Abstract
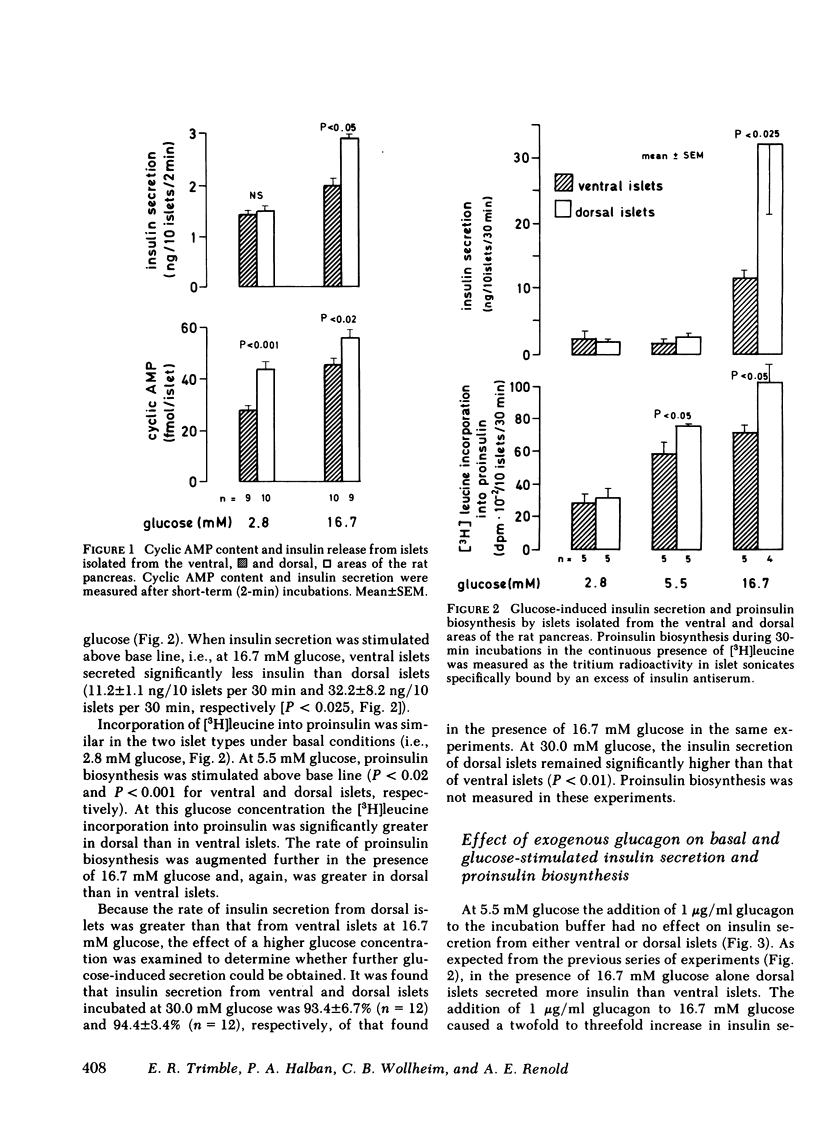
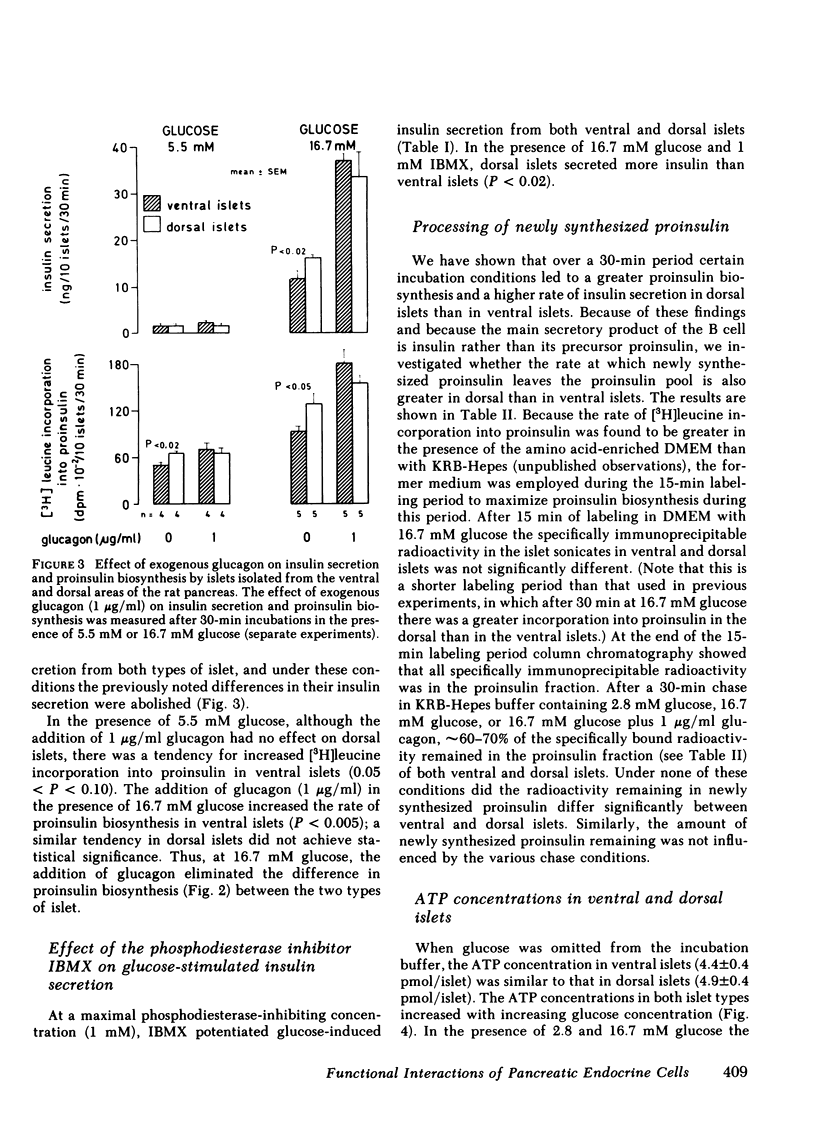
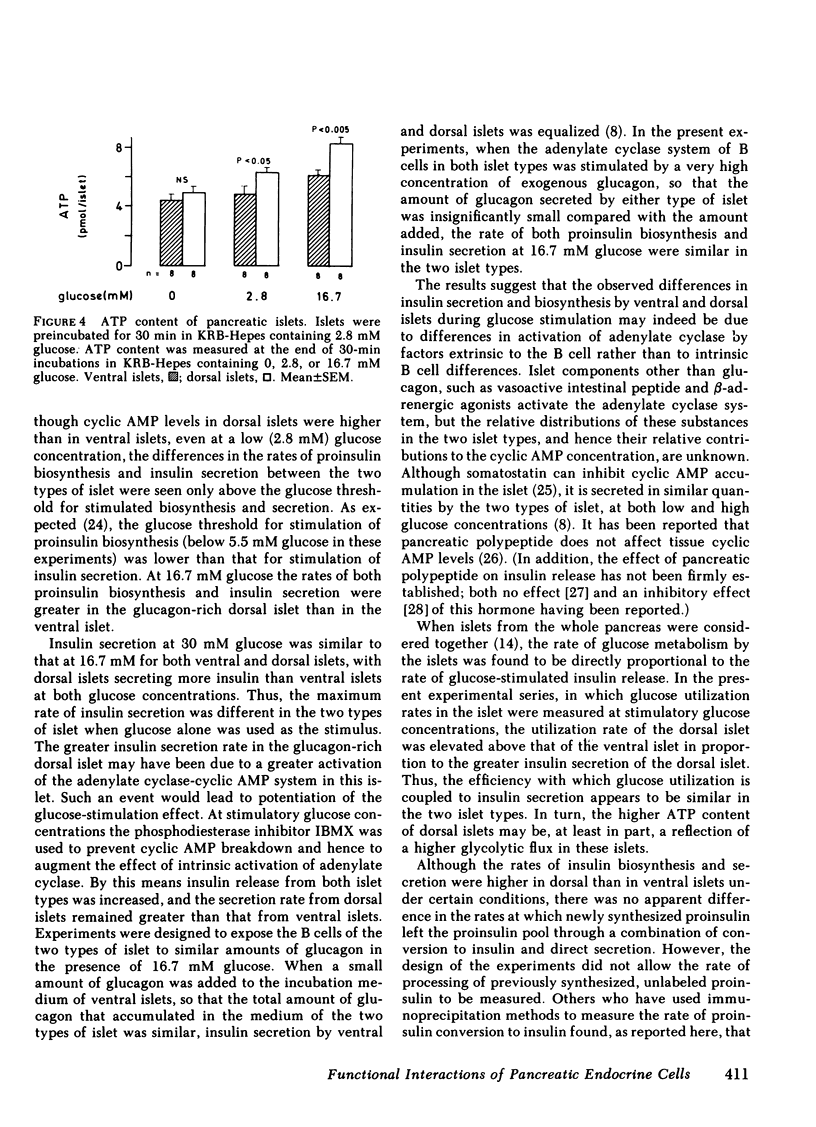
Do functional linkages between islet endocrine cells exist? The effect of differences in frequency and distribution of islet endocrine cells on B cell function was examined in islets from the ventral (ventral islets) and dorsal (dorsal islets) areas of the rat pancreas. Dorsal islets contained 10 times as much glucagon as ventral islets, whereas insulin and total protein contents were similar. Basal rates of insulin secretion and proinsulin biosynthesis were similar in the two types of islet, but, under conditions of glucose stimulation, both insulin secretion and proinsulin biosynthesis were significantly greater in the glucagon-rich dorsal islets. Similarly, glucose utilization rates an ATP levels were greater in dorsal islets. In contrast, the rates of processing of newly synthesized proinsulin were similar in ventral and dorsal islets. That the islet glucagon content may have affected B cell function is inferred from two independent findings. Firstly, basal and glucose-stimulated cyclic AMP contents of glucagon-rich dorsal islets were greater than those of ventral islets. Secondly, in the presence of excess exogenous glucagon (1 microgram/ml), the differences in glucose-induced insulin secretion and proinsulin biosynthesis rates between the two types of islets were eliminated. These results strongly suggest that changes in the relative proportions of the different islet endocrine cells exert marked effects on islet function. In particular, a greater A cell and glucagon content is associated with higher rates of glucose-induced insulin secretion and biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Hermansen K., Iversen J. Pancreatic polypeptide, glucagon and insulin secretion from the isolated perfused canine pancreas. Diabetologia. 1978 Jun;14(6):413–417. doi: 10.1007/BF01228136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Verspohl E. Pyridine nucleotides in pancreatic islets during inhibition of insulin release by exogenous insulin. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1469–1476. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Bunce J., Lowry M., Hansen S. E., Hedeskov C. J. The effect of sugars on (pro)insulin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):517–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1740517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cailla H. L., Racine-Weisbuch M. S., Delaage M. A. Adenosine 3',5' cyclic monophosphate assay at 10-15 mole level. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro A., Grill V., Efendić S., Luft R. Studies on the mechanisms of somatostatin action on insulin release. IV. effect of somatostatin on cyclic AMP levels and phosphodiesterase activity in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1977 Jun;85(2):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck W. P., Texter E. C., Jr, Lasater J. M., Hightower N. C., Jr Influence of glucagon on pancreatic exocrine secretion in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Apr;58(4):532–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. A., Henderson J. R. The arrangement of endocrine and exocrine pancreatic microcirculation observed in the living rabbit. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1980 Apr;65(2):151–158. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1980.sp002499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Renold A. E. Long-term exposure of isolated pancreatic islets to mannoheptulose: evidence for insulin degradation in the beta cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 1;29(19):2625–2633. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Islet-activating protein. Enhanced insulin secretion and cyclic AMP accumulation in pancreatic islets due to activation of native calcium ionophores. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohen E., Kohen C., Thorell B., Mintz D. H., Rabinovitch A. Intercellular communication in pancreatic islet monolayer cultures: a microfluorometric study. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):862–865. doi: 10.1126/science.35828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson N., Kramlinger K. G., Mayrand R. R., Lender E. J. Blood flow to the rabbit pancreas with special reference to the islets of Langerhans. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):466–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Evans D. C., Chance R. E., Spray G. F. Bovine pancreatic peptide: action on gastric and pancreatic secretion in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):E311–E315. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.3.E311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Sundler F., Ahrén B., Alumets J., Håkanson R. Somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide, substance P, and neurotensin: cellular distribution and effects on stimulated insulin secretion in the mouse. Endocrinology. 1979 Mar;104(3):832–838. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-3-832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Denef J. F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Nonrandom distribution of gap junctions between pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):C114–C119. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.3.C114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P. Electrophysiological evidence for coupling between beta cells of pancreatic islets. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):502–504. doi: 10.1038/262502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse-Lagae F., Ravazzola M., Rouiller D., Renold A. E., Perrelet A., Unger R. A morphological basis for intercellular communication between alpha- and beta-cells in the endocrine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1066–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI108154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Marichal M., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XIV. Glucose regulation of insular biosynthetic activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Nov;93(5):1001–1011. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-5-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis S., Schlegel W., Lehmann E., Dollinger H. C., Zoupas C. Effects of somatostatin on the exocrine pancreas and the release of duodenal hormones. Metabolism. 1978 Sep;27(9 Suppl 1):1321–1328. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Williams J. A., Kanno T. Potentiation of cholecystokinin-induced exocrine secretion by both exogenous and endogenous insulin in isolated and perfused rat pancreata. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):777–782. doi: 10.1172/JCI109727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauder P., Arends J., Schindler B., Ebert R., Frerichs H. Permissive effect of glucose on the glucagon-induced accumulation of cAMP in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1977 Apr;13(2):171–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00745146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. S., Corkey B., Williamson J. R., Rubenstein A. H. Effect of bovine pancreatic polypeptide on isolated rat liver cells. Endocrinology. 1980 Apr;106(4):1178–1181. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-4-1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. E., Williams S. G. Use of the liquid scintillation spectrometer for determining adenosine triphosphate by the luciferase enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söling H. D., Unger K. O. The role of insulin in the regulation of -amylase synthesis in the rat pancreas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;2(4):199–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1972.tb00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S. Coupling of peptides to albumin with difluorodinitrobenzene. Anal Biochem. 1976 Apr;71(2):367–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Renold A. E. Ventral and dorsal areas of rat pancreas: islet hormone content and secretion. Am J Physiol. 1981 Apr;240(4):E422–E427. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.4.E422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Dobbs R. E., Orci L. Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretion in the regulation of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:307–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl E. J., Händel M., Ammon H. P. Pentosephosphate shunt activity of rat pancreatic islets: its dependence on glucose concentration. Endocrinology. 1979 Nov;105(5):1269–1274. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-5-1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. The role of extracellular Ca++ and islet calcium stores in the regulation of biphasic insulin release. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Matschinsky F. M. Sequential analysis of the releasing and fuel function of glucose in isolated perifused pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1977 Jan;100(1):1–8. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


