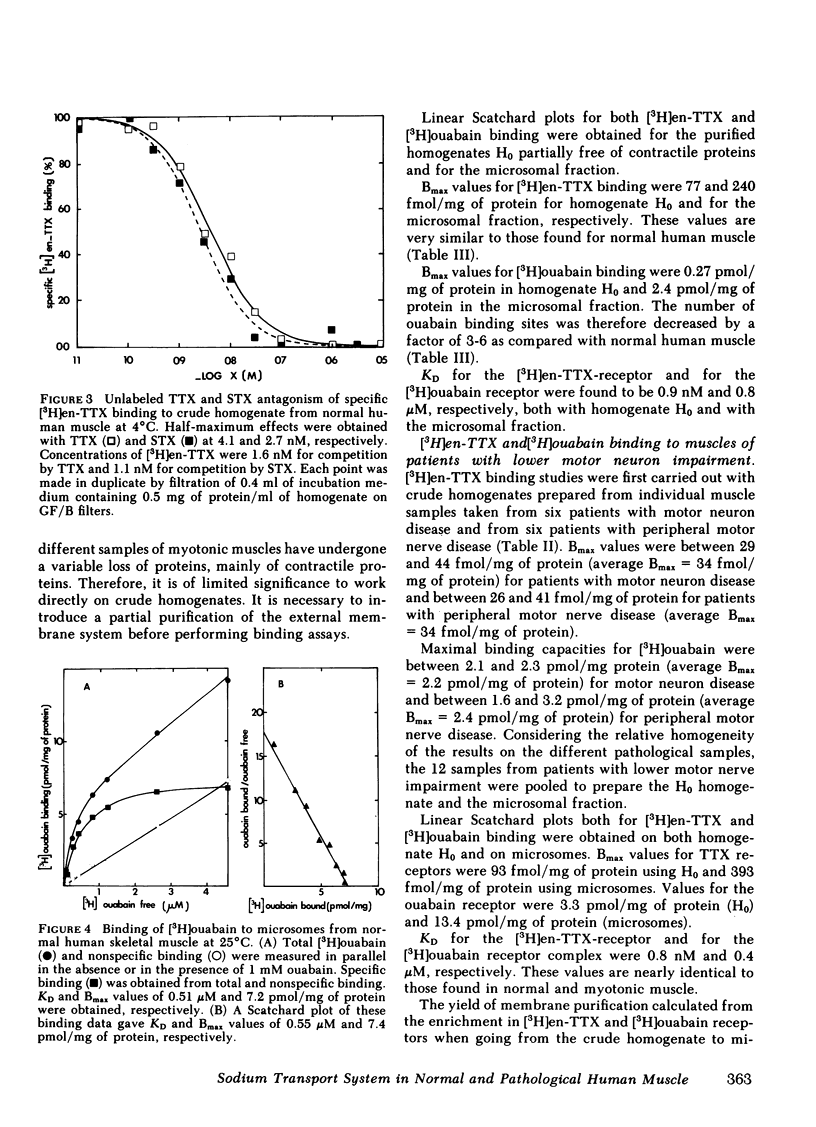
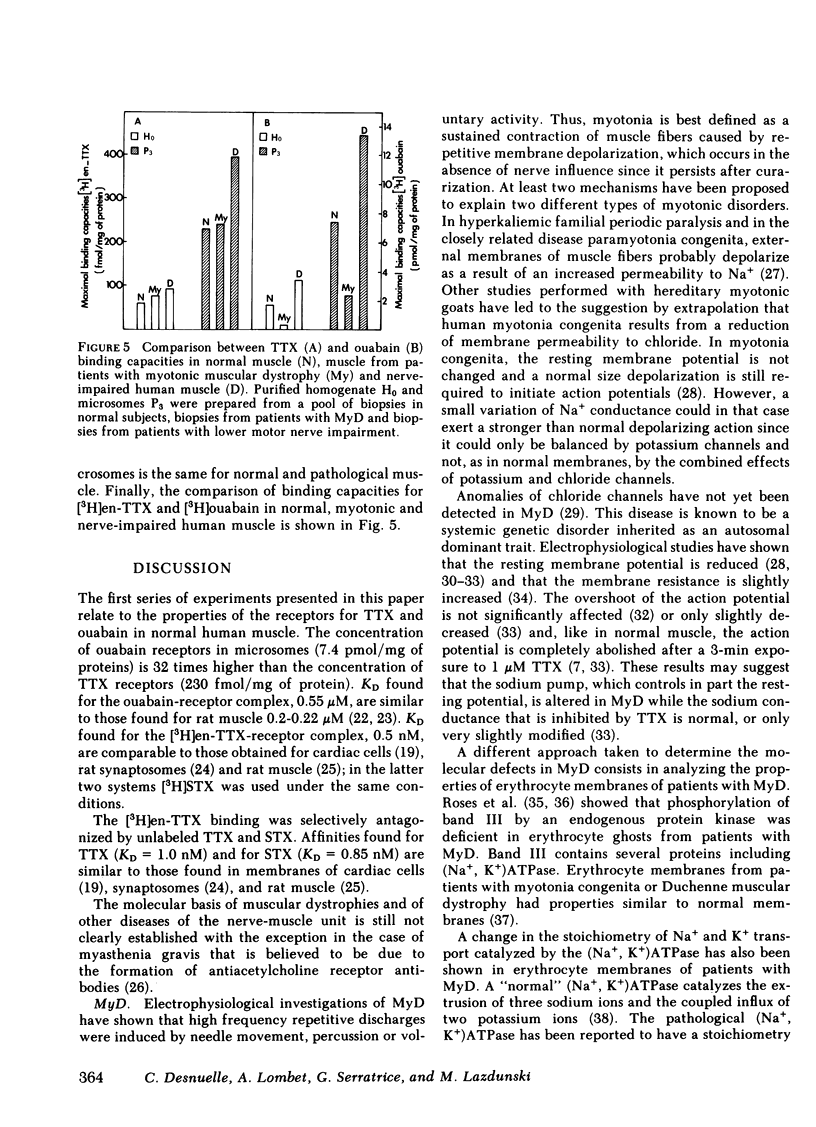
Levels of sodium pump and of sodium channels were measured at different stages of membrane purification. Microsomal fractions of normal human muscle have maximal binding capacities for tetrodotoxin of 230 fmol/mg of protein and of 7.4 pmol/mg of protein for ouabain.
Dissociation constant for the complexes formed by the tetrodotoxin derivative and by ouabain with their respective receptors were 0.52 nM and 0.55 μM, respectively.
