Abstract
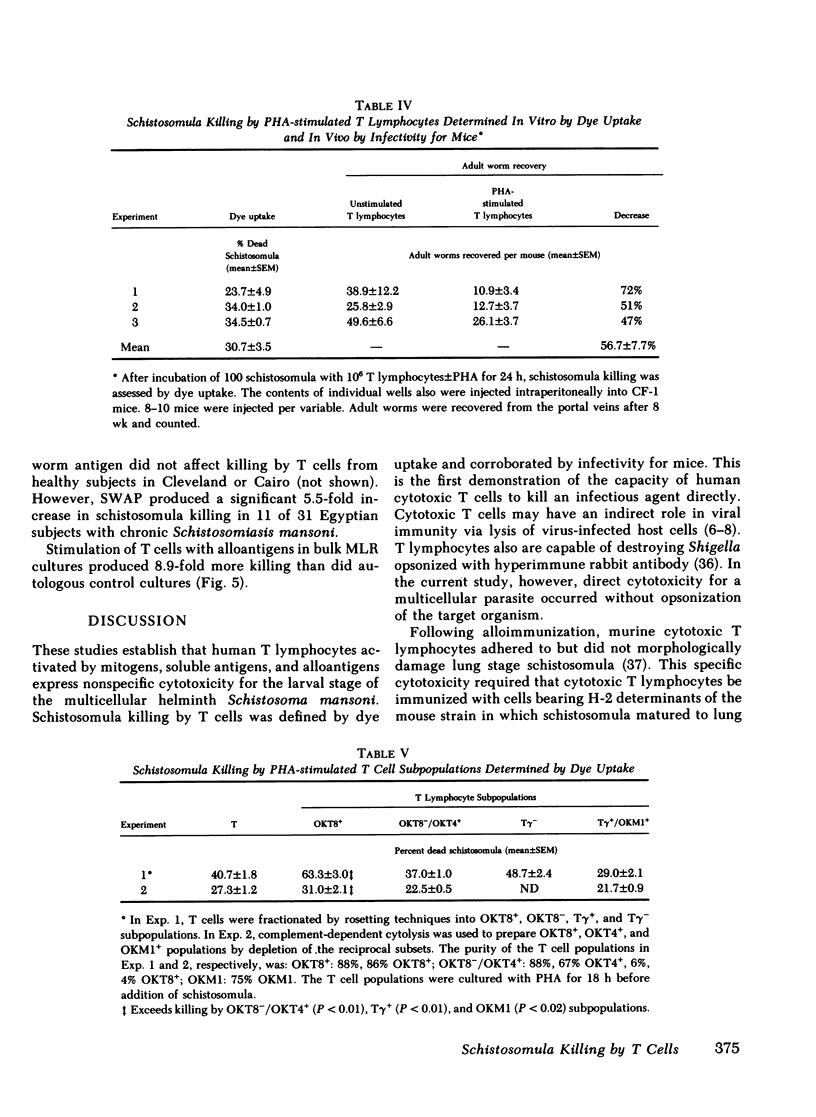
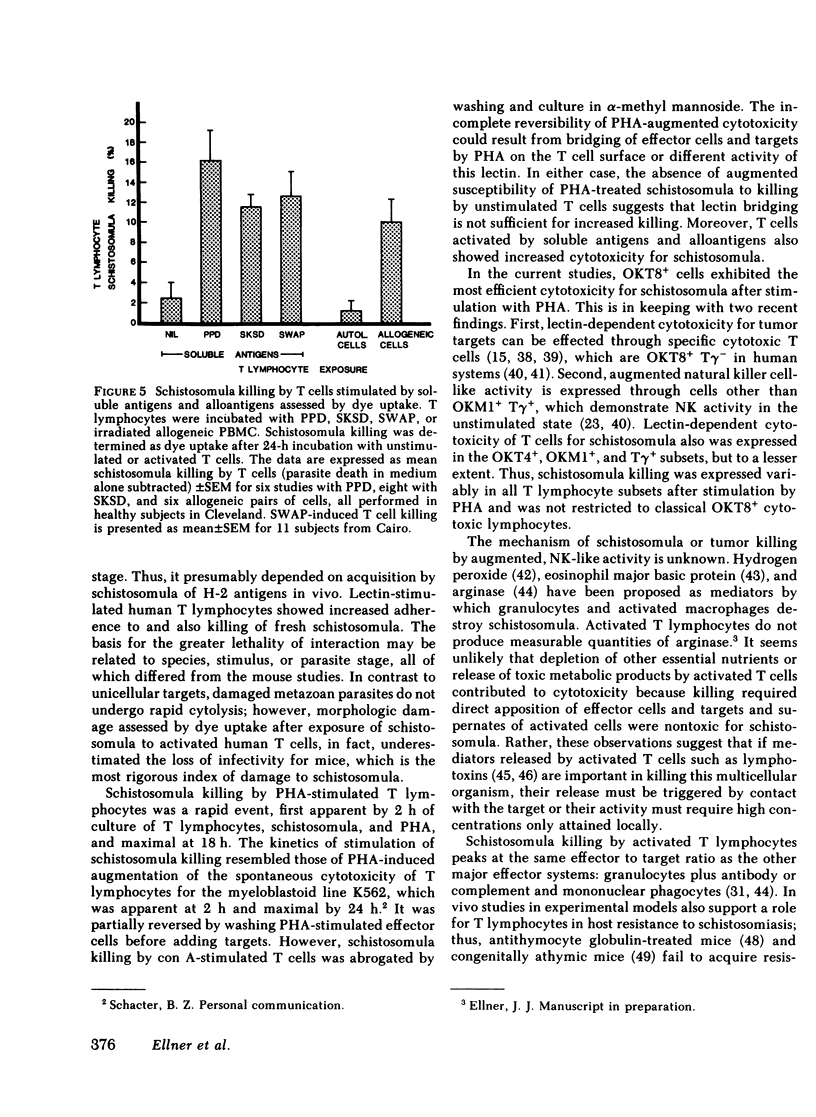
The role of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in host defenses against infectious agents is unknown as these cells have not previously been demonstrated to kill microorganisms directly. We studied the cytotoxicity of T lymphocytes purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy subjects for the multicellular schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Unstimulated and phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated T cells were cultured with schistosomula at a 5,000:1 effector/target (E:T) ratio for 18 h at 37 degrees C. Unstimulated T cells killed 2.1 +/- 0.6% of schistosomula as judged by dye uptake and did not change their infectivity for mice. In contrast, PHA-stimulated T cells killed 41.3 +/- 3.1% of schistosomula by dye uptake and 56.7 +/- 7.7% of these organisms could not mature to adult worms in vivo. Killing was associated with and dependent on increased binding of PHA-stimulated T lymphocytes to schistosomula. Significant schistosomula killing first was noted after 2 h of exposure to T cells to PHA and peaked at 24; enhanced killing by PHA-stimulated cells was observed at an E:T ratio of 500:1 and was maximal at 5,000:1. Exposure of T lymphocytes to oxidative mitogens, soluble antigens, and alloantigens also resulted in enhanced killing of schistomula. These studies show that T lymphocytes activated by a variety of stimuli develop the capacity to kill schistosomula of Schistoma mansoni. Direct killing of infectious agents by cytotoxic T cells may contribute to host resistance to infections.
Full text
PDF


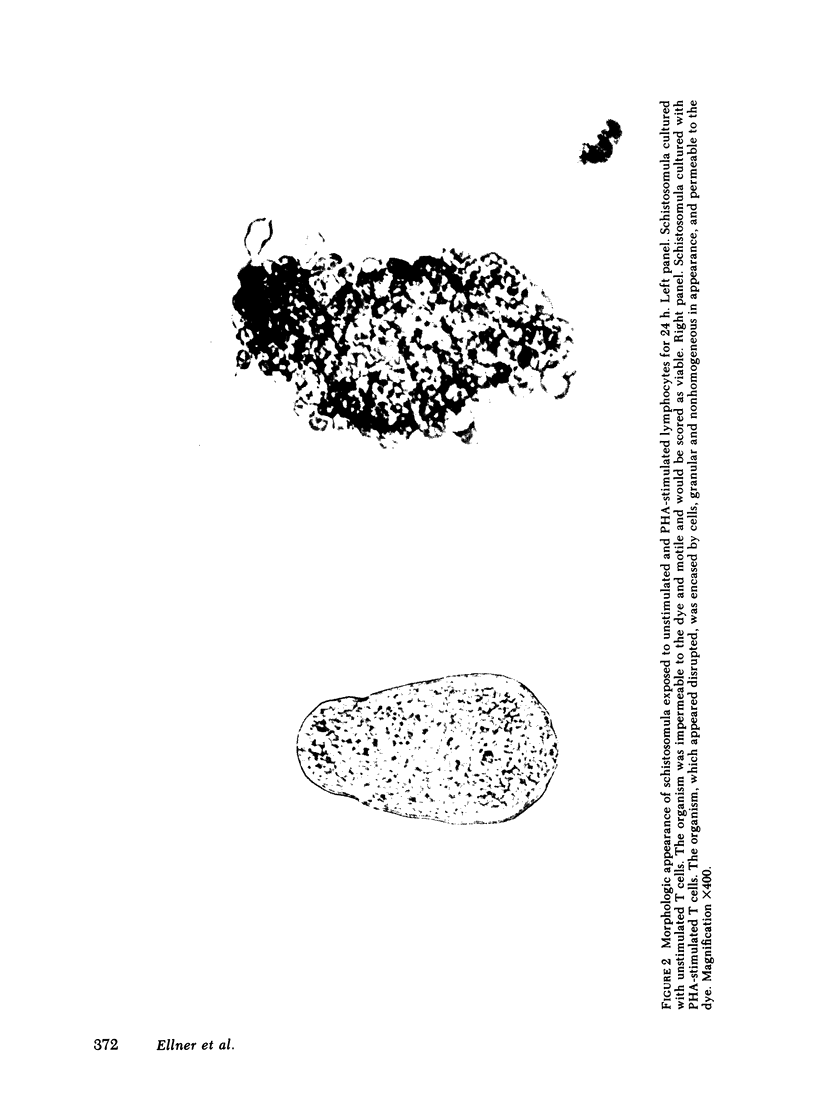


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Stejskal V., Harfast B. An in vitro method for study of human lymphocyte cytotoxicity against mumps-virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar A. R., Smithers S. R., Kay A. B. Killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni coated with antibody and/or complement by human leukocytes in vitro: requirement for complement in preferential killing by eosinophils. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Ferluga J., Janossy G. Non-specific cytotoxicity by T cells activated with plant mitogens in vitro and the requirement for plant agents during the killing reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):573–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J., Cohn M. Cytotoxic effects of antigen- and mitogen-induced T cells on various targets. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bout D. T., Joseph M., David J. R., Capron A. R. In vitro killing of S. mansoni schistosomula by lymphokine-activated mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. P., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. III. Evidence that cytotoxic T lymphocytes lyse both antigen-specific and -nonspecific targets pretreated with lectins or periodate. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):208–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. P., Burakoff S. J., Sher A. Specificity of alloreactive T lymphocytes that adhere to lung stage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2516–2518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E. Nonspecific cytotoxic effects of antigen-transformed lymphocytes. Kinetics, cell-requirements and the role of recruitment. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Mahmoud A. A., Sher A., Rees P. H. Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):727–729. doi: 10.1038/256727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert D. M., Lightbody J. J., Kaplan J., Jaroszewski J., Peterson W. D., Jr, Rosenberg J. C. Cytotoxicity of human peripheral lymphocytes in cell-mediated lympholysis; antibody-dependent cell-mediated lympholysis and natural cytotoxicity assays after mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civil R. H., Warren K. S., Mahmoud A. A. Conditions for bacille Calmette-Guérin-induced resistance to infection with Schistosoma mansoni in mice. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):550–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G., Cook J. A., Freeman G. L., Jr, Bartholomew R. K., Jordan P. Immune responses during human schistosomiasis mansoni. I. In vitro lymphocyte blastogenic responses to heterogeneous antigenic preparations from schistosome eggs, worms and cercariae. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;53(5):420–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A., Wistar R., Chen P. Immune response of guinea pigs to Schistosoma mansoni. I. In vitro effects of antibody and neutrophils, eosinophils and macrophages on schistosomula. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):74–82. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Mahmoud A. A. Killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by normal human monocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):949–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human peripheral blood: evaluation by a modified reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLM G., PERLMANN P., WERNER B. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ-INDUCED CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF NORMAL LYMPHOID CELLS ON CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Nature. 1964 Aug 22;203:841–843. doi: 10.1038/203841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiserodt J. C., Granger G. A. In vitro lymphocyte cytotoxicity. II. Unstable lymphotoxins (beta-LT) secreted and inactivated by mitogen-stimulated human lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiserodt J. C., Tiangco G. J., Granger G. A. The LT system in experimental animals. I. Rapid release of high levels of lymphotoxin (LT) activity from murine lymphocytes during the interaction with lectin-treated allogeneic or xenogeneic target cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Pross H. Surface markers on human b and t lymphocytes. VI. Cytotoxicity against cell lines as a functional marker for lymphocyte subpopulations. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):596–605. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph M., Capron A., Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V. Cytotoxicity of human and baboon mononuclear phagocytes against schistosomula in vitro: induction by immune complexes containing IgE and Schistosoma mansoni antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jul;33(1):48–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazura J. W., Fanning M. M., Blumer J. L., Mahmoud A. A. Role of cell-generated hydrogen peroxide in granulocyte-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):93–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI110037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labowskie R., Edelman R., Rustigian R., Bellanti J. A. Studies of cell-mediated immunity to measles virus by in vitro lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):233–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Summers P. L., Reeder A. A., Bertovich M. J., Formal S. B. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity: K lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes are effective against shigella. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2778–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Peters P. A., Civil R. H., Remington J. S. In vitro killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by BCG and C. parvum-activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1655–1657. doi: 10.2196/41502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S., Peters P. A. A role for the eosinophil in acquired resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infection as determined by antieosinophil serum. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):805–813. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Klein E., Argov S. Disappearance of the NK effect after explantation of lymphocytes and generation of similar nonspecific cytotoxicity correlated to the level of blastogenesis in activated cultures. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2458–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Bundy B. M., Pitchon H. E., Blaese R. M., Strober W. The effector cells in human peripheral blood mediating mitogen-induced cellular cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1472–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A. Induction of lymphocyte cytotoxicity by modification of the effector or target cells with periodate or with neuraminidase and galactose oxidase. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds G. R., Ellner J. J., Kearse L. A., Jr, Kazura J. W., Mahmoud A. A. Role of arginase in killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1557–1562. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds G. R., Mahmoud A. A. Role of host granulomatous response in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. eosinophil-mediated destruction of eggs. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1191–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI109970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono A., Amos D. B., Koren H. S. Selective cellular natural killing against human leukaemic T cells and thymus. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):546–548. doi: 10.1038/266546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., DiConza J. J., Gold J. A., Reid W. A. Schistosomiasis in the congenitally athymic (nude) mouse. I. Thymic dependency of eosinophilia, granuloma formation, and host morbidity. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E. B., McCoy J. L., Green S. S., Donnelly F. C., Siwarski D. F., Levine P. H., Herberman R. B. Destruction of human lymphoid tissue-culture cell lines by human peripheral lymphocytes in 51Cr-release cellular cytotoxicity assays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):345–352. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens R. P., Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocyte- mediated cytolysis. VIII. The use of con A to delineate a distinctive killer T cell subpopulation. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Koprowski H. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. II. Interferon induction and activation of natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Lief F. S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. I. Characterization of the effector lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter B., Kleinhenz M. E., Edmonds K., Ellner J. J. Spontaneous cytotoxicity of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells for the lymphoblastoid cell line CCRF-CEM: augmentation by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):640–648. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. I. Time course and target spectrum of several distinct concomitant cytotoxic activities. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Masucci G., Poros A., Klein E., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. II. Anti-K562 effectors are distinct from allospecific CTL and can be generated from NK-depleted T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Pichler W. J., Nelson D. L. Fc receptors on human T-lymphocytes. III. Characterization of subpopulations involved in cell-mediated lympholysis and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):599–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Hieny S., James S. L., Asofsky R. Mechanisms of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice vaccinated with irradiated cercariae. II. Analysis of immunity in hosts deficient in T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, or complement. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1880–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Reactivity of lymphocytes from normal persons on cultured tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2898–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof D., Check I. J., Matutis A., Hunter R. L., Fitch F. W. Studies on stimulation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity by skin test antigens. I. Candida antigen stimulation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro correlated with the skin test response to candida antigen in vivo. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2790–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Human natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity against fetal fibroblasts. I. General characteristics of the cytotoxic activity. Cell Immunol. 1977 Oct;33(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Eskra L., Borden E. C., Horoszewicz J., Carter W. A. Activation of human natural killer cells cytotoxic for human leukemia cells by purified interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Kung P. C. Monoclonal antibodies which distinguish between human NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):394–396. doi: 10.1038/288394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]