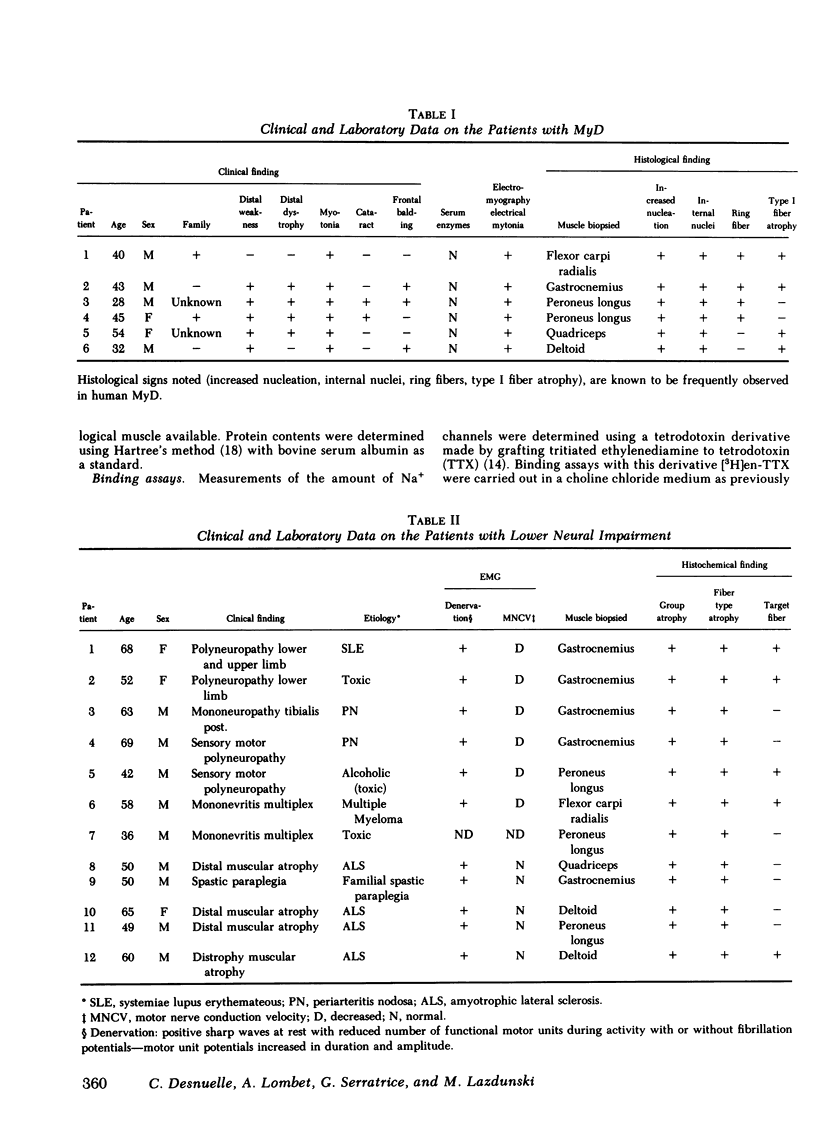
In muscles from patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy, the maximal binding capacity for tetrodotoxin, i.e., the number of Na+ channels was found to be very similar to that found for normal muscle. The maximal binding capacity for ouabain, i.e., the number of Na+ pumps was three- to sixfold lower than in normal muscle. Dissociation constants for the complexes formed with the tetrodotoxin derivative and with ouabain were the same as for normal muscle.
In muscles from patients with lower motor nerve impairment, the maximal binding capacities for tetrodotoxin and for ouabain were twice as high as in normal muscle. Again, dissociation constants for the complexes formed with the tetrodotoxin derivative and with ouabain were nearly unchanged as compared with normal muscle.
These results suggest that sodium transport systems involved in the generation of action potentials and/or in the regulation of the resting potential are altered both in myotonic muscular dystrophy and in lower motor neuron impairment.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. L. A simple digital-computer program for estimating the parameters of the hill equation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Myotonia. An evaluation of the chloride hypothesis. Arch Neurol. 1975 Mar;32(3):175–180. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490450055007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Weigele J. B. Characteristics of saxitoxin binding to the sodium channel of sarcolemma isolated from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Balerna M., Lombet A., Romey G., Lazdunski M. Synthesis of new, highly radioactive tetrodotoxin derivatives and their binding properties to the sodium channel. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):617–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festoff B. W., Oliver K. L., Reddy N. B. In vitro studies of skeletal muscle membranes. Effects of denervation on the macromolecular components of cation transport in red and white skeletal muscle. J Membr Biol. 1977 Apr 22;32(3-4):345–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01905227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. The action of cardiac glycosides on sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):148–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The stoicheiometry of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):217–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grampp W., Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Inhibition of denervation changes in skeletal muscle by blockers of protein synthesis. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):743–754. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruener R., Stern L. Z., Markovitz D., Gerdes C. Electrophysiologic properties of intercostal muscle fibers in human neuromuscular diseases. Muscle Nerve. 1979 May-Jun;2(3):165–172. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruener R., Stern L. Z., Payne C., Hannapel L. Hyperthyroid myopathy. Intracellular electrophysiological measurements in biopsied human intercostal muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Mar;24(3):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Richman E., Barrett C., Warnick J. E., Albuquerque E. X. The mechanism by which degenerating peripheral nerve produces extrajunctional acetylcholine sensitivity in mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp Neurol. 1980 Jun;68(3):465–476. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(80)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W., Alston W., Rowe G. A study of individual neuro-muscular junctions in myotonia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1966 Dec;21(6):521–537. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(66)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull K. L., Jr, Roses A. D. Stoichiometry of sodium and potassium transport in erythrocytes from patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):169–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACETYLCHOLINE SENSITIVITY IN NERVE-FREE SEGMENTS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:389–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Dau P. Biology of myasthenia gravis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:337–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipicky R. J., Bryant S. H. Ion content, potassium efflux and cable properties of myotonic, human, external-intercostal muscle. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1971;96:34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipicky R. J., Bryant S. H. Sodium, potassium, and chloride fluxes in intercostal muscle from normal goats and goats with hereditary myotonia. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):89–111. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Renaud J. F., Chicheportiche R., Lazdunski M. A cardiac tetrodotoxin binding component: biochemical identification, characterization, and properties. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Schwartz A. Mechanism of cardiac glycoside inhibition of the (Na+-K+)-dependent ATPase from cardiac tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Mrozek K. The electrical properties of muscle fiber membranes in dystrophia myotonica and myotonia congenita. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):441–447. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merickel M., Gray R., Chauvin P., Appel S. Cultured muscle from myotonic muscular dystrophy patients: altered membrane electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plishker G. A., Gitelman H. J., Appel S. H. Myotonic muscular dystrophy: altered calcium transport in erythrocytes. Science. 1978 Apr 21;200(4339):323–325. doi: 10.1126/science.635589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to normal and denervated muscle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(1):129P–130P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roses A. D., Appel S. H. Phosphorylation of component a of the human erythrocyte membrane in myotonic muscular dystrophy. J Membr Biol. 1975;20(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01870627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi B., Vuilleumier P., Gache C., Balerna M., Lazdunski M. Affinity labeling of the digitalis receptor with p-nitrophenyltriazene-ouabain, a highly specific alkylating agent. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9936–9941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. P. Biochemistry of muscle membranes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Jan-Feb;3(1):3–20. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaha F. J., Guth L., Albers R. W. The neural regulation of gene expression in the muscle cell. Exp Neurol. 1970 May;27(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Lindenmayer G. E., Allen J. C. The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Mar;27(01):3–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Pellissier J. F., Faugere M. C., Gastaut J. L. Centronuclear myopathy: possible central nervous system origin. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Jan-Feb;1(1):62–69. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele J. B., Barchi R. L. Analysis of saxitoxin binding in isolated rat synaptosomes using a rapid filtration assay. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 15;91(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


